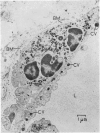
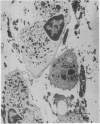
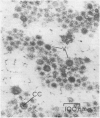
Abstract
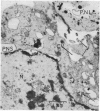
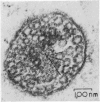
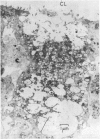
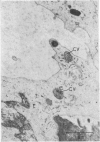
Four patients are described who developed pseudomembranous colitis in association with clindamycin therapy. Rectal biopsies from two patients were studied with the electron microscope and compared with the ultrastructural appearance of the rectal mucosa from seven normal people. Ultrastructural evidence for a viral colitis was obtained. The significance of the clindamycin therapy to the viral colitis and the contribution of the viral colitis to the clinical state are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen L. E., McNeill C. J., Wells R. F. Clindamycin-associated colitis. JAMA. 1973 Mar 19;223(12):1379–1380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEARING W. H., BAGGENTOSS A. H., WEED L. A. Studies on the relationship of Staphylococcus aureus to pseudomembranous enteritis and to postantibiotic enteritis. Gastroenterology. 1960 Mar;38:441–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck W. P., Viteli A. L., Howard P. H. Letter: Lincomycin, clindamycin, and colitis. Lancet. 1974 Feb 16;1(7851):272–273. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92584-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes A. M., Bridgwater F. A., Williams D. N., Oon J., Grimshaw G. J. Clinical and bacteriological studies with clindamycin. Br Med J. 1970 Jun 20;2(5711):703–704. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5711.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Spanknebel G., Weinstein L., Plaut A. G., Nahas L., Levitan R. Studies of intestinal microflora. 8. Effect of lincomycin on the microbial population of the human intestine. J Infect Dis. 1969 Sep;120(3):298–304. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.3.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulston S. J., McGovern V. J. Pseudo-membranous colitis. Gut. 1965 Jun;6(3):207–212. doi: 10.1136/gut.6.3.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALE H. W., Jr, COSGRIFF J. H., Jr Pseudomembranous enterocolitis. Am J Surg. 1957 Nov;94(5):710–717. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(57)90854-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON G. G., HAIGHT T. H., KASS E. H., WOMACK C. R., GOCKE T. M., FINLAND M. Terramycin therapy of pneumonia: clinical and bacteriologic studies in 91 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1951 Dec;35(6):1175–1202. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-35-6-1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLECKNER M. S., BARGEN J. A., BAGGENSTOSS A. H. Pseudomembranous enterocolitis: clinicopathologic study of fourteen cases in which the disease was not preceded by an operation. Gastroenterology. 1952 Jun;21(2):212–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGehee R. F., Jr, Smith C. B., Wilcox C., Finland M. Comparative studies of antibacterial activity in vitro and absorption and excretion of lincomycin and clinimycin. Am J Med Sci. 1968 Nov;256(5):279–292. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196811000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGovern V. J., Goulston S. J. Ischaemic enterocolitis. Gut. 1965 Jun;6(3):213–220. doi: 10.1136/gut.6.3.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKAY D. G., HARDAWAY R. M., 3rd, WAHLE G. H., Jr, HALL R. M. Experimental pseudomembranous enterocolitis; production by means of thrombosis of intestinal mucosal capillaries. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1955 Jun;95(6):779–787. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1955.00250120015002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARCE C., DINEEN P. A study of pseudomembranous enterocolitis. Am J Surg. 1960 Mar;99:292–300. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(60)90163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETTET J. D., BAGGENSTOSS A. H., DEARING W. H., JUDD E. S., Jr Postoperative pseudomembranous enterocolitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1954 May;98(5):546–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON K. C., JARETT L., FINKE E. H. Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 1960 Nov;35:313–323. doi: 10.3109/10520296009114754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPEARE G. S. Staphylococcus Pseudomembranous enterocolitis, a complication of antibiotic therapy. Am J Surg. 1954 Oct;88(4):523–524. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(54)90287-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. J., Nicholson G. I., Kerr A. R. Lincomycin as a cause of pseudomembranous colitis. Lancet. 1973 Dec 1;2(7840):1232–1234. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90973-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedesco F. J., Stanley R. J., Alpers D. H. Diagnostic features of clindamycin-associated pseudomembranous colitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 Apr 11;290(15):841–843. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197404112901508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]