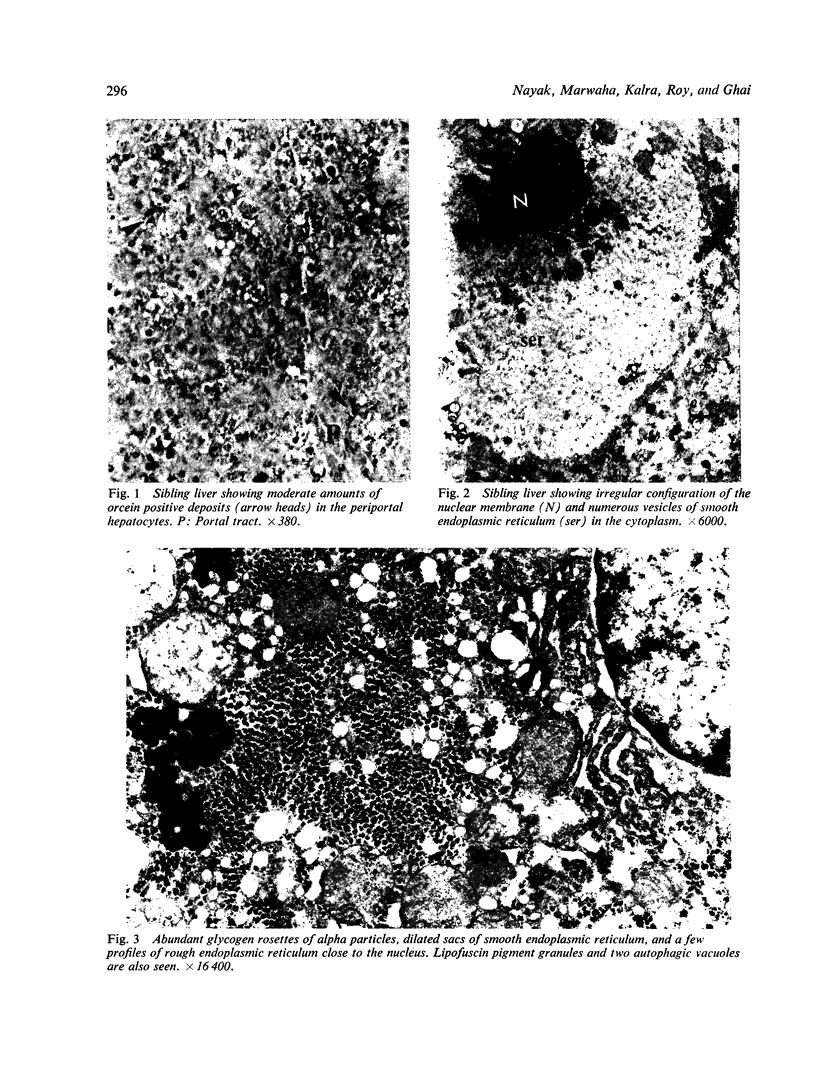
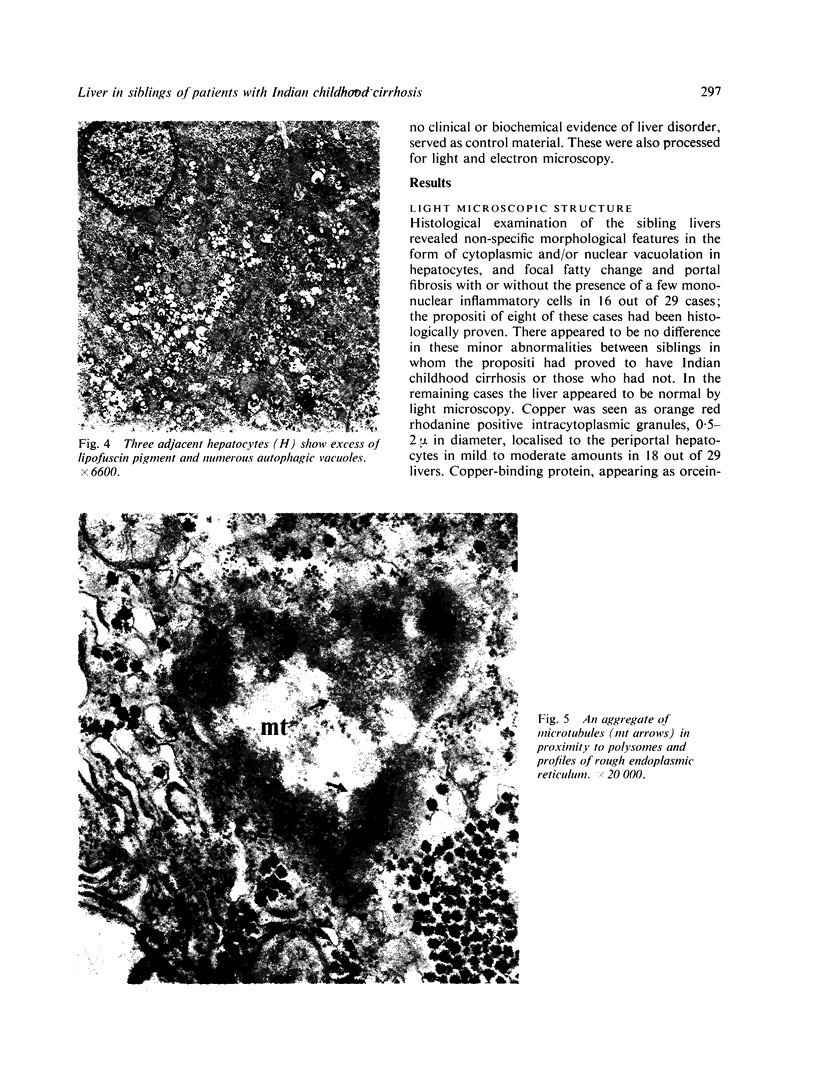
Abstract
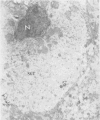
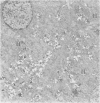
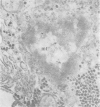
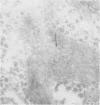
Liver biopsies from 29 siblings of patients with Indian childhood cirrhosis (ICC) and from two age-matched controls were examined by routine light and transmission electron microscopy. Histochemical stainings for copper and copper-binding protein were also carried out. The mild and non-specific structural alterations that were observed did not differ from those seen in control livers, even though a slight to moderate excess of copper and copper-binding protein was demonstrated in the majority. Aggregates of microtubules seen in some siblings, as well as in control livers, may indicate the preconditions for development of Mallory hyaline. It is possible that these features suggest a susceptibility for the development of ICC but not early disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chawla V., Chandra R. K., Verma I. C., Ghai O. P. An epidemiologic approach to Indian childhood cirrhosis. Indian Pediatr. 1973 Feb;10(2):73–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma M. H., Biempica L. The normal human liver cell. Cytochemical and ultrastructural studies. Am J Pathol. 1971 Mar;62(3):353–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak N. C., Ramalingaswami V. Indian childhood cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1975 May;4(2):333–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak N. C., Roy S. Morphological types of hepatocellular hyalin in Indian childhood cirrhosis: an ultrastructural study. Gut. 1976 Oct;17(10):791–796. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.10.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak N. C., Sachdeva R. Localization of hepatitis B surface antigen in conventional paraffin sections of the liver. Comparison of immunofluorescence, immunoperoxidase, and orcein staining methods with regard to their specificity and reliability as antigen marker. Am J Pathol. 1975 Dec;81(3):479–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak N. C., Visalakshi S., Singh M., Chawla V., Chandra R. K., Ramalingaswami V. Indian childhood cirrhosis--a re-evaluation of its pathomorphologic features and their significance in the light of clinical data and natural history of the disease. Indian J Med Res. 1972 Feb;60(2):246–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parekh S. R., Patel B. D. Epidemiologic survey of Indian childhood cirrhosis. Indian Pediatr. 1972 Aug;9(8):431–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel B. D., Parekh S. R., Chitale A. R. Histopathological evolution of Indian childhood cirrhosis with emphasis on criteria of early diagnosis. Indian Pediatr. 1974 Jan;11(1):19–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Goldfischer S., Sternlieb I., Nayak N. C., Madhavan T. V. Cytoplasmic copper and its toxic effects. Studies in Indian childhood cirrhosis. Lancet. 1979 Jun 9;1(8128):1205–1208. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91894-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portmann B., Tanner M. S., Mowat A. P., Williams R. Orcein-positive liver deposits in Indian childhood cirrhosis. Lancet. 1978 Jun 24;1(8078):1338–1340. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92407-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim J. S., Franks K. E., French S. W., Caldwell M. G. Mallory bodies compared with microfilament hyperplasia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1977 Aug;101(8):401–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. A., McIntosh J. R. Biochemistry and physiology of microtubules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:699–720. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner M. S., Portmann B., Mowat A. P., Williams R., Pandit A. N., Mills C. F., Bremner I. Increased hepatic copper concentration in Indian childhood cirrhosis. Lancet. 1979 Jun 9;1(8128):1203–1205. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91893-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel A., Holbrook K. A., Steinmann B., Gitzelmann R., Byers P. H. Abnormal collagen fibril structure in the gravis form (type I) of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Lab Invest. 1979 Feb;40(2):201–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin M., Larsson H., Edström A. Tubulin sulfhydryl groups and polymerization in vitro. Effects of di- and trivalent cations. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Jun;107(1):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90403-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Wehland J., Herzog W. Griseofulvin interacts with microtubules both in vivo and in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 25;102(4):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoo H., Minick O. T., Batti F., Kent G. Morphologic variants of alcoholic hyalin. Am J Pathol. 1972 Oct;69(1):25–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]