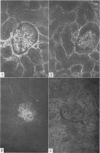
Abstract
Attempts were made to produce antisera to solubilized tissue fractions rich in basement membranes and reticulin. Murine tissue fractions solubilized with sodium hydroxide elicited precipitating antibodies upon injection into rabbits. Although no nephrotoxic effect was observed upon injecting the rabbit antisera into mice, the antisera were fixed to the glomerular basement membrane, and not elsewhere, within 5 minutes of injection and remained fixed for at least 3 weeks.
Specificity studies suggested that in addition to unique antigens, reticulin and epithelial basement membranes share a common antigen which is responsible for the similar in vitro immunofluorescence produced by antisera to tissue fractions rich in one or the other of these components.
Full text
PDF



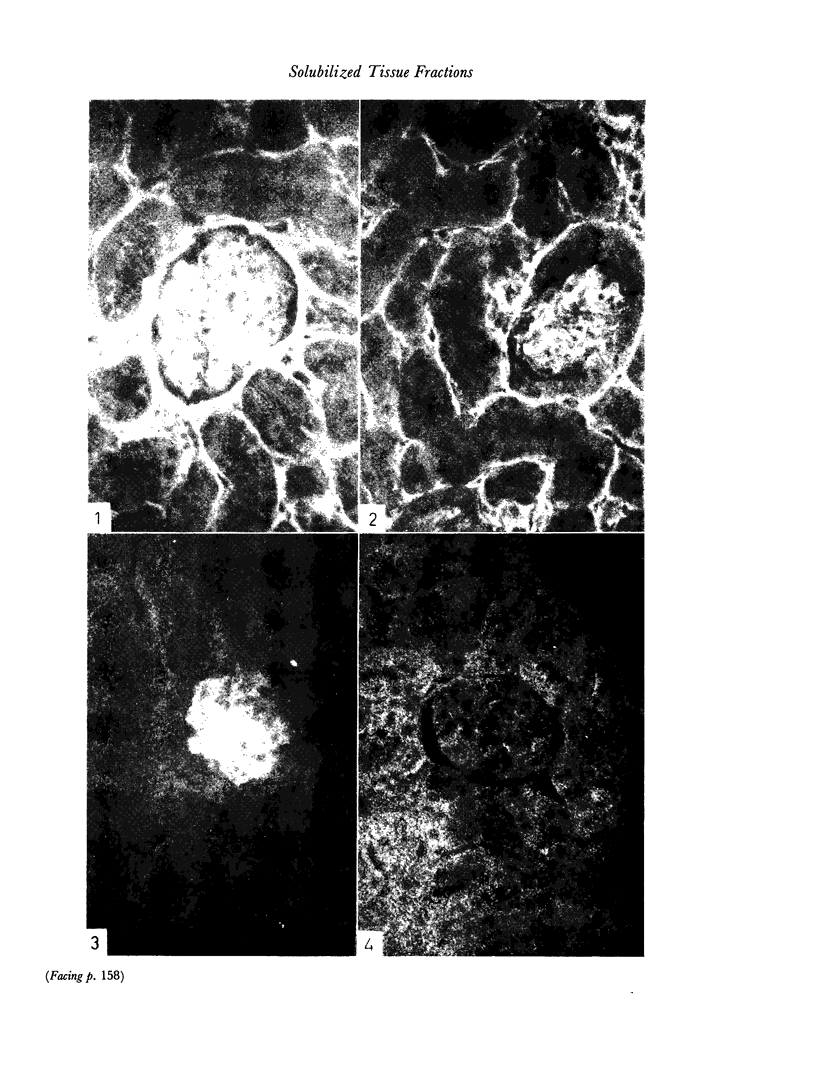



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAXTER J. H., GOODMAN H. C. Nephrotoxic serum nephritis in rats. II. Preparation and characterization of a soluble protective factor produced by trypsin digestion of rat tissue homogenates. J Exp Med. 1956 Oct 1;104(4):487–490. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. V. The adsorption of proteins on erythrocytes treated with tannic acid and subsequent hemagglutination by antiprotein sera. J Exp Med. 1951 Feb;93(2):107–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.2.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUICKSHANK B., HILL A. G. The histochemical identification of a connective-tissue antigen in the rat. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):283–289. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., FELDMAN J. D., VAZQUEZ J. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis. The pathogenesis of a laboratory model resembling the spectrum of human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1961 May 1;113:899–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.5.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISEN H. N., PRESSMAN D. The zone of localization of antibodies VIII. Some properties of the antigen responsible for the renal localization of anti-kidney serum. J Immunol. 1950 Jun;64(6):487–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENSPON S. A., KRAKOWER C. A. Direct evidence for the antigenicity of the glomeruli in the production of nephrotoxic serums. AMA Arch Pathol. 1950 Mar;49(3):291–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASSON M. W., BEVANS M., SEEGAL B. C. Immediate or delayed nephritis in rats produced by duck anti-rat-kidney sera. AMA Arch Pathol. 1957 Aug;64(2):192–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAKOWER C. A., GREENSPON S. A. Localization of the nephrotoxic antigen within the isolated renal glomerulus. AMA Arch Pathol. 1951 Jun;51(6):629–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKOWITZ A. S. Interactions of anti-glomerular basement membrane antisera. Immunology. 1960 Apr;3:117–125. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELLORS R. C., SIEGEL M., PRESSMAN D. Analytic pathology: histochemical demonstration of antibody localization in tissues, with special reference to the antigenic components of kidney and lung. Lab Invest. 1955 Mar-Apr;4(2):69–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J., Sargent A. U., Cohen J. J. Whole antiserum versus the gamma-globulin fraction of antiserum in the indirect fluorescent antibody technique. Immunology. 1965 Aug;9(2):101–105. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORTEGA L. G., MELLORS R. C. Analytical pathology. IV. The role of localized antibodies in the pathogenesis of nephrotoxic nephritis in the rat. J Exp Med. 1956 Jul 1;104(1):151–157. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIERCE G. B., Jr, MIDGLEY A. R., Jr, RAM J. S., FELDMAN J. D. Pariental yolk sac carcinoma: clue to the histogenesis of Riechert's membrane of the mouse embryo. Am J Pathol. 1962 Nov;41:549–566. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIERCE G. B., Jr, MIDGLEY A. R., Jr, SRI RAM J. The histogenesis of basement membranes. J Exp Med. 1963 Mar 1;117:339–348. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.3.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESSMAN D. The zone of localization of antitissue antibodies as determined by the use of radioactive tracers. J Allergy. 1951 Sep;22(5):387–396. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(51)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHBARD S., WATSON R. F. Antigenicity of rat collagen. Demonstration of antibody to rat collagen in the renal glomeruli of rats by fluorescence microscopy. J Exp Med. 1961 Jun 1;113:1041–1051. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.6.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHBARD S., WATSON R. F. Renal glomerular lesions induced by rabbit antirat collagen serum in rats prepared with adjuvant. J Exp Med. 1959 Jun 1;109(6):633–648. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.6.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEBLAY R. W., LEPPER M. H. Some immunologic properties of human and dog glomerular basement membrane. I. Isolation of human glomerular basement membrane; similar or identical complement-fixing antigens in human and dog glomerular basement membrane preparations. J Immunol. 1961 Dec;87:627–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]