Abstract
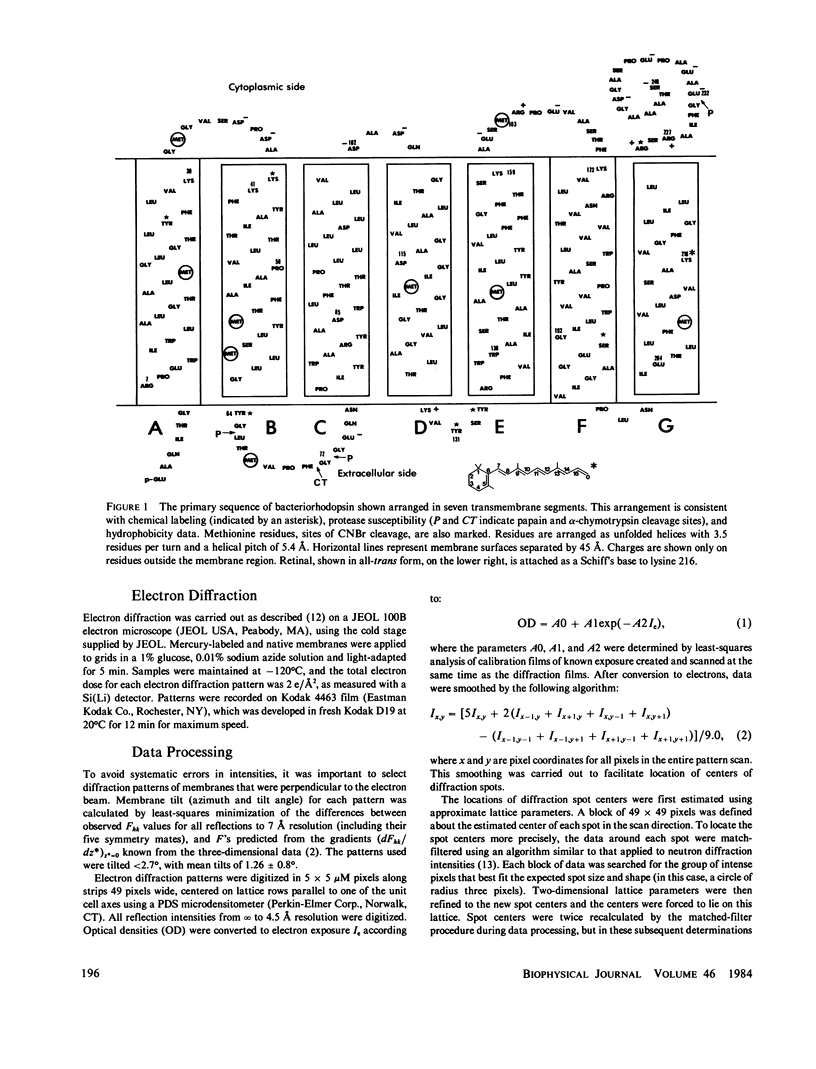
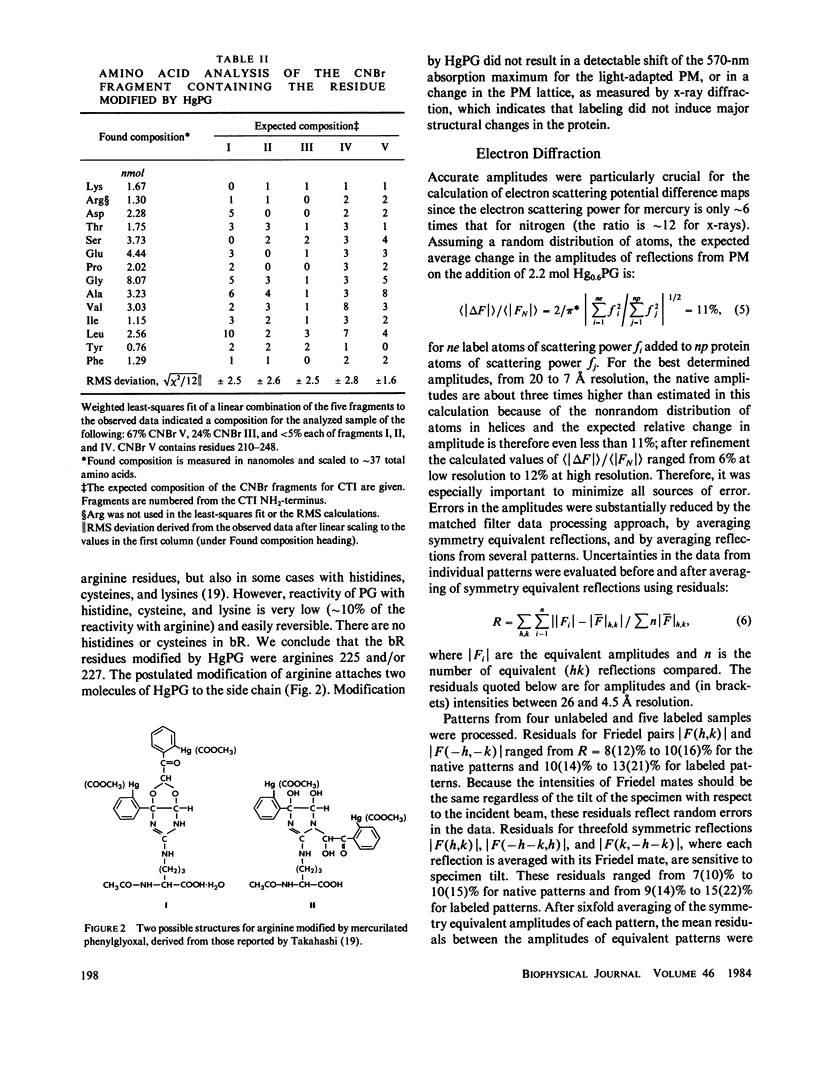
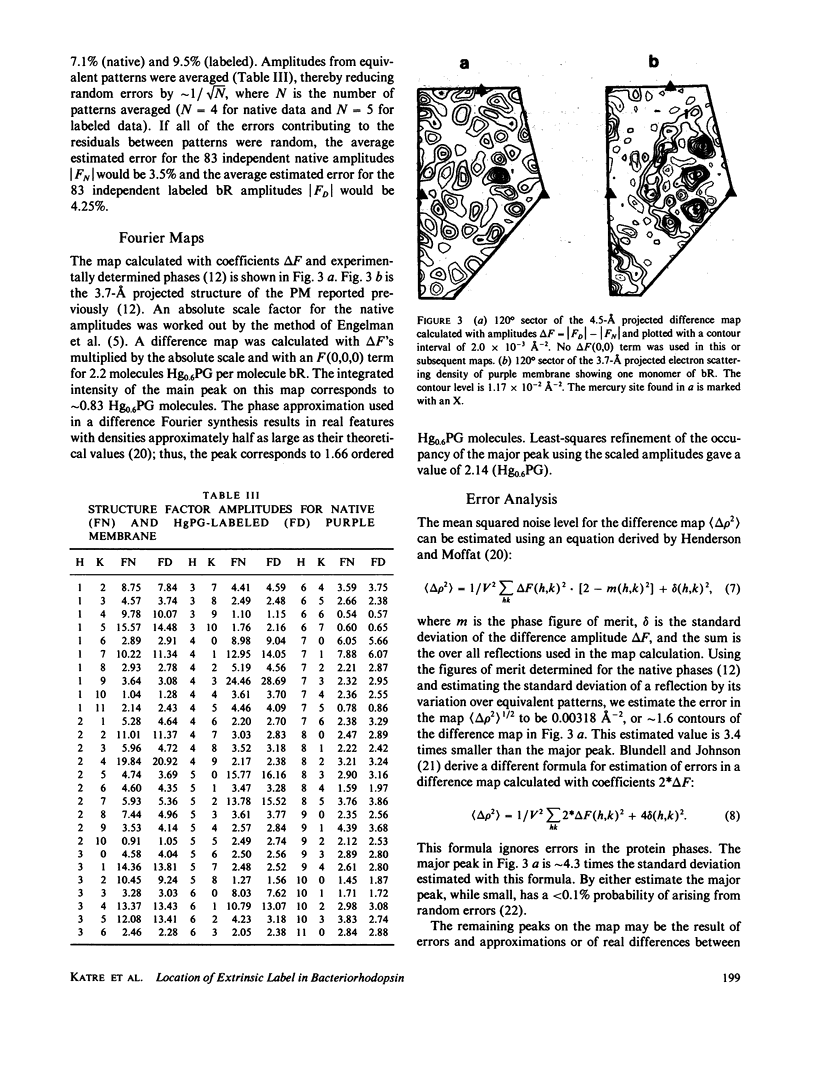
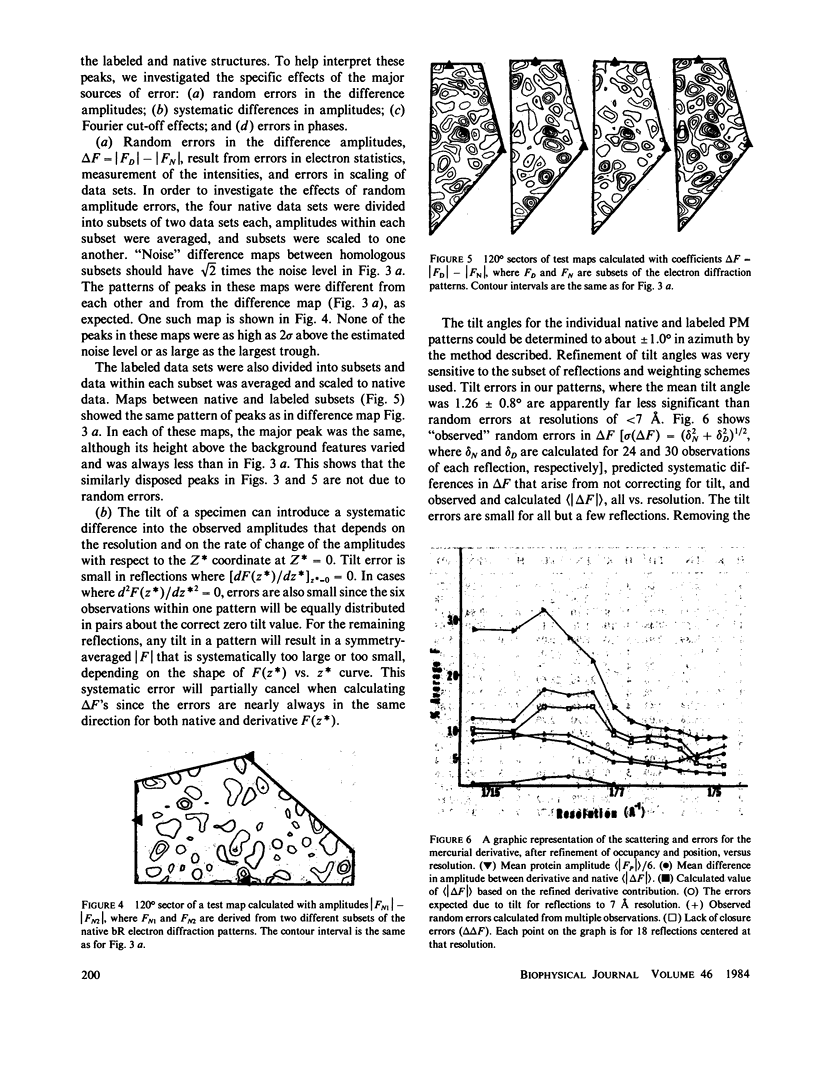
We located a heavy metal label, mercurilated phenylglyoxal, in both the primary sequence and in the tertiary structure of bacteriorhodopsin. This label modified arginines 225 and 227, which are on the COOH-terminal helix (G). In the projected electron potential difference map, the major site is close to the central inner helix. From this result we conclude that helix 1 could not be the COOH-terminal helix G. We tested the multiple isomorphous replacement method for obtaining phases for purple membrane by electron diffraction.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agard D. A., Stroud R. M. Linking regions between helices in bacteriorhodopsin revealed. Biophys J. 1982 Mar;37(3):589–602. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont M. E., Wiggins J. W., Hayward S. B. Location of platinum binding sites on bacteriorhodopsin by electron diffraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2947–2951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Henderson R., McLachlan A. D., Wallace B. A. Path of the polypeptide in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2023–2027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward S. B., Stroud R. M. Projected structure of purple membrane determined to 3.7 A resolution by low temperature electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):491–517. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Unwin P. N. Three-dimensional model of purple membrane obtained by electron microscopy. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):28–32. doi: 10.1038/257028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARUSH F., KLINMAN N. R., MARKS R. AN ASSAY METHOD FOR DISULFIDE GROUPS BY FLUORESCENCE QUENCHING. Anal Biochem. 1964 Sep;9:100–114. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUT J., SIEKER L. C., HIGH D. F., FREER S. T. Chymotrypsinogen: a three-dimensional fourier synthesis at 5 angstrom resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Aug;48:1417–1424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.8.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katre N. V., Wolber P. K., Stoeckenius W., Stroud R. M. Attachment site(s) of retinal in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4068–4072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorana H. G., Gerber G. E., Herlihy W. C., Gray C. P., Anderegg R. J., Nihei K., Biemann K. Amino acid sequence of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5046–5050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. I., Mowery P. C., Stoeckenius W., Crespi H. L., Schoenborn B. P. Location of the chromophore in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4726–4730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama T., Kimura Y., Kinosita K., Jr, Ikegami A. Location and orientation of the chromophore in bacteriorhodopsin. Analysis by fluorescence energy transfer. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 5;153(2):337–359. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov Y. A., Abdulaev N. G., Feigina M. Y., Kiselev A. V., Lobanov N. A. The structural basis of the functioning of bacteriorhodopsin: an overview. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 15;100(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80338-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehorek M., Heyn M. P. Binding of all-trans-retinal to the purple membrane. Evidence for cooperativity and determination of the extinction coefficient. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):4977–4983. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and related pigments of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:587–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroud R. M., Kay L. M., Dickerson R. E. The structure of bovine trypsin: electron density maps of the inhibited enzyme at 5 Angstrom and at 2-7 Angstron resolution. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 25;83(2):185–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90387-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K. The reaction of phenylglyoxal with arginine residues in proteins. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6171–6179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trewhella J., Anderson S., Fox R., Gogol E., Khan S., Engelman D., Zaccai G. Assignment of segments of the bacteriorhodopsin sequence to positions in the structural map. Biophys J. 1983 Jun;42(3):233–241. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84391-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


