Abstract
Injection of neonatal Balb/c or C57Bl/6 mice with C57Bl/6 x Balb/c)F1 lymphoid cells leads to transient chimerism and runting, and to splenomegaly, deficient T-cell function and a gradual replacement of lymphoid organs with abnormal reticular cells. Activated MuLV can be isolated from such mice. It is proposed that either graft-versus-host or host-versus-graft allogeneic reactivity activates endogenous MuLV virus, which then causes functional and morphological abnormalities in the lymphoid organs.
Full text
PDF





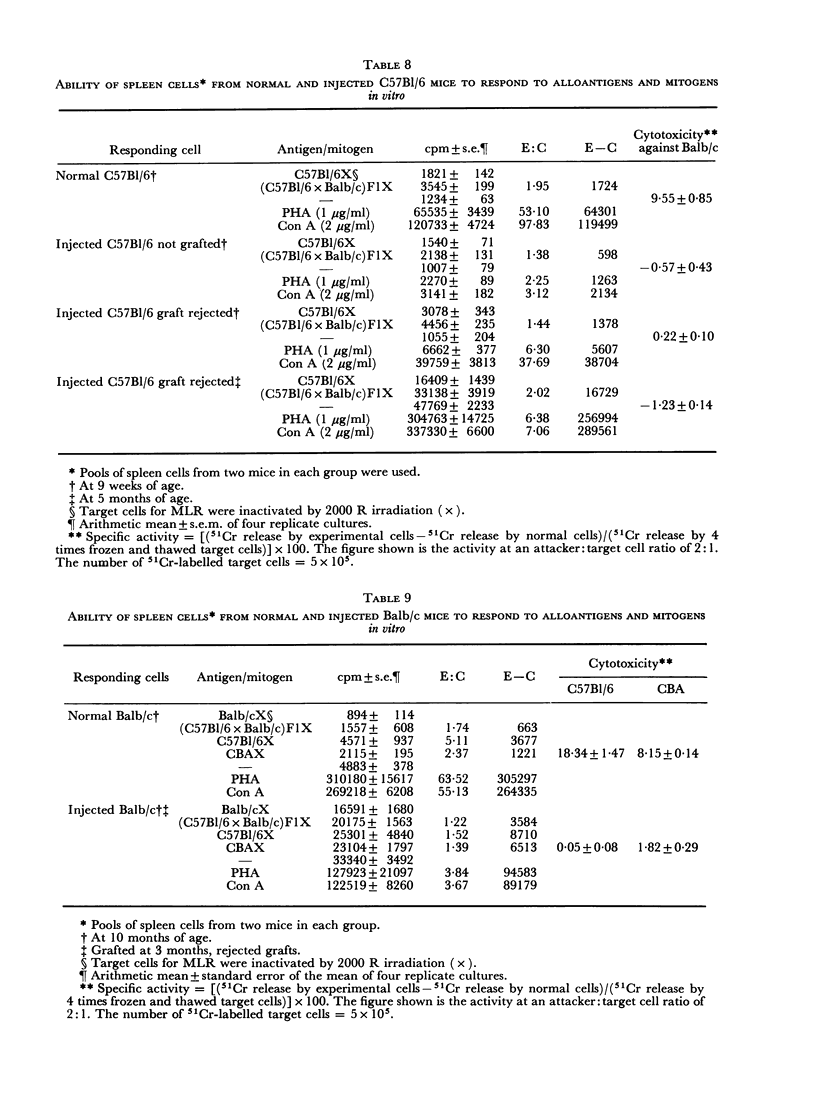

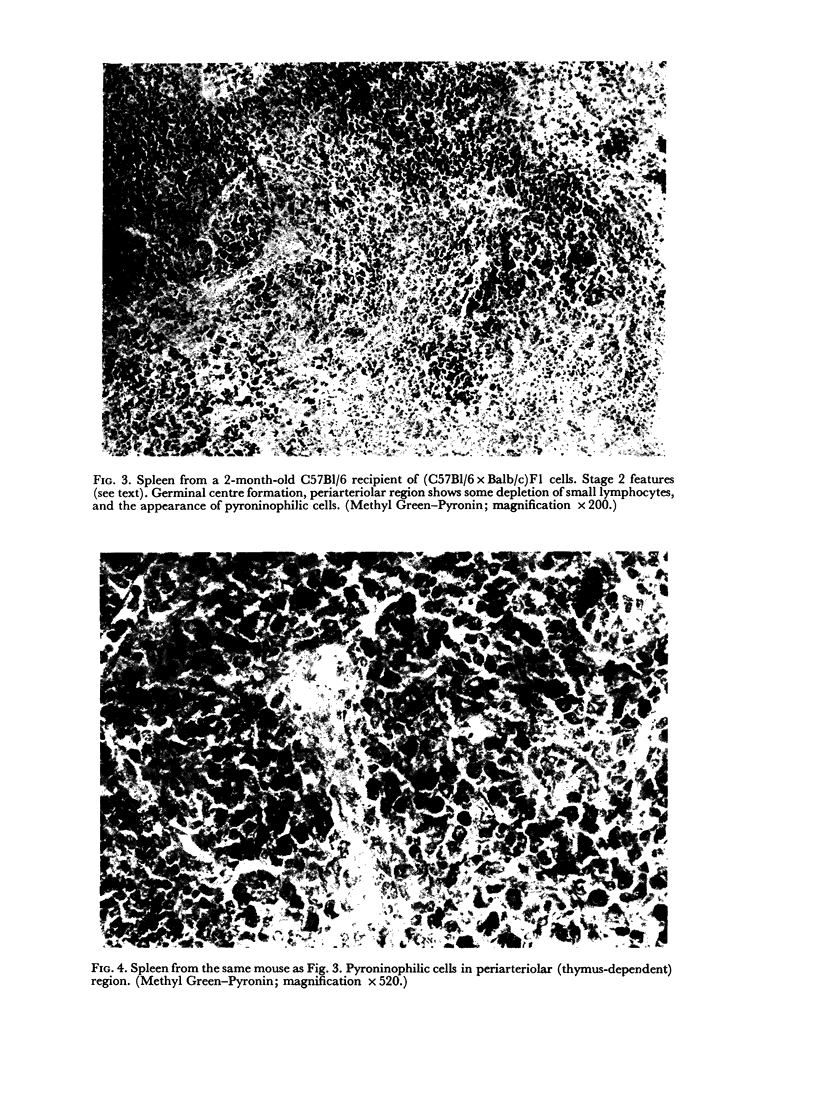
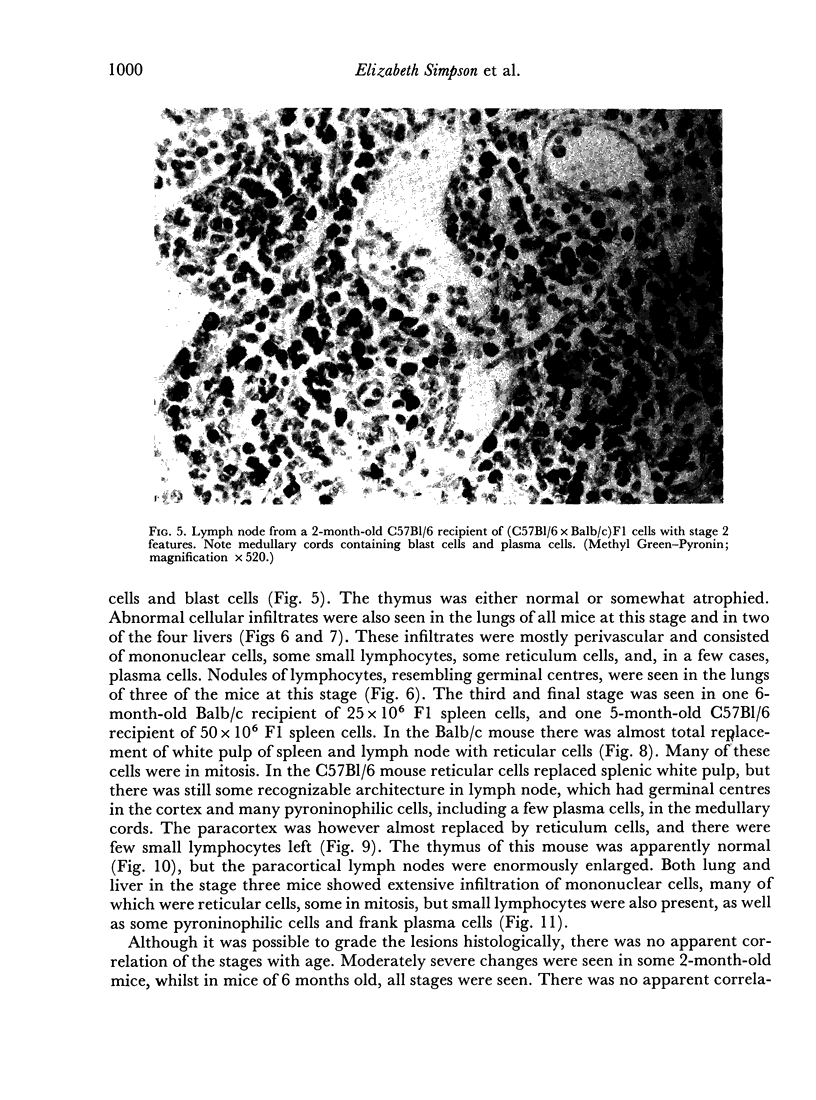
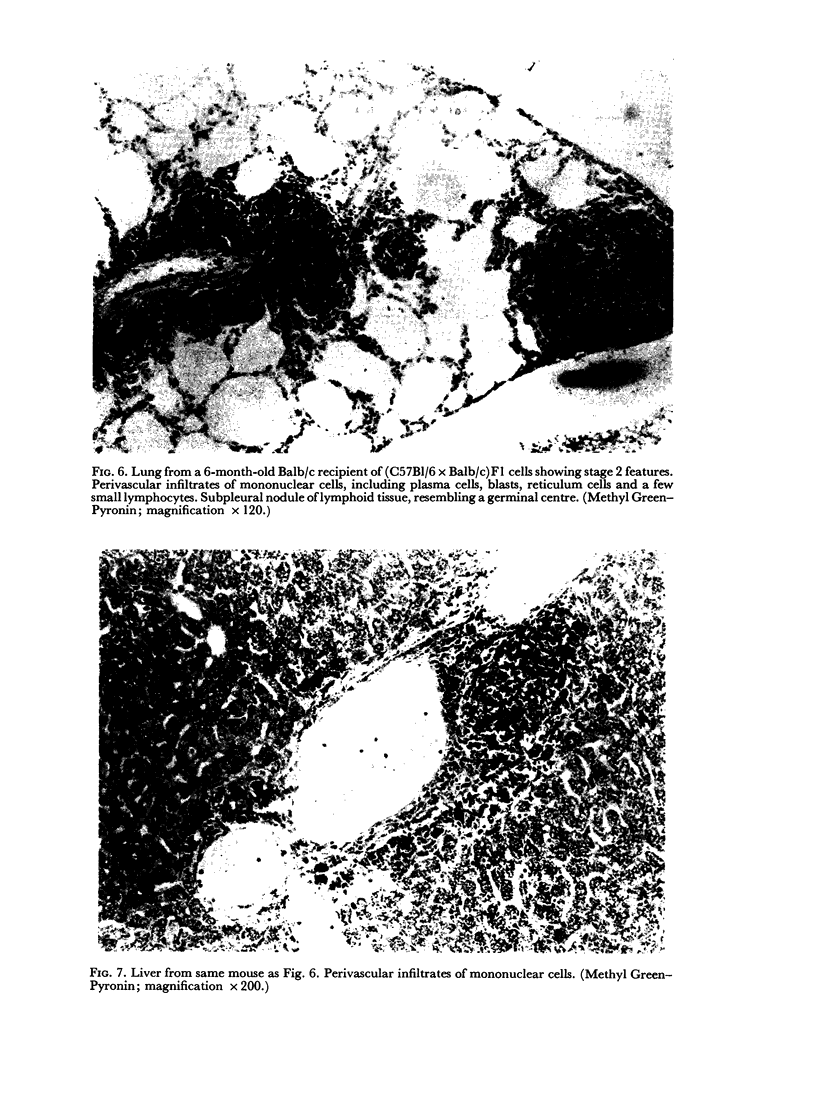




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong M. Y., Black F. L., Richards F. F. Tumour induction by cell-free extracts derived from mice with graft versus host disease. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 2;235(57):153–154. doi: 10.1038/newbio235153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong M. Y., Gleichmann E., Gleichmann H., Beldotti L., Andre-Schwartz J., Schwartz R. S. Chronic allogeneic disease. II. Development of lymphomas. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):417–439. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong M. Y., Ruddle N. H., Lipman M. B., Richards F. F. Tumor induction by immunologically activated murine leukemia virus. J Exp Med. 1973 May 1;137(5):1163–1179. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.5.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley P. C., Brent L., Brooks C., Medawar P. B., Simpson E. In vitro reactivity of lymphoid cells from tolerant mice. Transplant Proc. 1973 Mar;5(1):679–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Asofsky R. Synergy among lymphoid cells mediating the graft-versus-host response. II. Synergy in graft-versus-host reactions produced by Balb-c lymphoid cells of differing anatomic origin. J Exp Med. 1970 Feb;131(2):235–246. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleichmann E., Gleichmann H., Schwartz R. S. Immunologic induction of malignant lymphoma: genetic factors in the graft-versus-host model. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):793–804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. S., Black P. H., Tracy G. S., Leibowitz S., Schwartz R. S. Leukemia virus activation in chronic allogeneic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1914–1917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. S., Phillips S. M., Solnik C., Black P. H., Schwartz R. S., Carpenter C. B. Activation of leukemia viruses by graft-versus-host and mixed lymphocyte reactions in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1069–1072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lance E. M., Boyse E. A., Cooper S., Carswell E. A. Rejection of skin allografts by irradiation chimeras: evidence for skin-specific transplantation barrier. Transplant Proc. 1971 Mar;3(1):864–868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell R. I., Dutton R. W. Immunization of dissociated spleen cell cultures from normal mice. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):423–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E. Transient appearance of PHA-reactive thymocytes in the foetal mouse. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 11;242(119):184–185. doi: 10.1038/newbio242184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramseier H., Lindenmann J. F1 hybrid animals: reactivity against recognition structures of parental strain lymphoid cells. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1969;34(6):379–387. doi: 10.1159/000162189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Hartley J. W. Studies of genetic transmission of murine leukemia virus by AKR mice. II. Crosses with Fv-1 b strains of mice. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1286–1301. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMONSEN M. Graft versus host reactions. Their natural history, and applicability as tools of research. Prog Allergy. 1962;6:349–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. S., Beldotti L. Malignant lymphomas following allogenic disease: transition from an immunological to a neoplastic disorder. Science. 1965 Sep 24;149(3691):1511–1514. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3691.1511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silobrcić V. Life-long tolerance and chimerism in parental mice induced with F 1 hybrid cells. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Nov;1(5):313–315. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. Genetic factors influencing C-type RNA virus induction. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):175–184. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunderlich J. R., Canty T. G. Cell mediated immunity induced in vitro. Nature. 1970 Oct 3;228(5266):62–63. doi: 10.1038/228062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]