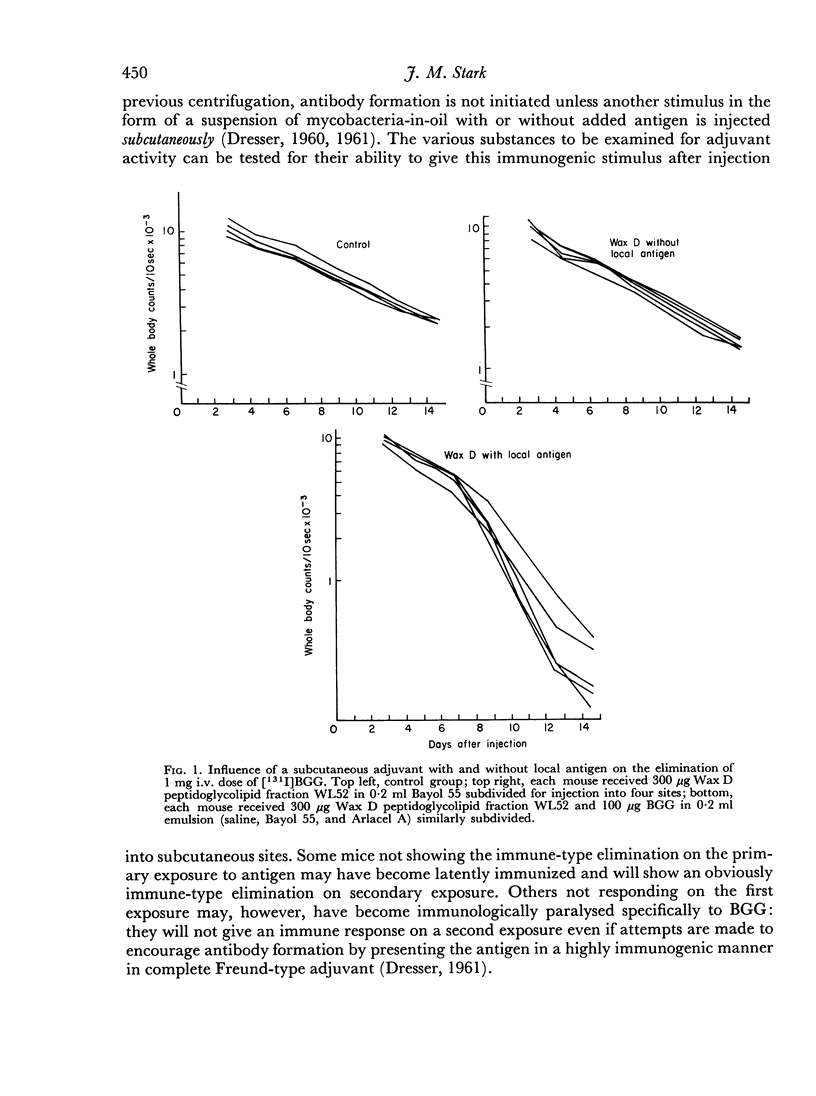
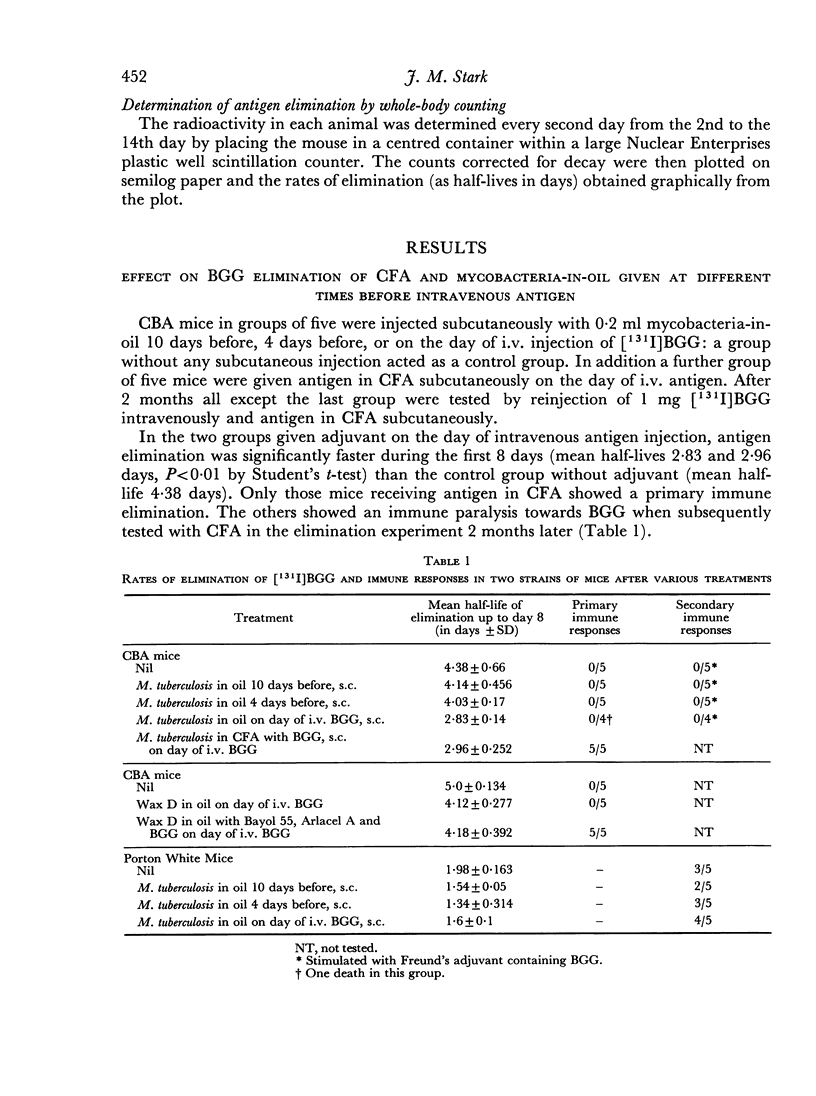
Abstract
Two series of experiments are described in which elimination of [131I]BGG is observed in CBA mice treated with mycobacterial adjuvants. Neither mycobacteria in oil nor Wax D in oil induced immune-type elimination in the first series where control mice catabolized the antigen relatively slowly (mean half-lives of 4.38 and 5.0 days). In a second series where control mice showed faster catabolism (mean half-lives 3.82 and 2.96 days) the adjuvants did induce immune elimination. It was found also that such adjuvants invariably accelerated the elimination rate in the pre-immune period of elimination.
Porton White mice eliminated the antigen rapidly and even mice not given adjuvant frequently gave a secondary immune response on a further exposure to antigen.
The results suggest that increases in the rate of antigen catabolism contribute to adjuvant activity in this model.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIOZZI G., BENACERRAF B., GRUMBACH F., HALPERN B. N., LEVADITI J., RIST N. Etude de l'activité granulopexique du système réticulo-endothélial au cours de l'infection tuberculeuse expérimentale de la souris. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1954 Sep;87(3):291–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRESSER D. W. Effectiveness of lipid and lipidophilic substances as adjuvants. Nature. 1961 Sep 16;191:1169–1171. doi: 10.1038/1911169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRESSER D. W. Elimination of 131-I-labelled protein antigens from the circulation of the mouse. Immunology. 1960 Oct;3:289–295. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S., DIXON F. J., Jr The effect of antigen concentration on the initiation of detectable antibody synthesis in rabbits. J Immunol. 1960 Sep;85:250–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEWELL I. A. Seasonal variation of the phagocytic activity of the reticulo-endothelial system. Immunology. 1960 Oct;3:371–375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark J. M. Rate of antigen catabolism and immunogenicity of [131-I]BGG in mice. II. Immunogenicity of [131-I]BGG and adjuvant action after alteration of the metabolic rate by various means. Immunology. 1970 Sep;19(3):457–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE R. G., JOLLES P., SAMOUR D., LEDERER E. CORRELATION OF ADJUVANT ACTIVITY AND CHEMICAL STRUCTURE OF WAX D FRACTIONS OF MYCOBACTERIA. Immunology. 1964 Mar;7:158–171. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE R. G., MARSHALL A. H. The role of various chemical fractions of M. tuberculosis and other Mycobacteria in the production of allergic encephalomyelitis. Immunology. 1958 Apr;1(2):111–122. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


