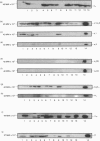
Abstract
The molecular mechanisms underlying B- and T-cell development are, as yet, poorly understood. However, as G proteins regulate a diverse range of biological responses including growth, proliferation and differentiation, we have investigated differential expression of G proteins during B- and T-cell development with the aim of identifying key signals involved in lymphocyte maturation. Differential expression of beta 1/2 and alpha-subunits of the Gs-, i- and q-families was found throughout lymphoid development. Most strikingly, G alpha i1 and G alpha i1 were very weakly, or not expressed in pre-, immature and mature B cells, thymocytes or mature T cells, but strongly induced in mature B-lymphoblastoid cell lines, some of which have been used as models of germinal centre B cells, suggesting that expression of these G proteins may correlate with the later stages of B-cell development. In contrast, G alpha 16 expression was highest in T cells and pre-B cells and progressively declined with B-cell maturation. These findings suggest that G proteins, and the signals they regulate, such as ion channels and/or adenylate cyclase (G alpha s/i) and phospholipase C (G beta gamma and G alpha 11/16) are differentially regulated in lymphoid cells in a maturation-and lineage-dependent manner.
Full text
PDF



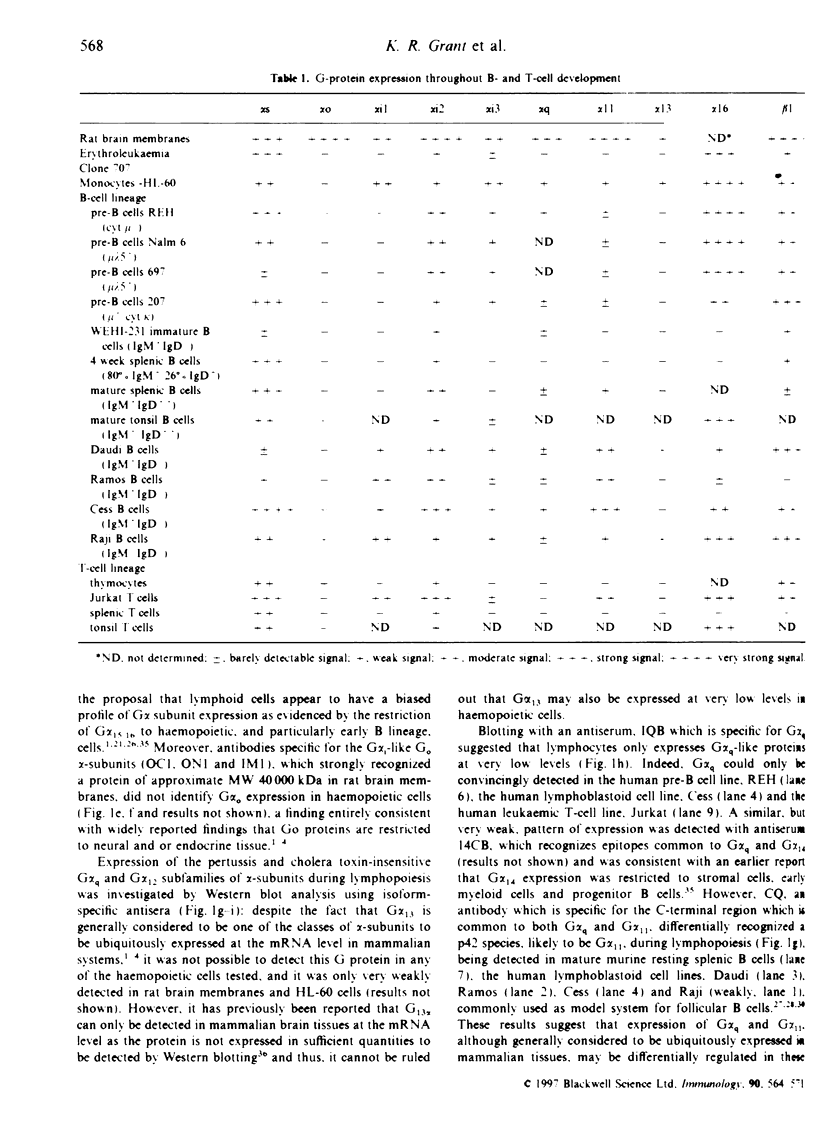



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amatruda T. T., 3rd, Steele D. A., Slepak V. Z., Simon M. I. G alpha 16, a G protein alpha subunit specifically expressed in hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5587–5591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aragay A. M., Katz A., Simon M. I. The G alpha q and G alpha 11 proteins couple the thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor to phospholipase C in GH3 rat pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):24983–24988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Graber S. G., Waldo G. L., Harden T. K., Garrison J. C. Selective activation of phospholipase C by recombinant G-protein alpha- and beta gamma-subunits. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2814–2819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Iyengar R. Inhibition of cloned adenylyl cyclases by mutant-activated Gi-alpha and specific suppression of type 2 adenylyl cyclase inhibition by phorbol ester treatment. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12253–12256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowd D. R., Miesfeld R. L. Evidence that glucocorticoid- and cyclic AMP-induced apoptotic pathways in lymphocytes share distal events. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3600–3608. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falloon J., Malech H., Milligan G., Unson C., Kahn R., Goldsmith P., Spiegel A. Detection of the major pertussis toxin substrate of human leukocytes with antisera raised against synthetic peptides. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):352–356. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federman A. D., Conklin B. R., Schrader K. A., Reed R. R., Bourne H. R. Hormonal stimulation of adenylyl cyclase through Gi-protein beta gamma subunits. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):159–161. doi: 10.1038/356159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. J., Stewart A., Courtney C. A., Fleming M. C., Reid P., Jackson C. G., Wise A., Wakelam M. J., Harnett M. M. Antigen receptors on immature, but not mature, B and T cells are coupled to cytosolic phospholipase A2 activation: expression and activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 correlate with lymphocyte maturation. J Immunol. 1996 Mar 15;156(6):2054–2061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Jakway J. P., DeFranco A. L. Involvement of a guanine-nucleotide-binding component in membrane IgM-stimulated phosphoinositide breakdown. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 1;139(11):3604–3613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Gierschik P., Milligan G., Unson C. G., Vinitsky R., Malech H. L., Spiegel A. M. Antibodies directed against synthetic peptides distinguish between GTP-binding proteins in neutrophil and brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14683–14688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant K. R., Harnett M. M., Milligan G., Harnett W. Characterization of heterotrimeric G-proteins in adult Acanthocheilonema viteae. Biochem J. 1996 Dec 1;320(Pt 2):459–466. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnett M. M., Klaus G. G. G protein coupling of antigen receptor-stimulated polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in B cells. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3135–3139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnett M., Rigley K. The role of G-proteins versus protein tyrosine kinases in the regulation of lymphocyte activation. Immunol Today. 1992 Dec;13(12):482–486. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90022-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Gilman A. G. G proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90005-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelsema C. L., Axelrod J. Stimulation of phospholipase A2 activity in bovine rod outer segments by the beta gamma subunits of transducin and its inhibition by the alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M. The adenylate cyclase-cAMP-protein kinase A pathway and regulation of the immune response. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):222–229. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y., Arinze I. J. Ontogeny of guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins in rabbit liver. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 1;274(Pt 2):439–444. doi: 10.1042/bj2740439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimata H., Yoshida A. Effect of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I on immunoglobulin production by and growth of human B cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 Mar;78(3):635–641. doi: 10.1210/jcem.78.3.8126135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Scherübl H., Hescheler J., Schultz G., Wittig B. Different beta-subunits determine G-protein interaction with transmembrane receptors. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):424–426. doi: 10.1038/358424a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Scherübl H., Hescheler J., Schultz G., Wittig B. Selectivity in signal transduction determined by gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):832–834. doi: 10.1126/science.8094261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. A., Smallwood P. M., Moen P. T., Jr, Helman L. J., Ahn T. G. Molecular cloning of beta 3 subunit, a third form of the G protein beta-subunit polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2329–2333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapara M. Y., Bommert K., Bargou R. C., Leng C., Beck C., Ludwig W. D., Gierschik P., Dörken B. G protein subunit G alpha 16 expression is restricted to progenitor B cells during human B-cell differentiation. Blood. 1995 Apr 1;85(7):1836–1842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Orrenius S., Jondal M. Agents that elevate cAMP stimulate DNA fragmentation in thymocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 15;145(4):1227–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melamed I., Wang G., Roifman C. M. Antigen receptor-mediated protein tyrosine kinase activity is regulated by a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 1;149(1):169–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Mullaney I., Mitchell F. M. Immunological identification of the alpha subunit of G13, a novel guanine nucleotide binding protein. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 3;297(1-2):186–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80357-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. Signal sorting by G-protein-linked receptors. Adv Pharmacol. 1995;32:1–29. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)61010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nel A. E., Ledbetter J. A., Williams K., Ho P., Akerley B., Franklin K., Katz R. Activation of MAP-2 kinase activity by the CD2 receptor in Jurkat T cells can be reversed by CD45 phosphatase. Immunology. 1991 Jun;73(2):129–133. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pronin A. N., Gautam N. Interaction between G-protein beta and gamma subunit types is selective. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6220–6224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schattner E. J., Elkon K. B., Yoo D. H., Tumang J., Krammer P. H., Crow M. K., Friedman S. M. CD40 ligation induces Apo-1/Fas expression on human B lymphocytes and facilitates apoptosis through the Apo-1/Fas pathway. J Exp Med. 1995 Nov 1;182(5):1557–1565. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.5.1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider U., Schwenk H. U., Bornkamm G. Characterization of EBV-genome negative "null" and "T" cell lines derived from children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and leukemic transformed non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Int J Cancer. 1977 May 15;19(5):621–626. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smrcka A. V., Sternweis P. C. Regulation of purified subtypes of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C beta by G protein alpha and beta gamma subunits. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9667–9674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voyno-Yasenetskaya T., Conklin B. R., Gilbert R. L., Hooley R., Bourne H. R., Barber D. L. G alpha 13 stimulates Na-H exchange. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):4721–4724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Shoback D., Stobo J. Role of T3 surface molecules in human T-cell activation: T3-dependent activation results in an increase in cytoplasmic free calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4169–4173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie T. M., Scherle P. A., Strathmann M. P., Slepak V. Z., Simon M. I. Characterization of G-protein alpha subunits in the Gq class: expression in murine tissues and in stromal and hematopoietic cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10049–10053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu N., Bradley L., Ambdukar I., Gutkind J. S. A mutant alpha subunit of G12 potentiates the eicosanoid pathway and is highly oncogenic in NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6741–6745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Weizsäcker E., Strathmann M. P., Simon M. I. Diversity among the beta subunits of heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins: characterization of a novel beta-subunit cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 28;183(1):350–356. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91650-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]