Abstract
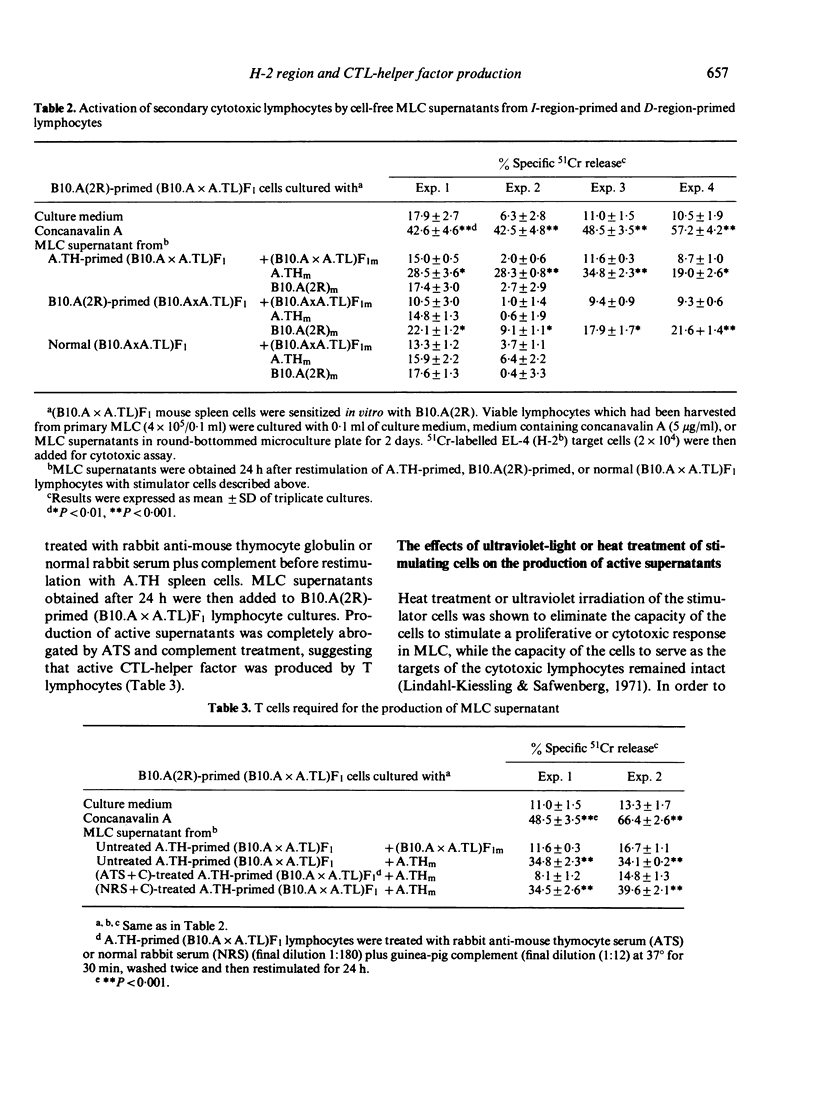
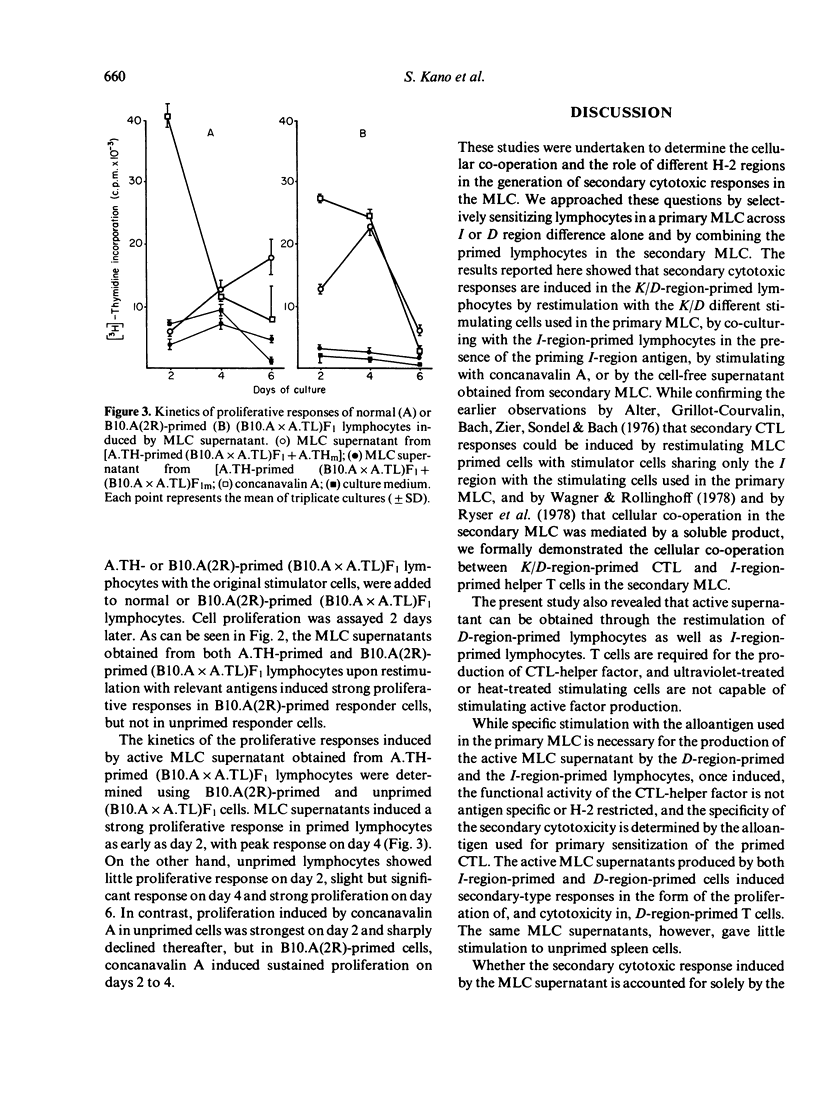
Cell co-operation in the generation of secondary cytotoxic responses was studied by selectively sensitizing lymphocytes in mixed lymphocyte culture (MLC) across I or D region difference and by combining the primed lymphocytes in the secondary MLC. Secondary cytotoxic responses were induced in D-region-primed lymphocytes by restimulation with the original priming D-region antigens, by co-culturing with the I-region-primed lymphocytes in the presence of the priming I-region antigens, or by cell-free supernatants obtained 24 h after the restimulation of D-region-primed lymphocytes and I-region-primed lymphocytes, The active MLC supernatants produced by both I-region-primed and D-region-primed cells also induced accelerated proliferative responses in D-region-primed lymphocytes. Heat-treatment or ultraviolet irradiation of the stimulator cells eliminated the capacity of the cells to induce the production of CTL-helper factor in I-region-primed and D-region-primed lymphocytes. It was concluded that both I-region-primed and D-region-primed lymphocytes produce a cell-free factor which induces proliferation and secondary cytotoxicity in D-region-primed lymphocytes. The possible participation of D-region reactive helper T cells and D-region reactive cytotoxic T cells in the cytotoxic responses to D-region antigens in the absence of I-region difference is discussed.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alter B. J., Grillot-Courvalin C., Bach M. L., Zier K. S., Sondel P. M., Bach F. H. Secondary cell-mediated lympholysis: importance of H-2 LD and SD factors. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1005–1014. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter B. J., Schendel D. J., Bach M. L., Bach F. H., Klein J., Stimpfling J. H. Cell-mediated lympholysis. Importance of serologically defined H-2 regions. J Exp Med. 1973 May 1;137(5):1303–1309. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.5.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. II. Cooperation between subclasses of Ly+ cells in the generation of killer activity. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1390–1399. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe D. A., Finke J. H. Soluble helper factor(s) participates in the generation of cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against syngeneic tumor cells. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):1156–1161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. Long term culture of tumour-specific cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):154–156. doi: 10.1038/268154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser M. T-T cell synergy in the in vitro generation of secondary cell-mediated cytotoxicity against syngeneic SV-40 transformed cells. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):973–979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty K. J., Misko I. S., Cooley M. A. Allogeneic stimulation modulates the in vitro response of T cells to transplantation antigen. Nature. 1974 May 17;249(454):275–276. doi: 10.1038/249275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Sordat B., Cerottini J. C., Brunner K. T. Generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in vitro. IV. Functional activation of memory cells in the absence of DNA synthesis. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):622–636. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melief C. J., van der Meulen M. Y., Christiaans B. J., de Greeve P. Cooperation between subclass of T lymphocytes in the in vitro generation of cytotoxicity against a mutant H-2K difference. An analysis with anti-Lyt antisera. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jan;9(1):7–12. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. A., Ruscetti F. W., Gallo R. Selective in vitro growth of T lymphocytes from normal human bone marrows. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1007–1008. doi: 10.1126/science.181845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabholz M., Vives J., Young H. M., Meo T., Miggiano V., Rijnbeek A., Shreffler D. C. Cell-mediated cell lysis in vitro: genetic control of killer cell production and target specificities in the mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1974 May;4(5):378–387. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panfili P. R., Dutton R. W. Alloantigen-induced T helper activity. I. Minimal genetic differences necessary to induce a positive allogeneic effect. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1897–1901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate J. M. Soluble factors substitute for T-T-cell collaboration in generation of T-killer lymphocytes. Nature. 1976 Mar 25;260(5549):329–331. doi: 10.1038/260329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revised nomenclature for antigen-nonspecific T cell proliferation and helper factors. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2928–2929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Spiess P. J., Schwarz S. In vitro growth of murine T cells. I. Production of factors necessary for T cell growth. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1946–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryser J. E., Cerottini J. C., Brunner K. T. Generation of cytolytic T lymphocytes in vitro. IX. induction of secondary CTL responses in primary long-term MLC by supernatants from secondary MLC. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):370–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausser J. L., Rosenberg S. A. In vitro growth of cytotoxic human lymphocytes. I. Growth of cells sensitized in vitro to alloantigens. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1491–1495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Panfili P. R. Helper cells activated by allogeneic H-2K or H-2D differences have a Ly phenotype distinct from those responsive to I differences. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):383–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uotila M., Rode H. N., Gordon J. Blastogenic factor: its role in the mixed leukocyte culture reaction. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Feb;8(2):133–138. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Röllinghoff M. T-T-cell interactions during the vitro cytotoxic allograft responses. I. Soluble products from activated Lyl+ T cells trigger autonomously antigen-primed Ly23+ T cells to cell proliferation and cytolytic activity. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1523–1538. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


