Abstract
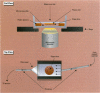
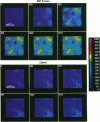
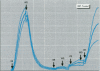
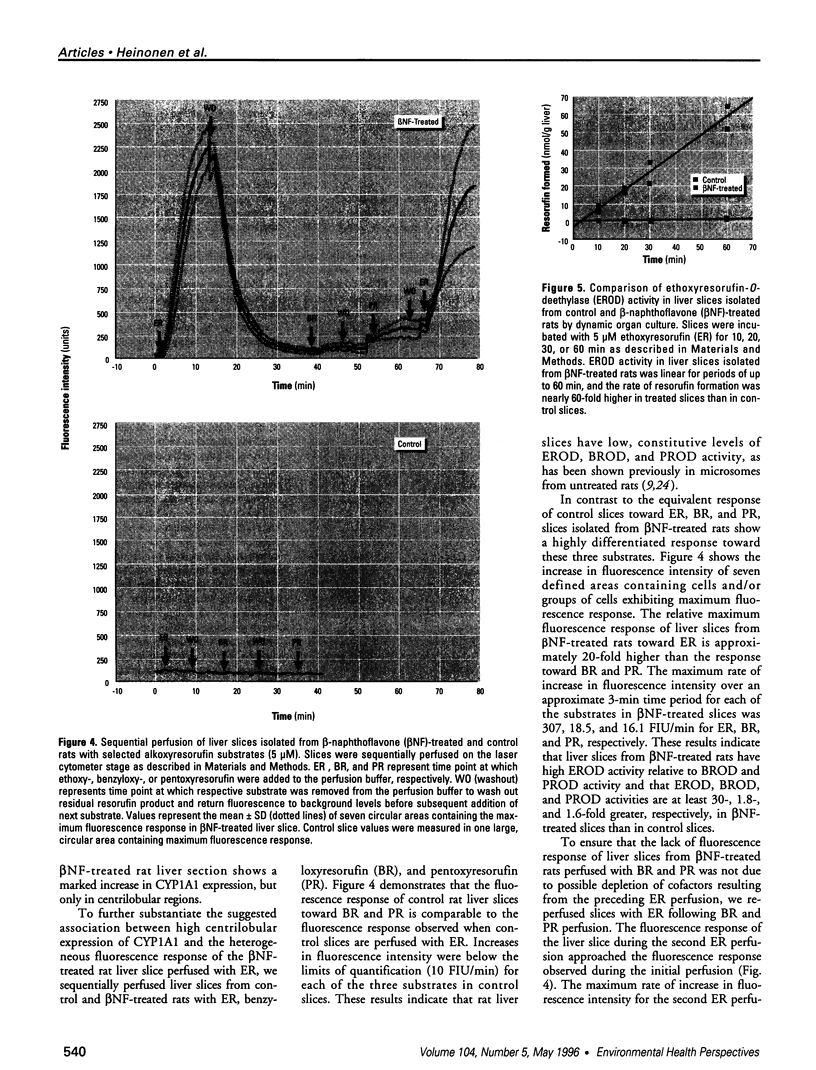
Characterizing constitutive activities and inducibility of various cytochrome P450 isozymes is important for elucidating species and individual differences in susceptibility to many toxicants. Although expression of certain P450s has been studied in homogenized tissues, the ability to assess functional enzyme activity without tissue disruption would further our understanding of interactive factors that modulate P450 activities. We used precision-cut, viable rat liver slices and confocal laser cytometry to determine the regional enzyme activities of P450 isozymes in situ. Livers from control and beta-naphthoflavone (beta NF)-treated rats were sectioned with a Krumdieck tissue slicer into 250-microns thick sections. A slice perfusion chamber that mounts on the cytometer stage was developed to allow for successive measurement of region-specific P450-dependent O-dealkylation of 7-ethoxy-, 7-pentoxy-, and 7-benzyloxyresorufin (EROD, PROD, and BROD activity, respectively) in the same liver slice. Images of the accumulated fluorescent resorufin product within the tissue were acquired using a confocal laser cytometer in confocal mode. As expected, slices isolated from beta NF-treated rats showed high levels of centrilobular EROD activity compared to slices from control rats, whereas PROD and BROD activities remained at control levels. These techniques should allow for the accurate quantification of regional and cell-specific P450 enzyme activity and, with subsequent analysis of the same slice, the ability to correlate specific P450 mRNAs or other factors with enzymatic activity. Moreover, these techniques should be amenable to examination of similar phenomena in other tissues such as lung and kidney, where marked heterogeneity in cellular P450 expression patterns is also known to occur.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anundi I., Lähteenmäki T., Rundgren M., Moldeus P., Lindros K. O. Zonation of acetaminophen metabolism and cytochrome P450 2E1-mediated toxicity studied in isolated periportal and perivenous hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Mar 24;45(6):1251–1259. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90277-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron J., Redick J. A., Guengerich F. P. An immunohistochemical study on the localization and distributions of phenobarbital- and 3-methylcholanthrene-inducible cytochromes P-450 within the livers of untreated rats. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5931–5937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron J., Redick J. A., Guengerich F. P. Effects of 3-methylcholanthrene, beta-naphthoflavone, and phenobarbital on the 3-methylcholanthrene-inducible isozyme of cytochrome P-450 within centrilobular, midzonal, and periportal hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):953–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bars R. G., Bell D. R., Elcombe C. R., Oinonen T., Jalava T., Lindros K. O. Zone-specific inducibility of cytochrome P450 2B1/2 is retained in isolated perivenous hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1992 Mar 15;282(Pt 3):635–638. doi: 10.1042/bj2820635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke M. D., Mayer R. T. Ethoxyresorufin: direct fluorimetric assay of a microsomal O-dealkylation which is preferentially inducible by 3-methylcholanthrene. Drug Metab Dispos. 1974 Nov-Dec;2(6):583–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke M. D., Orrenius S. The effect of albumin on the metabolism of ethoxyresorufin through O-deethylation and sulphate-conjugation using isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(11):1533–1538. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90481-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke M. D., Thompson S., Elcombe C. R., Halpert J., Haaparanta T., Mayer R. T. Ethoxy-, pentoxy- and benzyloxyphenoxazones and homologues: a series of substrates to distinguish between different induced cytochromes P-450. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Sep 15;34(18):3337–3345. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90355-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler R., Lindros K. O., Nordling A., Johansson I., Ingelman-Sundberg M. Zonation of cytochrome P450 isozyme expression and induction in rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 15;204(1):407–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Y., Eaton D. L. Association between responsiveness to phenobarbital induction of CYP2B1/2 and 3A1 in rat hepatic hyperplastic nodules and their zonal origin. Environ Health Perspect. 1993 Dec;101 (Suppl 5):185–190. doi: 10.1289/ehp.93101s5185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Y., Eaton D. L. Differential regulation of cytochrome(s) P450 2B1/2 by phenobarbital in hepatic hyperplastic nodules induced by aflatoxin B1 or diethylnitrosamine plus 2-acetylaminofluorene in male F344 rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;111(1):132–144. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(91)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Y., Farin F., Omiecinski C. J., Eaton D. L. Association between growth stimulation by phenobarbital and expression of cytochromes P450 1A1, 1A2, 2B1/2 and 3A1 in hepatic hyperplastic nodules in male F344 rats. Carcinogenesis. 1992 Apr;13(4):675–682. doi: 10.1093/carcin/13.4.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Y., White C. C., Eaton D. L. Decreased expression of cytochrome P450 mRNAs and related steroid hydroxylation activities in hepatic hyperplastic nodules in male F344 rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;123(1):151–159. doi: 10.1006/taap.1993.1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farin F. M., Omiecinski C. J. Regiospecific expression of cytochrome P-450s and microsomal epoxide hydrolase in human brain tissue. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1993 Oct-Nov;40(2-3):317–335. doi: 10.1080/15287399309531797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forscher P., Kaczmarek L. K., Buchanan J. A., Smith S. J. Cyclic AMP induces changes in distribution and transport of organelles within growth cones of Aplysia bag cell neurons. J Neurosci. 1987 Nov;7(11):3600–3611. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03600.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Shimada T. Oxidation of toxic and carcinogenic chemicals by human cytochrome P-450 enzymes. Chem Res Toxicol. 1991 Jul-Aug;4(4):391–407. doi: 10.1021/tx00022a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gähwiler B. H. Organotypic monolayer cultures of nervous tissue. J Neurosci Methods. 1981 Dec;4(4):329–342. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(81)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumdieck C. L., dos Santos J. E., Ho K. J. A new instrument for the rapid preparation of tissue slices. Anal Biochem. 1980 May 1;104(1):118–123. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90284-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindros K. O., Cai Y. A., Penttilä K. E. Role of ethanol-inducible cytochrome P-450 IIE1 in carbon tetrachloride-induced damage to centrilobular hepatocytes from ethanol-treated rats. Hepatology. 1990 Nov;12(5):1092–1097. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubet R. A., Mayer R. T., Cameron J. W., Nims R. W., Burke M. D., Wolff T., Guengerich F. P. Dealkylation of pentoxyresorufin: a rapid and sensitive assay for measuring induction of cytochrome(s) P-450 by phenobarbital and other xenobiotics in the rat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Apr;238(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90138-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubet R. A., Nims R. W., Mayer R. T., Cameron J. W., Schechtman L. M. Measurement of cytochrome P-450 dependent dealkylation of alkoxyphenoxazones in hepatic S9s and hepatocyte homogenates: effects of dicumarol. Mutat Res. 1985 Mar;142(3):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(85)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubet R. A., Syi J. L., Nelson J. O., Nims R. W. Induction of hepatic cytochrome P-450 mediated alkoxyresorufin O-dealkylase activities in different species by prototype P-450 inducers. Chem Biol Interact. 1990;75(3):325–339. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(90)90075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Elovaara E., Park S. S., Gelboin H. V., Hietanen E., Vainio H. Monoclonal antibody-directed characterization of benzene, ethoxyresorufin and pentoxyresorufin metabolism in rat liver microsomes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Sep 15;40(6):1255–1261. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90391-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Kamataki T., Waxman D. J., Guengerich F. P., Estabrook R. W., Feyereisen R., Gonzalez F. J., Coon M. J., Gunsalus I. C., Gotoh O. The P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, accession numbers, early trivial names of enzymes, and nomenclature. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Jan-Feb;12(1):1–51. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omiecinski C. J., Hassett C., Costa P. Developmental expression and in situ localization of the phenobarbital-inducible rat hepatic mRNAs for cytochromes CYP2B1, CYP2B2, CYP2C6, and CYP3A1. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;38(4):462–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu J. S., Kavanagh T. J., Reilly M. T., Omiecinski C. J. Direct determination of functional activity of cytochrome P-4501A1 and NADPH DT-diaphorase in hepatoma cell lines using noninvasive scanning laser cytometry. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1993 Oct-Nov;40(2-3):177–194. doi: 10.1080/15287399309531786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F., Gandolfi A. J., Krumdieck C. L., Putnam C. W., Zukoski C. F., 3rd, Davis W. M., Brendel K. Dynamic organ culture of precision liver slices for in vitro toxicology. Life Sci. 1985 Apr 8;36(14):1367–1375. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Sliedregt A., van Bezooijen C. F. Effect of different doses of 3-methylcholanthrene on the localization of the 3-methylcholanthrene-inducible isoenzymes of cytochrome P450 within the centrilobular and periportal zones of the rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Jun 1;39(11):1703–1708. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90114-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]