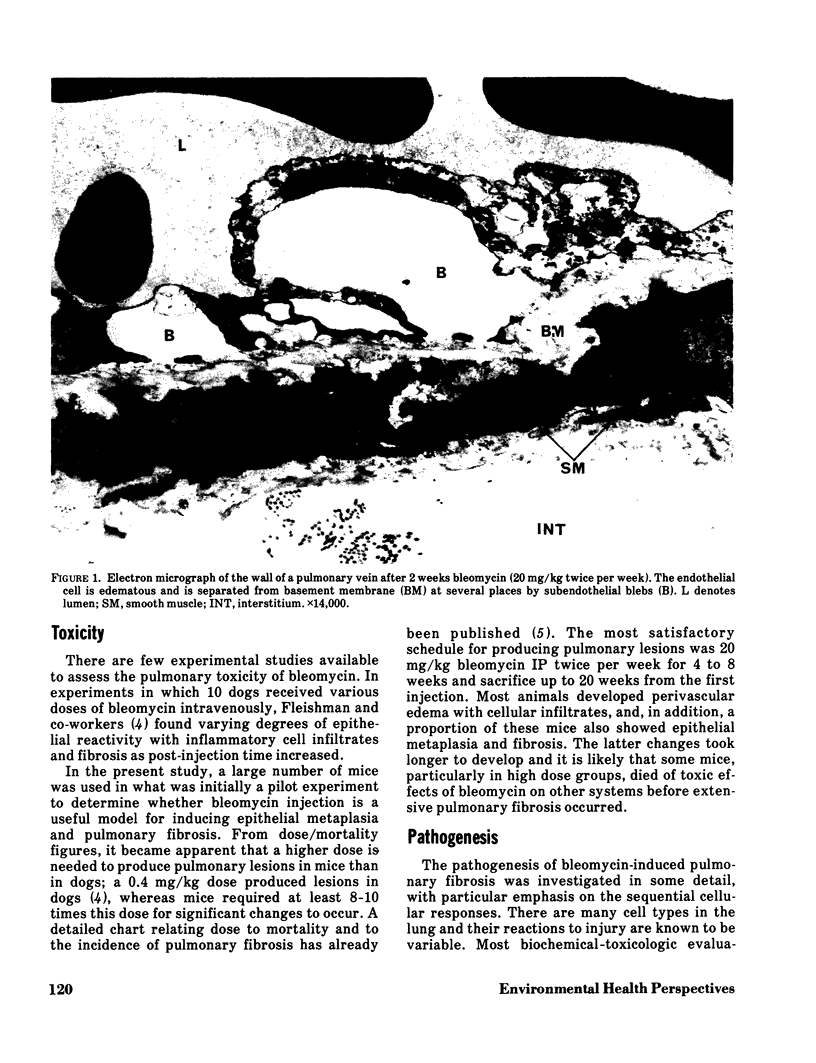
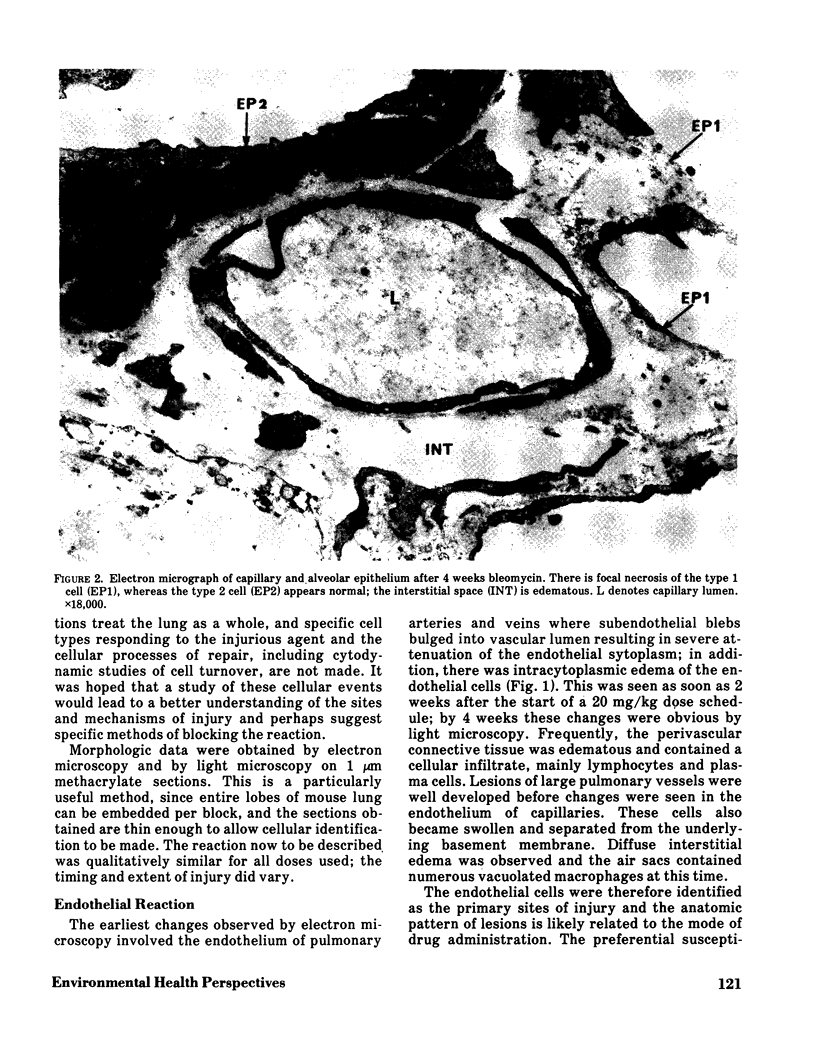
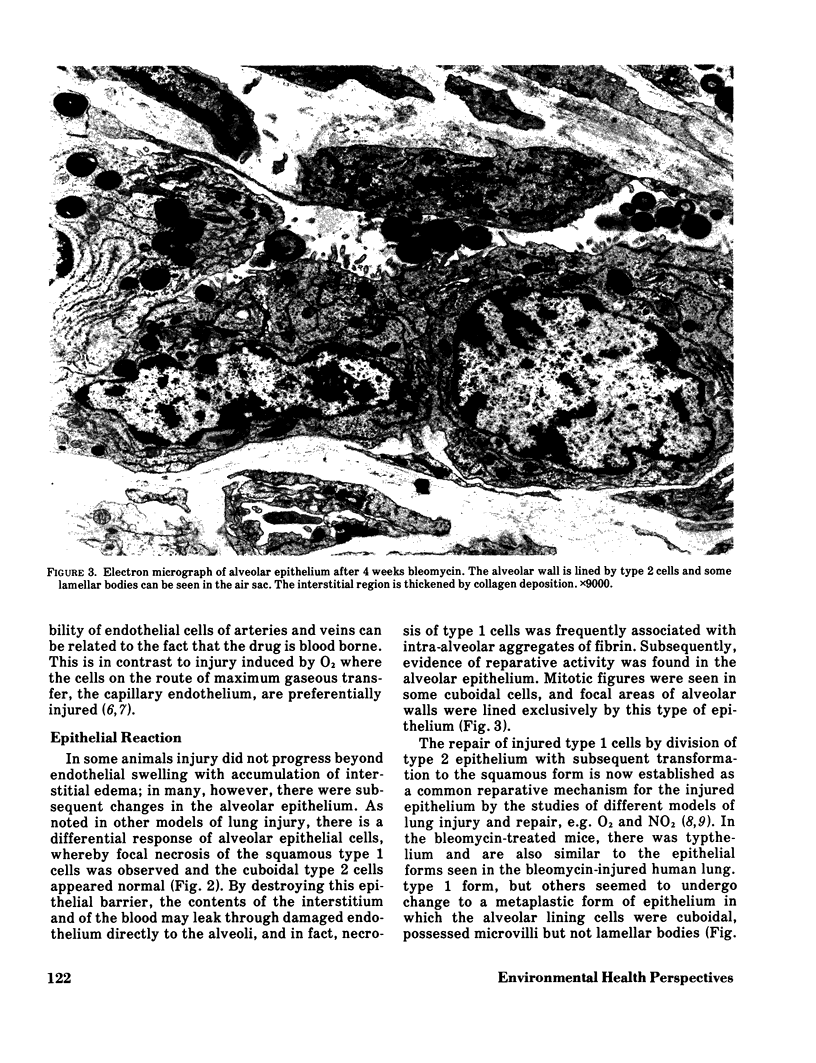
Abstract
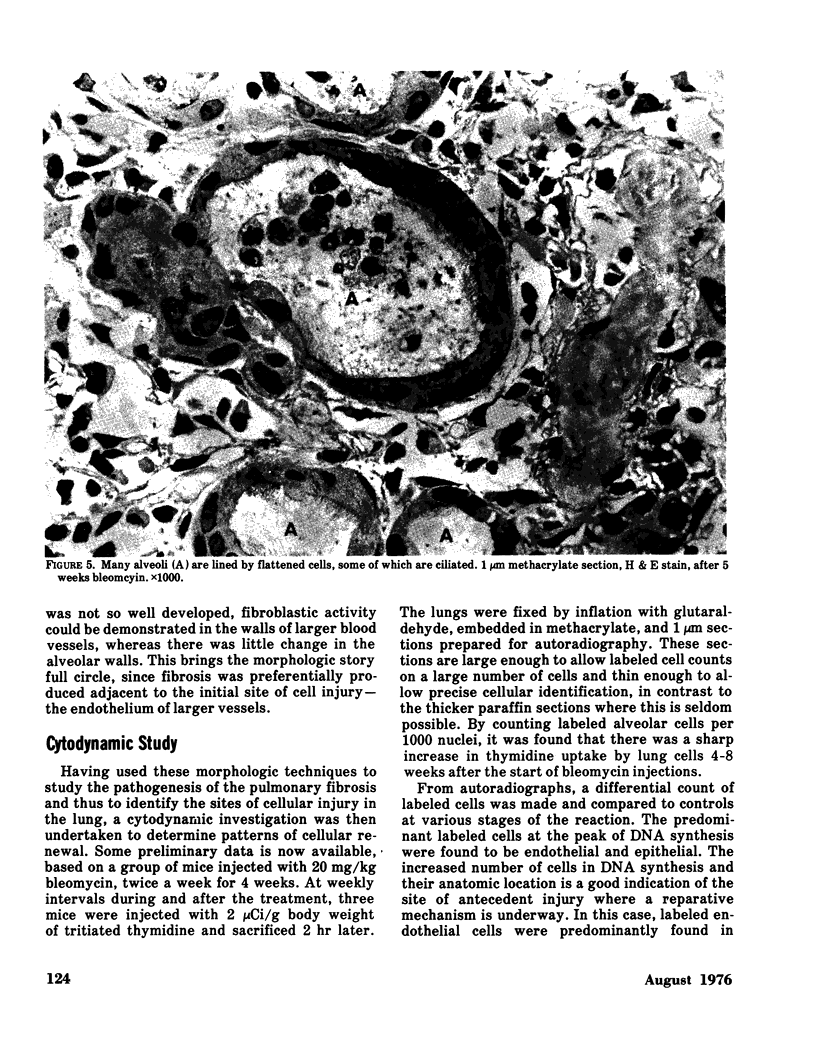
Diffuse pulmonary fibrosis is associated with bleomycin administration to humans. The sequential reactions of lung cells to this drug have now been investigated in mice following injection of 20 mg/kg bleomycin twice per week for 4 to 8 weeks. Cytoplasmic and subendothelial edema was first observed in large vessels and by 4 weeks involved the capillaries. The reaction in many animals did not progress further than endothelial lesions with accumulation of interstitial edema. However, 30% of mice subsequently showed necrosis of type 1 epithelium with a fibrinous exudate in the alveoli. Fibroblastic organization of the fibrin resulted in the deposition of intraalveolar collagen as well as extensive septal fibrosis by 8 weeks. Epithelial repair, normally accomplished by type 2 cell proliferation and transformation to type 1 cells, is characterized in this case by division and metaplasia of type 2 cells.The metaplastic cells were, however, capable of DNA synthesis and probably of further cell division. The results indicate that the pulmonary endothelium is the initial site of injury. Extensive damage to these cells could allow the drug access to interstitial and epithelial cells. Focal necrosis of type 1 epithelium is the critical event that triggers the exudation of fibrin and the subsequent reparative processes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. The pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Am J Pathol. 1974 Nov;77(2):185–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. The type 2 cell as progenitor of alveolar epithelial regeneration. A cytodynamic study in mice after exposure to oxygen. Lab Invest. 1974 Jan;30(1):35–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden D. H., Adamson I. Y. Endothelial regeneration as a marker of the differential vascular responses in oxygen-induced pulmonary edema. Lab Invest. 1974 Mar;30(3):350–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden D. H., Adamson I. Y., Wyatt J. P. Reaction of the lung cells to a high concentration of oxygen. Arch Pathol. 1968 Dec;86(6):671–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai L. S., Krishan A., Foley G. E. Effects of bleomycin on cells in culture: a quantitative cytochemical study. Cancer. 1974 Dec;34(6):1873–1877. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197412)34:6<1873::aid-cncr2820340603>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Cabral L. J., Stephens R. J., Freeman G. Renewal of alveolar epithelium in the rat following exposure to NO2. Am J Pathol. 1973 Feb;70(2):175–198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman A. P., Pietra G. G. Handling of bioactive materials by the lung (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 Oct 24;291(17):884–889. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197410242911706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman R. W., Baker J. R., Thompson G. R., Schaeppi U. H., Illievski V. R., Cooney D. A., Davis R. D. Bleomycin-induced interstitial pneumonia in dogs. Thorax. 1971 Nov;26(6):675–682. doi: 10.1136/thx.26.6.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto J. Radioautographic studies on the intracellular distribution of bleomycin-14C in mouse tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1974 Nov;34(11):2969–2974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paika K. D., Krishan A. Bleomycin-induced chromosmal aberrations in cultured mammalian cells. Cancer Res. 1973 May;33(5):961–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudders R. A., Hensley G. T. Bleomycin pulmonary toxicity. Chest. 1973 Apr;63(4):627–628. doi: 10.1378/chest.63.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H. Chemistry and mechanism of action of bleomycin. Fed Proc. 1974 Nov;33(11):2296–2302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Ishizuka M., Maeda K., Takeuchi T. Studies on bleomycin. Cancer. 1967 May;20(5):891–895. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(1967)20:5<891::aid-cncr2820200550>3.0.co;2-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Takeuchi T., Hori S., Sawa T., Ishizuka M. Studies on the mechanism of antitumor effect of bleomycin of squamous cell carcinoma. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Jul;25(7):409–420. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]