Abstract
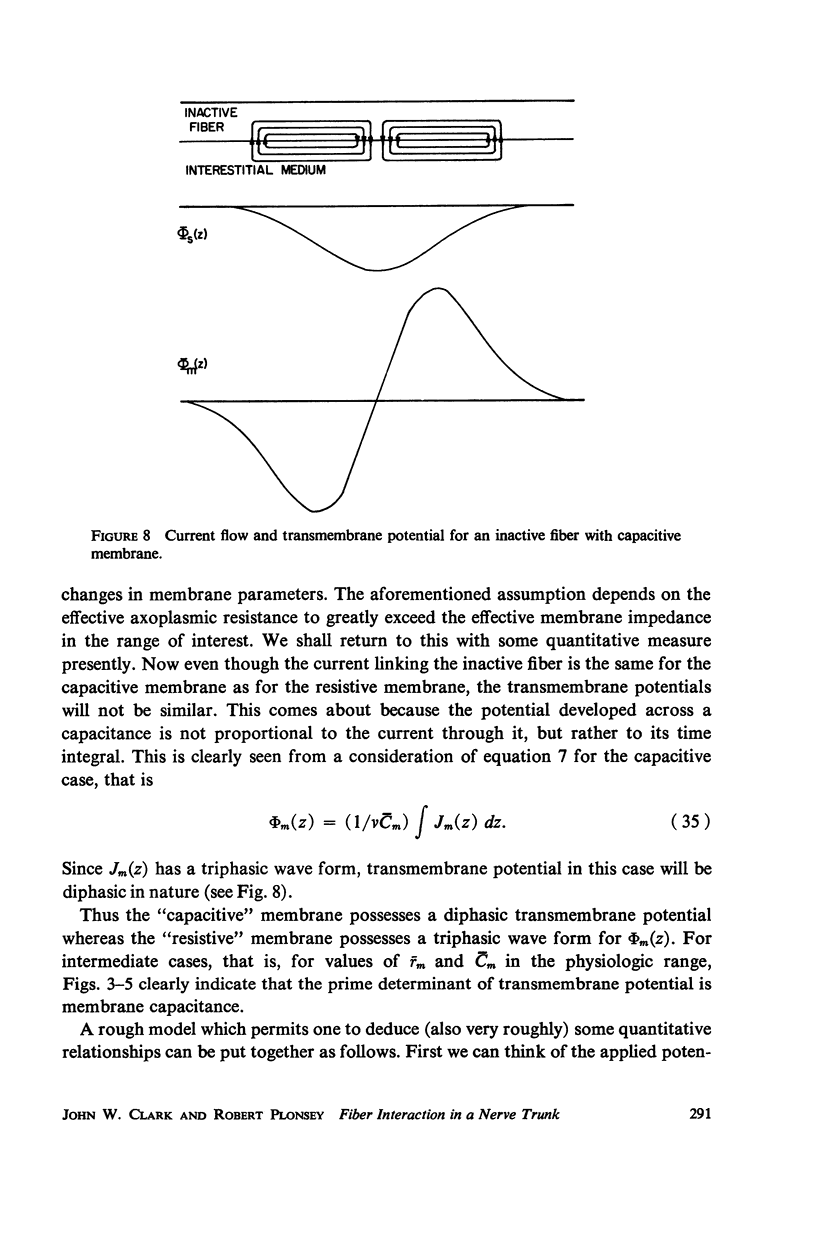
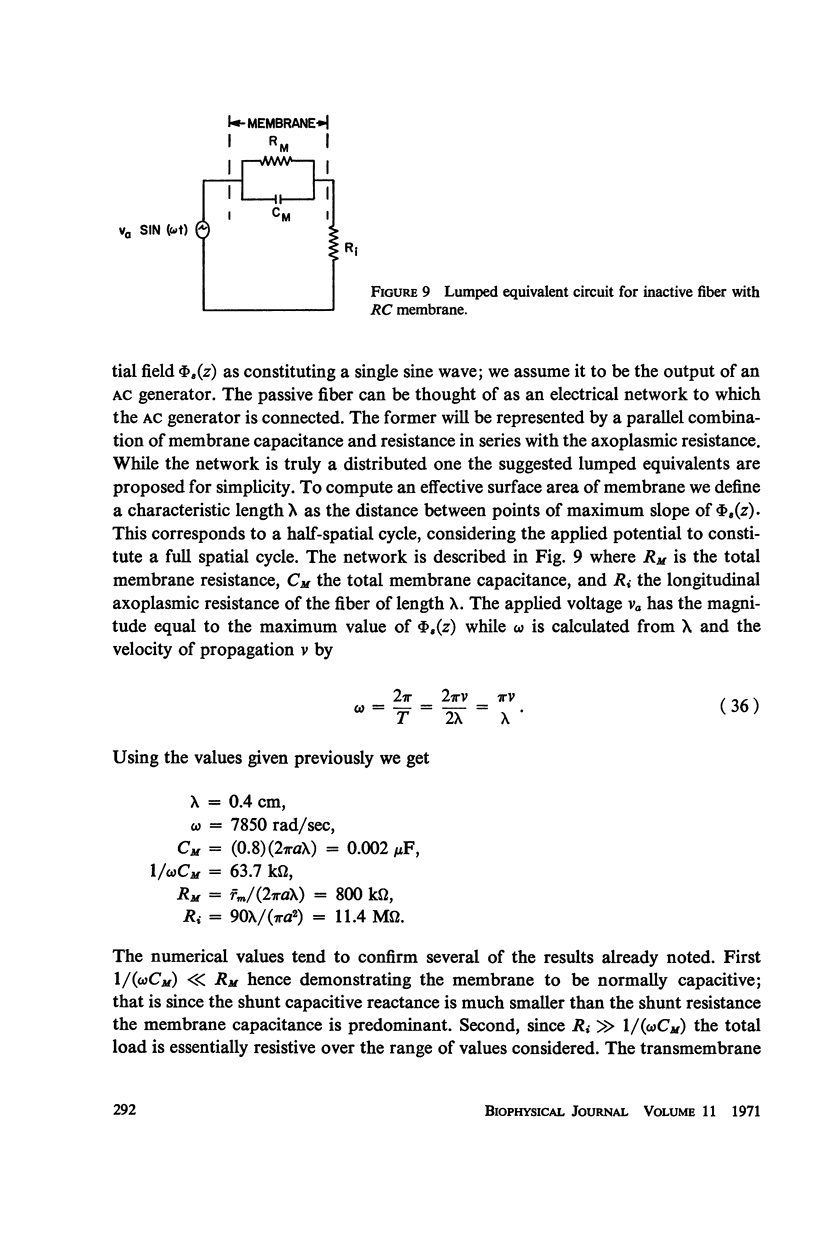
This paper is concerned with the nature of the transmembrane potential induced in an inactive nerve fiber lying in an impressed potential field within a nerve trunk. The impressed potential field is assumed to be produced by the synchronous activity of other fibers within the trunk; an expression for the induced transmembrane potential is obtained utilizing the principles of electromagnetic field theory. The results strongly indicate that membrane capacitance is the main determinant of the induced transmembrane potential wave form.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark J. W., Plonsey R. A mathematical study of nerve fiber interaction. Biophys J. 1970 Oct;10(10):937–957. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86344-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J., Plonsey R. A mathematical evaluation of the core conductor model. Biophys J. 1966 Jan;6(1):95–112. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(66)86642-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J., Plonsey R. The extracellular potential field of the single active nerve fiber in a volume conductor. Biophys J. 1968 Jul;8(7):842–864. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(68)86524-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


