Abstract
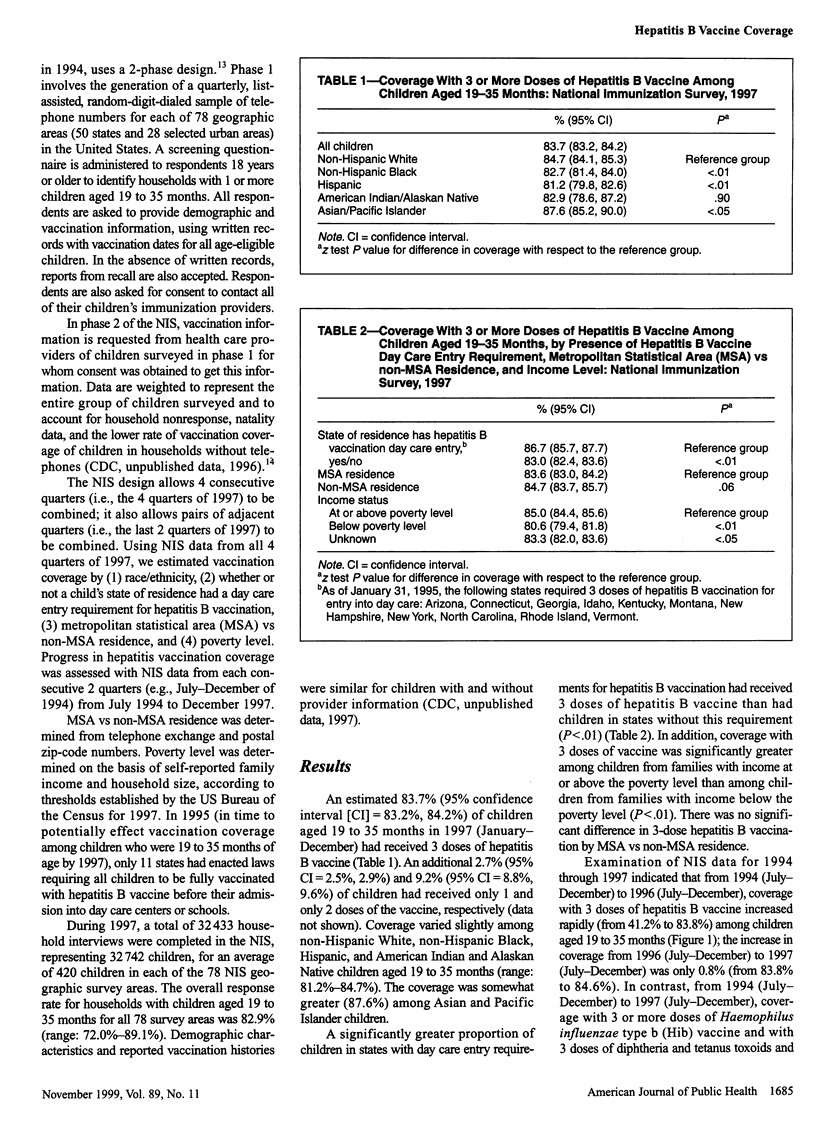
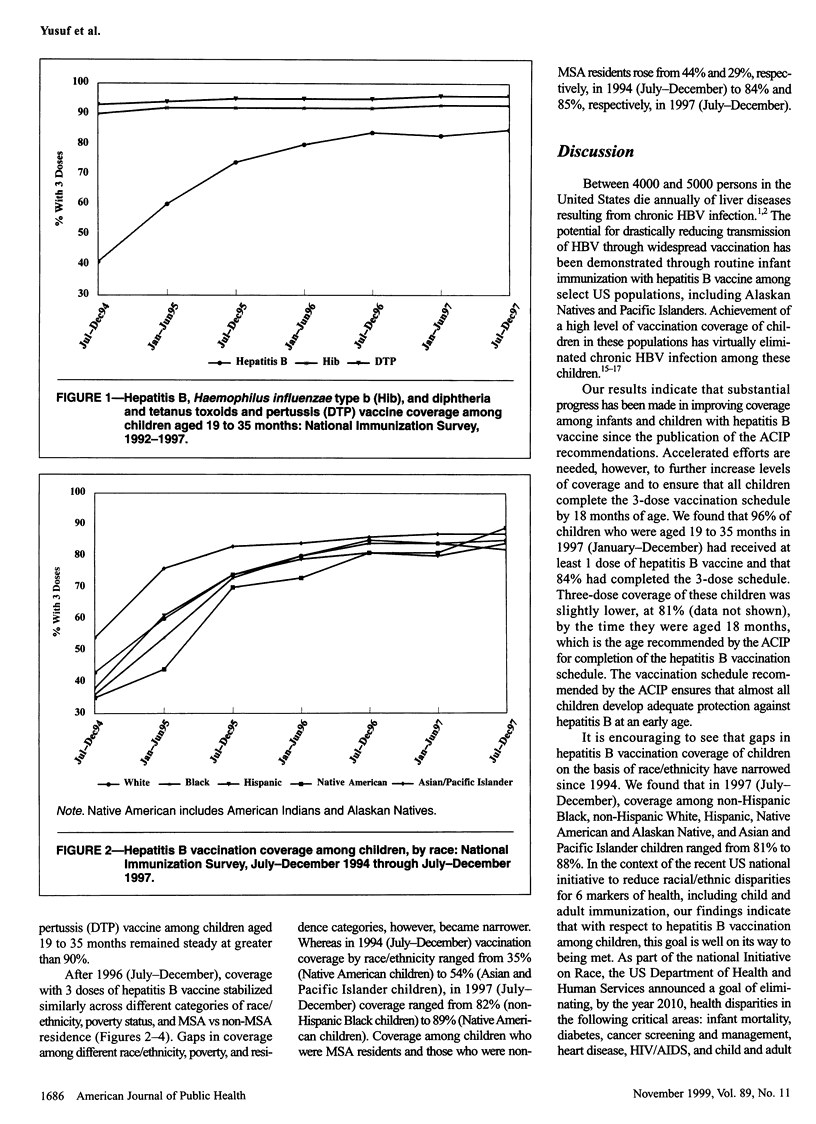
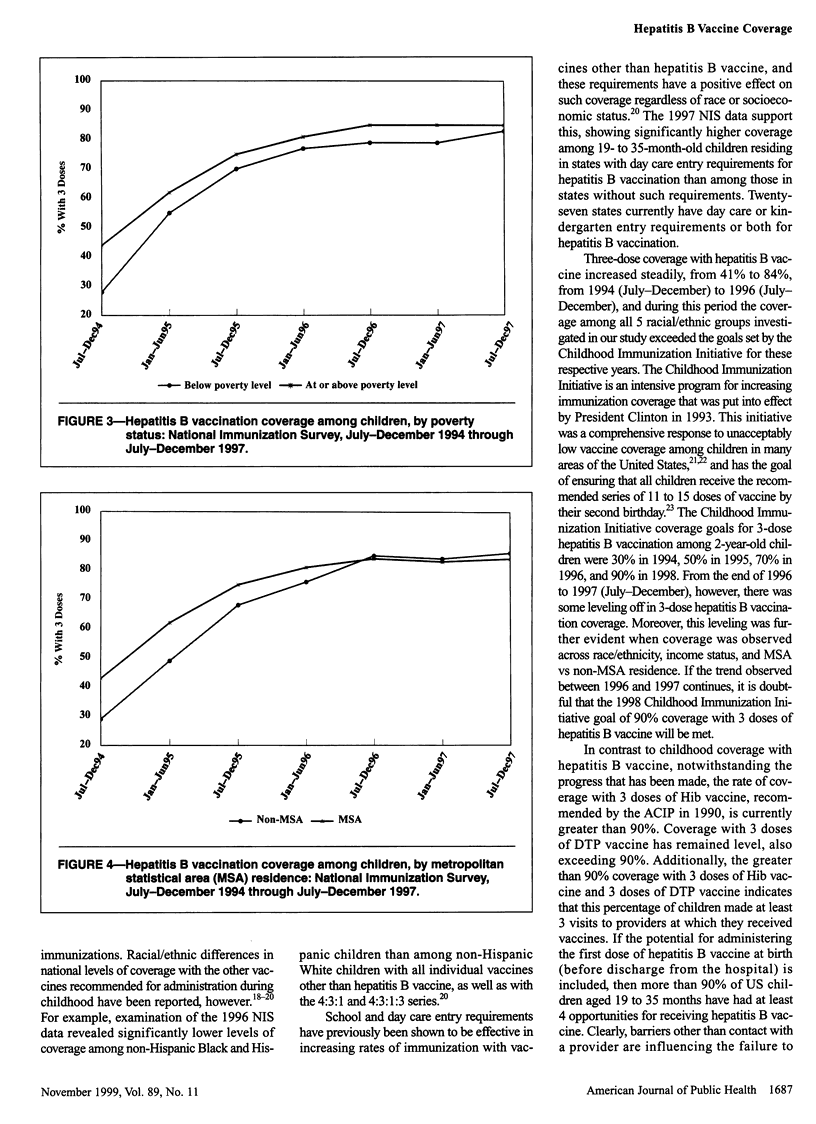
OBJECTIVES: This study was done to assess progress in hepatitis B vaccination of children from 1994 through 1997. METHODS: We used data from the National Immunization Survey (NIS), a random-digit-dialed telephone survey that includes a mail survey to verify vaccination providers' records. The NIS is conducted in 78 geographic areas (50 states and 28 selected urban areas) in the United States. RESULTS: A total of 32,433 household interviews were completed in the 1997 NIS. An estimated 83.7% of children aged 19 to 35 months received 3 or more doses of hepatitis B vaccine. Coverage with 3 doses was greater (86.7%) among children in states that had day care entry requirements for hepatitis B vaccination than among children in states without such requirements (83.0%) and was greater among children from families with incomes at or above the poverty level (85.0%) than among children below the poverty level (80.6%). Hepatitis B vaccination of children increased from 1994 through 1996, from 41% to 84%, but coverage reached a constant level of 84% to 85% in 1996/97. CONCLUSION: Although substantial progress has been made in fully vaccinating children against hepatitis B, greater efforts are needed to ensure that all infants receive 3 doses of hepatitis B vaccine.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Freed G. L., Bordley W. C., Clark S. J., Konrad T. R. Reactions of pediatricians to a new Centers for Disease Control recommendation for universal immunization of infants with hepatitis B vaccine. Pediatrics. 1993 Apr;91(4):699–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed G. L., Freeman V. A., Clark S. J., Konrad T. R., Pathman D. E. Pediatrician and family physician agreement with and adoption of universal hepatitis B immunization. J Fam Pract. 1996 Jun;42(6):587–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganiats T. G., Bowersox M. T., Ralph L. P. Universal neonatal hepatitis B immunization--are we jumping on the bandwagon too early? J Fam Pract. 1993 Feb;36(2):147–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halsey N. A. Discussion of Immunization Practices Advisory Committee/American Academy of Pediatrics recommendations for universal infant hepatitis B vaccination. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1993 May;12(5):446–449. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199305000-00038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBaron C. W., Chaney M., Baughman A. L., Dini E. F., Maes E., Dietz V., Bernier R. Impact of measurement and feedback on vaccination coverage in public clinics, 1988-1994. JAMA. 1997 Feb 26;277(8):631–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney F. J., Woodruff B. A., Erben J. J., Coleman P. J., Reid E. C., Schatz G. C., Kane M. A. Effect of a hepatitis B vaccination program on the prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jan;167(1):203–207. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.1.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon B. J., Rhoades E. R., Heyward W. L., Tower E., Ritter D., Lanier A. P., Wainwright R. B., Helminiak C. A comprehensive programme to reduce the incidence of hepatitis B virus infection and its sequelae in Alaskan natives. Lancet. 1987 Nov 14;2(8568):1134–1136. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91557-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathman D. E., Konrad T. R., Freed G. L., Freeman V. A., Koch G. G. The awareness-to-adherence model of the steps to clinical guideline compliance. The case of pediatric vaccine recommendations. Med Care. 1996 Sep;34(9):873–889. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199609000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poovorawan Y., Sanpavat S., Pongpunlert W., Chumdermpadetsuk S., Sentrakul P., Safary A. Protective efficacy of a recombinant DNA hepatitis B vaccine in neonates of HBe antigen-positive mothers. JAMA. 1989 Jun 9;261(22):3278–3281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro C. N., Margolis H. S. Impact of hepatitis B virus infection on women and children. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1992 Mar;6(1):75–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. E., Taylor P. E., Tong M. J., Toy P. T., Vyas G. N., Nair P. V., Weissman J. Y., Krugman S. Yeast-recombinant hepatitis B vaccine. Efficacy with hepatitis B immune globulin in prevention of perinatal hepatitis B virus transmission. JAMA. 1987 May 15;257(19):2612–2616. doi: 10.1001/jama.257.19.2612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff B. A., Stevenson J., Yusuf H., Kwong S. L., Todoroff K. P., Hadler J. L., Hoyt M. A., Mahoney F. J. Progress toward integrating hepatitis B vaccine into routine infant immunization schedules in the United States, 1991 through 1994. Connecticut Hepatitis B Project Group. Pediatrics. 1996 Jun;97(6 Pt 1):798–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


