Abstract
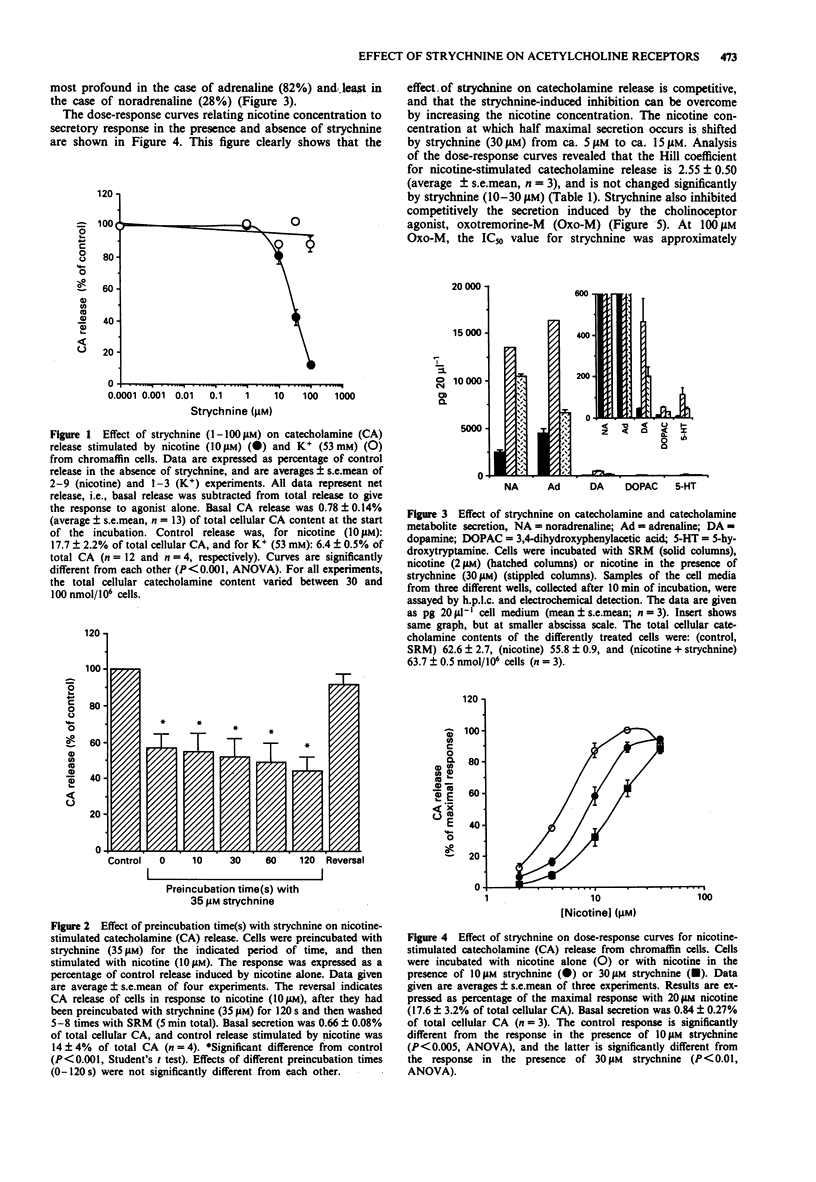
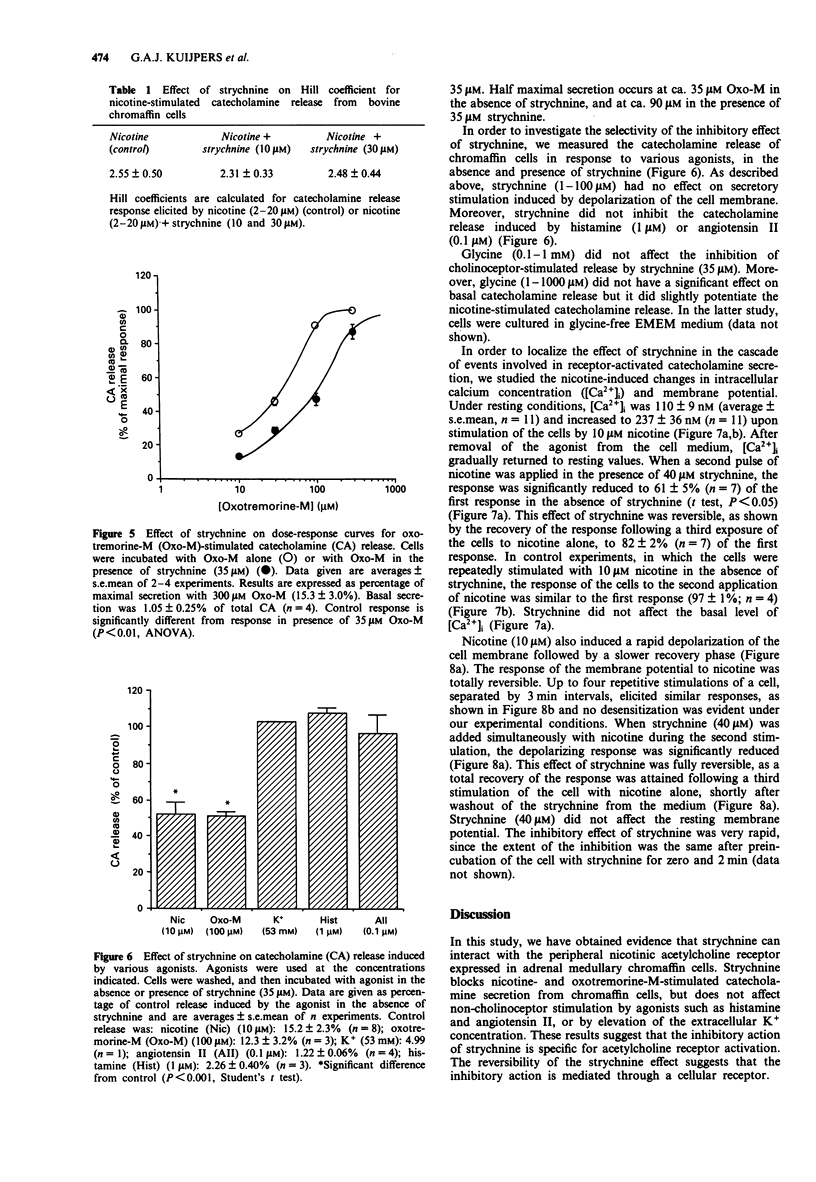
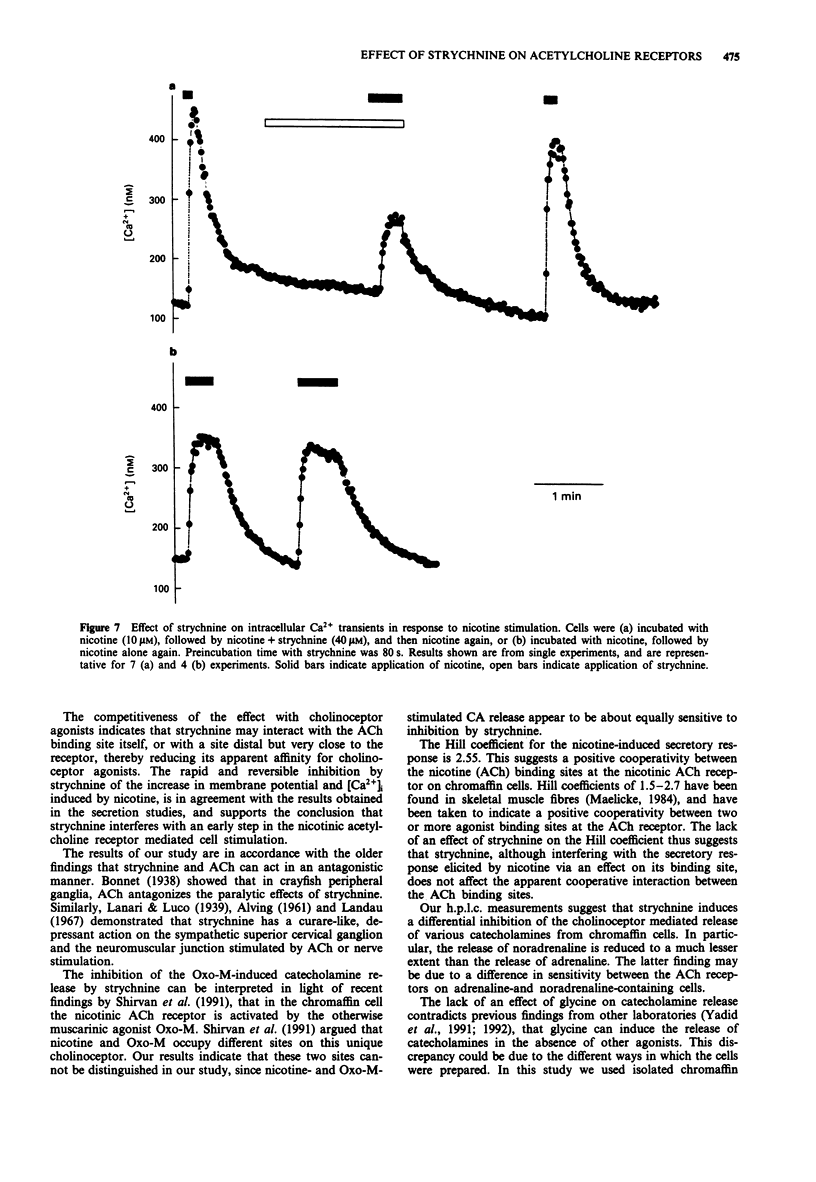
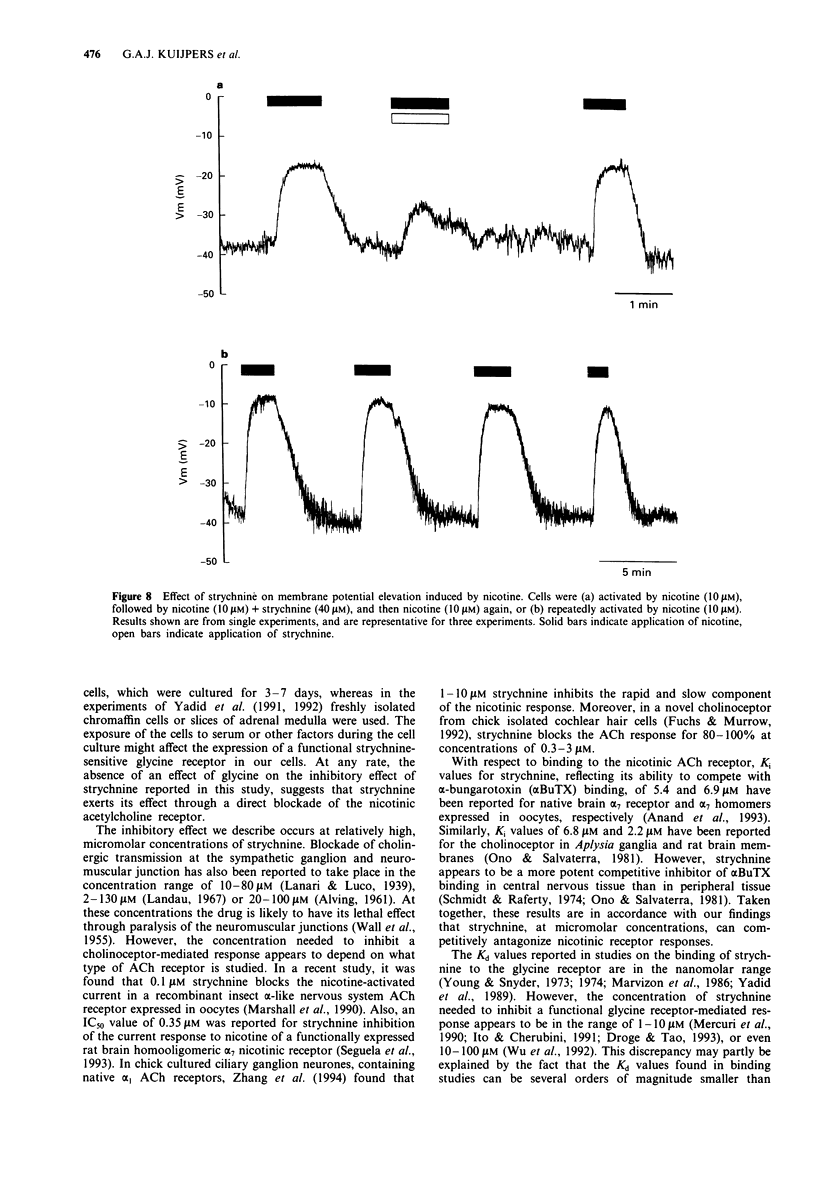
1. Strychnine, which is known as a potent and selective antagonist of the inhibitory glycine receptor in the central nervous system, inhibits the nicotinic stimulation of catecholamine release from bovine cultured adrenal chromaffin cells in a concentration-dependent (1-100 microM) manner. At 10 microM nicotine, the IC50 value for strychnine is approximately 30 microM. Strychnine also inhibits the nicotine-induced membrane depolarization and increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration. 2. The inhibitory action of strychnine is reversible and is selective for nicotinic stimulation, with no effect observed on secretion elicited by a high external K+ concentration, histamine or angiotensin II. 3. Strychnine competes with nicotine in its effect, but not modify the apparent positive cooperatively of the nicotine binding sites. In the absence of nicotine, strychnine has no effect on catecholamine release. Glycine does not affect catecholamine release nor the inhibitory action of strychnine on this release. 4. These results suggest that strychnine interacts with the agonist binding site of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in chromaffin cells, thus exerting a pharmacological effect independently of the glycine receptor.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALVING B. O. The action of strychnine at cholinergic junctions. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1961 Apr 1;131:123–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anand R., Peng X., Lindstrom J. Homomeric and native alpha 7 acetylcholine receptors exhibit remarkably similar but non-identical pharmacological properties, suggesting that the native receptor is a heteromeric protein complex. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jul 26;327(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80177-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beers W. H., Reich E. Structure and activity of acetylcholine. Nature. 1970 Dec 5;228(5275):917–922. doi: 10.1038/228917a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D., Almers W. Block of sodium conductance and gating current in squid giant axons poisoned with quaternary strychnine. Biophys J. 1979 Jul;27(1):57–73. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85202-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Duggan A. W., Johnston G. A. The specificity of strychnine as a glycine antagonist in the mammalian spinal cord. Exp Brain Res. 1971 Jun 29;12(5):547–565. doi: 10.1007/BF00234248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Hösli L., Johnston G. A. A pharmacological study of the depression of spinal neurones by glycine and related amino acids. Exp Brain Res. 1968;6(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00235443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A., Aprison M. H., Werman R. The effects of strychnine on the inhibition of interneurons by glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1969 Mar;8(2):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(69)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGroat W. C. The effects of glycine, GABA and strychnine on sacral parasympathetic preganglionic neurones. Brain Res. 1970 Mar 17;18(3):542–544. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droge M. H., Tao Y. Glycine effects on in vitro motor pattern generation in mouse spinal cord. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Aug 20;158(2):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90248-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frostholm A., Rotter A. Glycine receptor distribution in mouse CNS: autoradiographic localization of [3H]strychnine binding sites. Brain Res Bull. 1985 Nov;15(5):473–486. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(85)90038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. A., Murrow B. W. A novel cholinergic receptor mediates inhibition of chick cochlear hair cells. Proc Biol Sci. 1992 Apr 22;248(1321):35–40. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1992.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García Ramos J. On the mechanism of strychnine spikes. Acta Physiol Lat Am. 1974;24(2):124–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldinger A., Müller W. E. Stereospecific interaction of bicuculline with specific [3H]strychnine binding to rat spinal cord synaptosomal membranes. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Jan;16(1):91–95. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90107-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D., Pfeiffer F., Betz H. Photoaffinity-labelling of the glycine receptor of rat spinal cord. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Apr 5;131(3):519–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Rienitz A., Schmitt B., Methfessel C., Zensen M., Beyreuther K., Gundelfinger E. D., Betz H. The strychnine-binding subunit of the glycine receptor shows homology with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):215–220. doi: 10.1038/328215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Marty A. Muscarinic activation of ionic currents measured by a new whole-cell recording method. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):145–159. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Cherubini E. Strychnine-sensitive glycine responses of neonatal rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1991;440:67–83. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijpers G. A., Rosario L. M., Ornberg R. L. Role of intracellular pH in secretion from adrenal medulla chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):698–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau E. M. The effect of strychnine on the neuro-muscular junction of the rat. Life Sci. 1967 Dec 1;6(23):2515–2517. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90315-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livett B. G. Adrenal medullary chromaffin cells in vitro. Physiol Rev. 1984 Oct;64(4):1103–1161. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.4.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J., Buckingham S. D., Shingai R., Lunt G. G., Goosey M. W., Darlison M. G., Sattelle D. B., Barnard E. A. Sequence and functional expression of a single alpha subunit of an insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4391–4398. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07889.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvizón J. C., Vázquez J., García Calvo M., Mayor F., Jr, Ruíz Gómez A., Valdivieso F., Benavides J. The glycine receptor: pharmacological studies and mathematical modeling of the allosteric interaction between the glycine- and strychnine-binding sites. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Dec;30(6):590–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercuri N. B., Calabresi P., Bernardi G. Effects of glycine on neurons in the rat substantia nigra zona compacta: in vitro electrophysiological study. Synapse. 1990;5(3):190–200. doi: 10.1002/syn.890050304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill S. K., Bolger G. T. The effects of strychnine on the regulation of voltage-dependent calcium channels by dihydropyridines in brain and heart. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1990 Apr;35(4):833–840. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(90)90367-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono J. K., Salvaterra P. M. Snake alpha-toxin effects on cholinergic and noncholinergic responses of Aplysia californica neurons. J Neurosci. 1981 Mar;1(3):259–270. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-03-00259.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul I. A., Basile A. S., Rojas E., Youdim M. B., De Costa B., Skolnick P., Pollard H. B., Kuijpers G. A. Sigma receptors modulate nicotinic receptor function in adrenal chromaffin cells. FASEB J. 1993 Sep;7(12):1171–1178. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.12.8375616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer F., Simler R., Grenningloh G., Betz H. Monoclonal antibodies and peptide mapping reveal structural similarities between the subunits of the glycine receptor of rat spinal cord. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7224–7227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., York D. H. Strychnine block of neural and drug-induced inhibition in the cerebral cortex. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):922–923. doi: 10.1038/216922a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safronov B. V., Baev K. V., Batueva I. V., Rusin K. I., Suderevskaya E. I. Peculiarities of receptor-channel complexes for inhibitory mediators in the membranes of lamprey spinal cord neurones. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Jul 17;102(1):82–86. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90311-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Raftery M. A. The cation sensitivity of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. J Neurochem. 1974 Oct;23(4):617–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Darlison M. G., Fujita N., Burt D. R., Stephenson F. A., Rodriguez H., Rhee L. M., Ramachandran J., Reale V., Glencorse T. A. Sequence and functional expression of the GABA A receptor shows a ligand-gated receptor super-family. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):221–227. doi: 10.1038/328221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. I. Effects of strychnine on the potassium conductance of the frog node of Ranvier. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Jun;69(6):897–914. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.6.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. I. Effects of strychnine on the sodium conductance of the frog node of Ranvier. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Jun;69(6):915–926. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.6.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirvan M. H., Pollard H. B., Heldman E. Mixed nicotinic and muscarinic features of cholinergic receptor coupled to secretion in bovine chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4860–4864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séguéla P., Wadiche J., Dineley-Miller K., Dani J. A., Patrick J. W. Molecular cloning, functional properties, and distribution of rat brain alpha 7: a nicotinic cation channel highly permeable to calcium. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):596–604. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00596.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EULER U. S., FLODING I. A fluorimetric micromethod for differential estimation of adrenaline and noradrenaline. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1955;33(118):45–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL P. D., MCCULLOCH W. S., LETTVIN J. Y., PITTS W. H. Effects of strychnine with special reference to spinal afferent fibres. Epilepsia. 1955 Nov;4:29–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1955.tb03171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. L., Ziskind-Conhaim L., Sweet M. A. Early development of glycine- and GABA-mediated synapses in rat spinal cord. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):3935–3945. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-03935.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yadid G., Maor G., Youdim M. B., Silberman M., Zinder O. Autoradiographic localization of strychnine-sensitive glycine receptor in bovine adrenal medulla. Neurochem Res. 1993 Oct;18(10):1051–1055. doi: 10.1007/BF00966683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yadid G., Youdim M. B., Zinder O. High-affinity strychnine binding to adrenal medulla chromaffin cell membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan 17;175(3):365–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90579-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yadid G., Youdim M. B., Zinder O. Preferential release of epinephrine by glycine from adrenal chromaffin cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Oct 20;221(2-3):389–391. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90729-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yadid G., Zinder O., Youdim M. B. Effects of the glycine prodrug milacemide (2-N-pentylaminoacetamide) on catecholamine secretion from isolated adrenal medulla chromaffin cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;104(3):760–764. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12501.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto D. Dynamics of strychnine block of single sodium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:395–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Strychnine binding associated with glycine receptors of the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2832–2836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z. W., Vijayaraghavan S., Berg D. K. Neuronal acetylcholine receptors that bind alpha-bungarotoxin with high affinity function as ligand-gated ion channels. Neuron. 1994 Jan;12(1):167–177. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90161-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


