Abstract
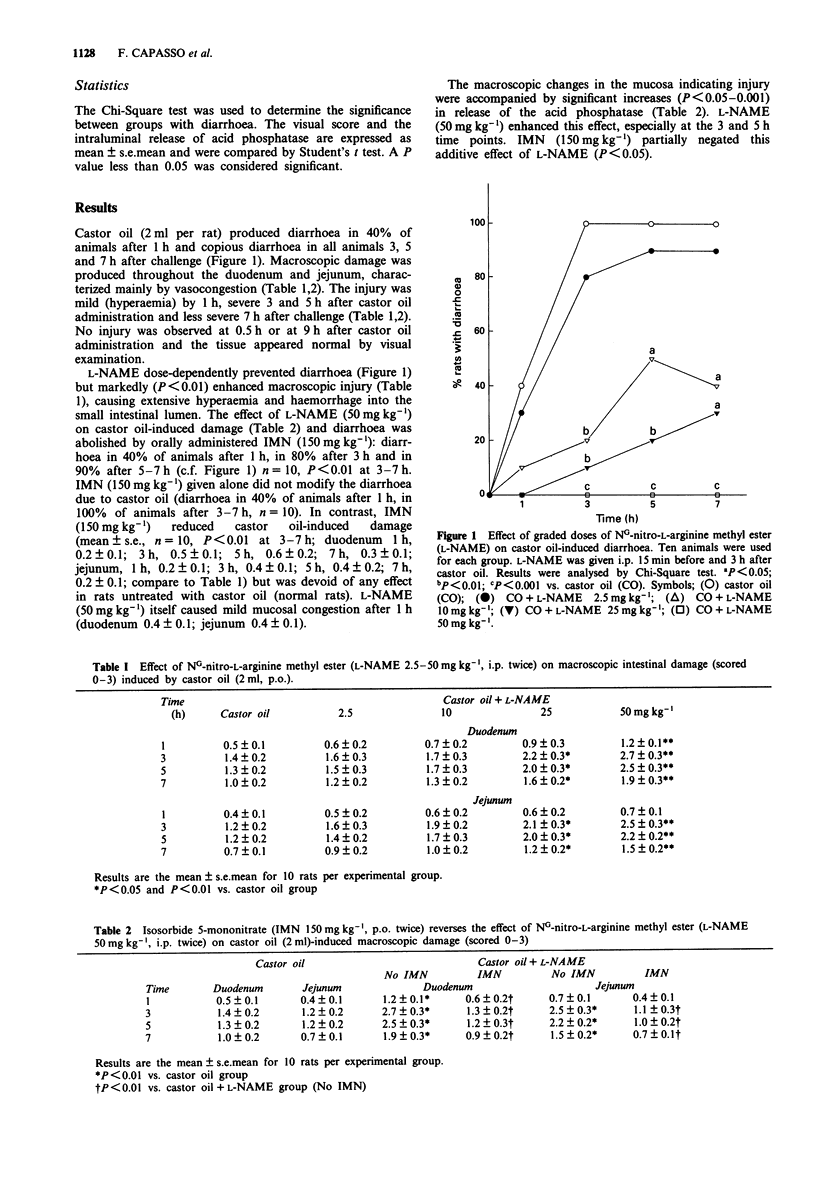
1. Castor oil (2 ml orally) produced diarrhoea in rats 1-7 h after challenge, which was associated with gross damage to the duodenal and jejunal mucosa. 2. The injury was accompanied by release of acid phosphatase into the gut lumen, indicating cellular injury. 3. Intraperitoneal injection of the nitric oxide (NO) synthase inhibitor NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, 2.5-50 mg kg-1 twice), prevented the diarrhoea. The dose of L-NAME (50 mg kg-1) completely blocked the diarrhoea but increased the release of acid phosphatase and worsened the gross damage. 4. The NO donating compound, isosorbide-5-mononitrate (IMN, 150 mg kg-1 twice) reversed the effects of L-NAME (50 mg kg-1) on castor oil-induced diarrhoea, gross damage and acid phosphatase release. 5. The apparent dissociation of the diarrhoeal and intestinal mucosal damaging effects of castor oil suggest that NO has a protective effect on the rat duodenal and jejunal mucosa, but that NO mediates, in part, the diarrhoea effect of this laxative.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beubler E., Juan H. Effect of ricinoleic acid and other laxatives on net water flux and prostaglandin E release by the rat colon. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;31(10):681–685. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1979.tb13628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J. Pharmacology of laxatives. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1977;17:355–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.17.040177.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boughton-Smith N. K., Evans S. M., Laszlo F., Whittle B. J., Moncada S. The induction of nitric oxide synthase and intestinal vascular permeability by endotoxin in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;110(3):1189–1195. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13940.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boughton-Smith N. K., Evans S. M., Whittle B. J., Moncada S. Induction of nitric oxide synthase in rat intestine and its association with tissue injury. Agents Actions. 1993;38(Spec No):C125–C126. doi: 10.1007/BF01991159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretagne J. F., Vidon N., L'Hirondel C., Bernier J. J. Increased cell loss in the human jejunum induced by laxatives (ricinoleic acid, dioctyl sodium sulphosuccinate, magnesium sulphate, bile salts). Gut. 1981 Apr;22(4):264–269. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.4.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capasso F., Mascolo N., Autore G., Romano V. Laxatives and the production of autacoids by rat colon. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1986 Aug;38(8):627–629. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1986.tb03097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline W. S., Lorenzsonn V., Benz L., Bass P., Olsen W. A. The effects of sodium ricinoleate on small intestinal function and structure. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):380–390. doi: 10.1172/JCI108482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbins J. W., Binder H. J. Effect of bile salts and fatty acids on the colonic absorption of oxalate. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jun;70(6):1096–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaginella T. S., Bass P. Laxatives: an update on mechanism of action. Life Sci. 1978 Sep 11;23(10):1001–1009. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaginella T. S., Chadwick V. S., Debongnie J. C., Lewis J. C., Phillips S. F. Perfusion of rabbit colon with ricinoleic acid: dose-related mucosal injury, fluid secretion, and increased permeability. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jul;73(1):95–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaginella T. S., Haddad A. C., Go V. L., Phillips S. F. Cytotoxicity of ricinoleic acid (castor oil) and other intestinal secretagogues on isolated intestinal epithelial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Apr;201(1):259–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaginella T. S., Phillips S. F., Dozois R. R., Go V. L. Stimulation of adenylate cyclase in homogenates of isolated intestinal epithelial cells from hamsters. Effects of gastrointestinal hormones, prostaglandins, and deoxycholic and ricinoleic acids. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jan;74(1):11–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaginella T., Bass P. Fatty acid inhibition of water absorption and energy production in the hamster jejunum. FEBS Lett. 1975 May 15;53(3):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullikson G. W., Cline W. S., Lorenzsonn V., Benz L., Olsen W. A., Bass P. Effects of anionic surfactants on hamster small intestinal membrane structure and function: relationship to surface activity. Gastroenterology. 1977 Sep;73(3):501–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzo A. A., Mascolo N., Autore G., Di Carlo G., Capasso F. Increased ex-vivo colonic generation of PAF induced by diphenylmethane stimulant laxatives in rats, mice, guinea-pigs and rabbits. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;45(10):916–918. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1993.tb05621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzo A. A., Mascolo N., Viola P., Capasso F. Inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase enhance rat ileum contractions induced by ricinoleic acid in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct 12;243(1):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90172-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Brzozowski T., Majka J., Pytko-Polonczyk J., Stachura J. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase delays healing of chronic gastric ulcers. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug 3;239(1-3):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90997-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laszlo F., Whittle B. J., Moncada S. Time-dependent enhancement or inhibition of endotoxin-induced vascular injury in rat intestine by nitric oxide synthase inhibitors. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;111(4):1309–1315. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14887.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNaughton W. K. Nitric oxide-donating compounds stimulate electrolyte transport in the guinea pig intestine in vitro. Life Sci. 1993;53(7):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90716-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascolo N., Izzo A. A., Autore G., Barbato F., Capasso F. Nitric oxide and castor oil-induced diarrhea. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Jan;268(1):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascolo N., Izzo A. A., Barbato F., Capasso F. Inhibitors of nitric oxide synthetase prevent castor-oil-induced diarrhoea in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Apr;108(4):861–864. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13478.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. J., Sadowska-Krowicka H., Chotinaruemol S., Kakkis J. L., Clark D. A. Amelioration of chronic ileitis by nitric oxide synthase inhibition. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jan;264(1):11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. J., Zhang X. J., Sadowska-Krowicka H., Chotinaruemol S., McIntyre J. A., Clark D. A., Bustamante S. A. Nitric oxide release in response to gut injury. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1993 Feb;28(2):149–154. doi: 10.3109/00365529309096062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAO S. The effect of ricinoleic acid and phenolphthalein on creatine phosphate levels. Biochem Pharmacol. 1963 Feb;12:216–217. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(63)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. A., Love A. H., Mitchell T. G., Neptune E. M., Jr Cathartics and the sodium pump. Nature. 1965 Jun 26;206(991):1367–1368. doi: 10.1038/2061367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto A., Autore G., Mascolo N., Sorrentino R., Biondi A., Izzo A. A., Capasso F. Time course of PAF formation by gastrointestinal tissue in rats after castor oil challenge. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;44(3):224–226. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1992.tb03586.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto A., Calignano A., Mascolo N., Autore G., Capasso F. Castor oil increases intestinal formation of platelet-activating factor and acid phosphatase release in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;96(4):872–874. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11897.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racusen L. C., Binder H. J. Ricinoleic acid stimulation of active anion secretion in colonic mucosa of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):743–749. doi: 10.1172/JCI109358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders D. R., Sillery J., Rachmilewitz D., Rubin C. E., Tytgat G. N. Effect of bisacodyl on the structure and function of rodent and human intestine. Gastroenterology. 1977 May;72(5 Pt 1):849–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders D. R., Sillery J., Surawica C., Tytgat G. N. Effect of phenolphthalein on the function and structure of rodent and human intestine. Am J Dig Dis. 1978 Oct;23(10):909–913. doi: 10.1007/BF01072465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon B., Kather H. Interaction of laxatives with enzymes of cyclic AMP metabolism from human colonic mucosa. Eur J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;10(3):231–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1980.tb00025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamai H., Gaginella T. S. Direct evidence for nitric oxide stimulation of electrolyte secretion in the rat colon. Free Radic Res Commun. 1993;19(4):229–239. doi: 10.3109/10715769309056511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepperman B. L., Brown J. F., Whittle B. J. Nitric oxide synthase induction and intestinal epithelial cell viability in rats. Am J Physiol. 1993 Aug;265(2 Pt 1):G214–G218. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.265.2.G214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. T., Xie Y., Musch M. W., Chang E. B. Sodium nitroprusside stimulates anion secretion and inhibits sodium chloride absorption in rat colon. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jul;266(1):224–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


