Abstract
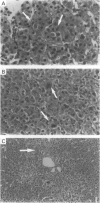
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) occurs in many communities and races. A form of PFIC in five children from two consanguineous marriages in an Irish kindred is described. In addition, a review of clinical information from the records of three deceased members of the kindred strongly implies that they also suffered from PFIC. The children had a history of neonatal diarrhoea, sepsis, and intermittent jaundice that ultimately became permanent. They suffered intractable pruritus and growth retardation. Despite evidence of severe cholestasis, serum gamma-glutamyl transferase and cholesterol were normal in these children. Sweat sodium concentration were raised in three children. Liver histology showed severe intrahepatic cholestasis and hepatocellular injury. Urinary bile acid analysis revealed a non-specific pattern consistent with chronic cholestasis. These children suffer from a form of PFIC remarkably similar to that occurring in members of the Byler kindred.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso E. M., Snover D. C., Montag A., Freese D. K., Whitington P. F. Histologic pathology of the liver in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1994 Feb;18(2):128–133. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199402000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballow M., Margolis C. Z., Schachtel B., Hsia Y. E. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Pediatrics. 1973 Jun;51(6):998–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton R. J., Iber F. L., Ruebner B. H., McKusick V. A. Byler disease. Fatal familial intrahepatic cholestasis in an Amish kindred. Am J Dis Child. 1969 Jan;117(1):112–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahms B. B. Hepatoma in familial cholestatic cirrhosis of childhood: its occurrence in twin brothers. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1979 Jan;103(1):30–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos R., de Wolf-Peeters C., Desmet V., Eggermont E., Van Acker K. Progressive intrahepatic cholestasis (Byler's disease): case report. Gut. 1975 Dec;16(12):943–950. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.12.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray O. P., Saunders R. A. Familial intrahepatic cholestatic jaundice in infancy. Arch Dis Child. 1966 Jun;41(217):320–328. doi: 10.1136/adc.41.217.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillemeier A. C., Hen J., Jr, Riely C. A., Dolan T. F., Jr, Gryboski J. D. Meconium peritonitis and increasing sweat chloride determinations in a case of familial progressive intrahepatic cholestasis. Pediatrics. 1982 Mar;69(3):325–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemin E., Dumont M., Bernard O., Erlinger S., Hadchouel M. Evidence for defective primary bile acid secretion in children with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (Byler disease). Eur J Pediatr. 1994 Jun;153(6):424–428. doi: 10.1007/BF01983406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. A., Rabin L., Buckley C. H., Webster G. K., Owens D. Progressive intrahepatic cholestasis of infancy and childhood. A clinicopathological study of patient surviving to the age of 18 years. Gastroenterology. 1976 Oct;71(4):675–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linarelli L. G., Williams C. N., Phillips M. J. Byler's disease: fatal intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr. 1972 Sep;81(3):484–492. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggiore G., Bernard O., Riely C. A., Hadchouel M., Lemonnier A., Alagille D. Normal serum gamma-glutamyl-transpeptidase activity identifies groups of infants with idiopathic cholestasis with poor prognosis. J Pediatr. 1987 Aug;111(2):251–252. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggiore G., De Giacomo C., Scotta M. S., Siena S., Maccario R., Vitiello A. Cell-mediated immunity in children with chronic cholestasis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1982;1(3):385–388. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198201030-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa M., Tazawa Y., Kobayashi Y., Yamada M., Suzuki H., Konno T., Tada K. Familial intrahepatic cholestasis associated with progressive neuromuscular disease and vitamin E deficiency. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984 Jun;3(3):385–389. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198406000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odiévre M., Gautier M., Hadchouel M., Alagille D. Severe familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Oct;48(10):806–812. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.10.806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Matsui A. Serum bile acid analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Jan 7;127(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Worthington J. A rapid method for the quantitative extraction of bile acids and their conjugates from serum using commercially available reverse-phase octadecylsilane bonded silica cartridges. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Oct 27;125(2):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90190-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjövall J., Lawson A. M., Setchell K. D. Mass spectrometry of bile acids. Methods Enzymol. 1985;111:63–113. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)11006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitington P. F., Freese D. K., Alonso E. M., Schwarzenberg S. J., Sharp H. L. Clinical and biochemical findings in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1994 Feb;18(2):134–141. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199402000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. N., Kaye R., Baker L., Hurwitz R., Senior J. R. Progressive familial cholestatic cirrhosis and bile acid metabolism. J Pediatr. 1972 Sep;81(3):493–500. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winklhofer-Roob B. M., Shmerling D. H., Solèr R., Briner J. Progressive idiopathic cholestasis presenting with profuse watery diarrhoea and recurrent infections (Byler's disease). Acta Paediatr. 1992 Aug;81(8):637–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1992.tb12320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]