Abstract
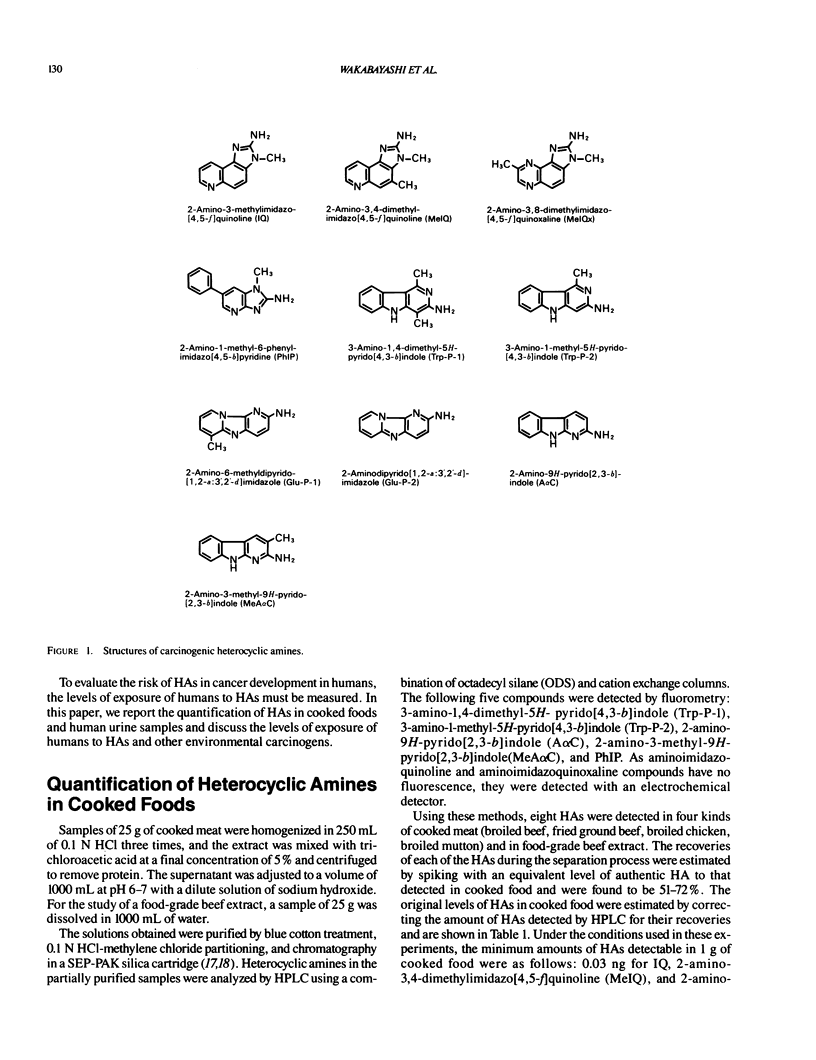
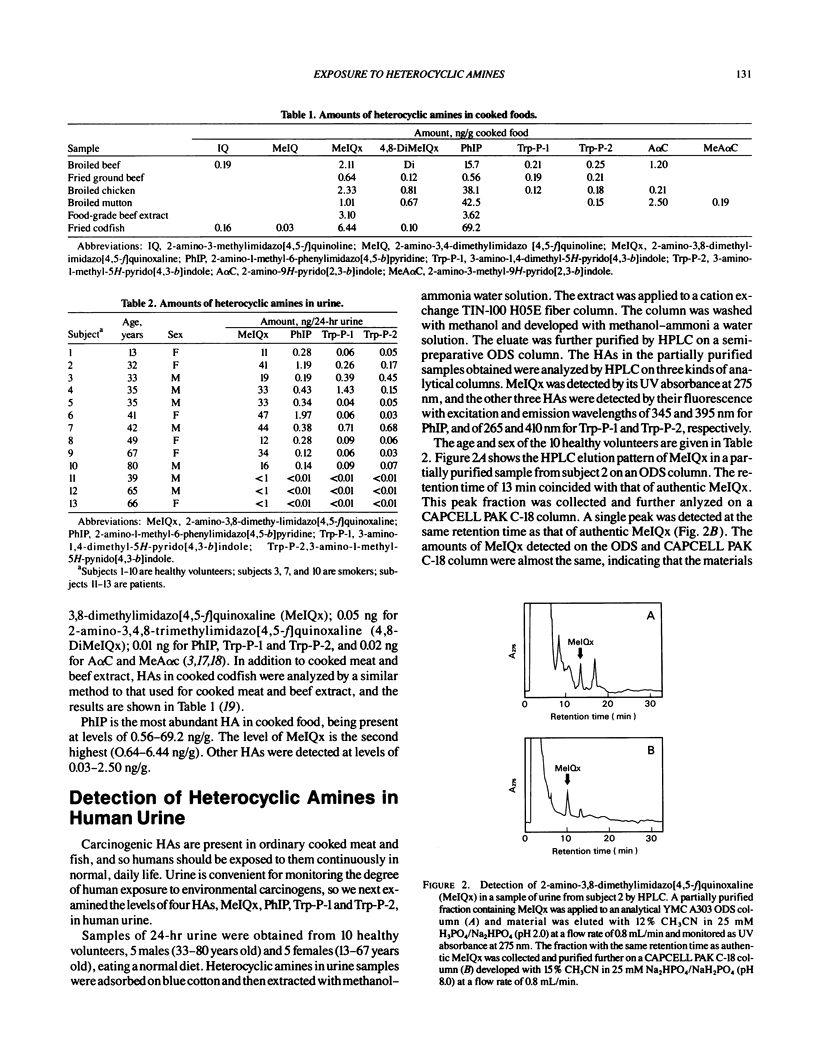
Many mutagenic heterocyclic amines (HAs) have been isolated from cooked foods and pyrolysates of amino acids and proteins, and the carcinogenicity of 10 of these HAs in rodents and of 1 in monkeys has been reported. Quantification of these carcinogenic HAs in various kinds of cooked foods indicated that the level of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (PhIP) was highest (0.56-69.2 ng/g), that of 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline (MeIQx) was second highest (0.64-6.44 ng/g), and those of other HAs were 0.03-2.50 ng/g. Heterocyclic amines were found in urine samples of 10 healthy volunteers consuming a normal diet, but HAs were not detectable in urine samples of three patients receiving parenteral alimentation. These results strongly suggest that humans are continuously exposed to HAs derived from food in the normal diet. Based on quantitative data on the levels of HAs in cooked foods and urine samples, the daily exposures to PhIP and MeIQx were estimated to be 0.1-13.8 micrograms and 0.2-2.6 micrograms per person, respectively. These levels of carcinogenic HAs are in the same range as those of other carcinogens such as N-nitrosodimethylamine and benzo[a]pyrene to which humans are exposed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson R. H., Thorgeirsson U. P., Snyderwine E. G., Thorgeirsson S. S., Reeves J., Dalgard D. W., Takayama S., Sugimura T. Carcinogenicity of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline in nonhuman primates: induction of tumors in three macaques. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1990 Jan;81(1):10–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1990.tb02500.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esumi H., Ohgaki H., Kohzen E., Takayama S., Sugimura T. Induction of lymphoma in CDF1 mice by the food mutagen, 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1989 Dec;80(12):1176–1178. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1989.tb01651.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felton J. S., Knize M. G., Shen N. H., Lewis P. R., Andresen B. D., Happe J., Hatch F. T. The isolation and identification of a new mutagen from fried ground beef: 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (PhIP). Carcinogenesis. 1986 Jul;7(7):1081–1086. doi: 10.1093/carcin/7.7.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito N., Hasegawa R., Sano M., Tamano S., Esumi H., Takayama S., Sugimura T. A new colon and mammary carcinogen in cooked food, 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (PhIP). Carcinogenesis. 1991 Aug;12(8):1503–1506. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.8.1503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito N., Hasegawa R., Shirai T., Fukushima S., Hakoi K., Takaba K., Iwasaki S., Wakabayashi K., Nagao M., Sugimura T. Enhancement of GST-P positive liver cell foci development by combined treatment of rats with five heterocyclic amines at low doses. Carcinogenesis. 1991 May;12(5):767–772. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.5.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jägerstad M., Olsson K., Grivas S., Negishi C., Wakabayashi K., Tsuda M., Sato S., Sugimura T. Formation of 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline in a model system by heating creatinine, glycine and glucose. Mutat Res. 1984 May;126(3):239–244. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(84)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knize M. G., Roper M., Shen N. H., Felton J. S. Proposed structures for an amino-dimethylimidazofuropyridine mutagen in cooked meats. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Dec;11(12):2259–2262. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.12.2259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray S., Gooderham N. J., Boobis A. R., Davies D. S. Detection and measurement of MeIQx in human urine after ingestion of a cooked meat meal. Carcinogenesis. 1989 Apr;10(4):763–765. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.4.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nukaya H., Watanabe H., Ishida H., Tsuji K., Suwa Y., Wakabayashi K., Nagao M., Sugimura T., Kosuge T. Isolation and structural determination of a mutagenic substance in creatine pyrolysate. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1991 Feb;39(2):533–535. doi: 10.1248/cpb.39.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohgaki H., Takayama S., Sugimura T. Carcinogenicities of heterocyclic amines in cooked food. Mutat Res. 1991 Mar-Apr;259(3-4):399–410. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(91)90130-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanlan R. A. Formation and occurrence of nitrosamines in food. Cancer Res. 1983 May;43(5 Suppl):2435s–2440s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioya M., Wakabayashi K., Sato S., Nagao M., Sugimura T. Formation of a mutagen, 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]-pyridine (PhIP) in cooked beef, by heating a mixture containing creatinine, phenylalanine and glucose. Mutat Res. 1987 Jul-Aug;191(3-4):133–138. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(87)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderwine E. G., Yamashita K., Adamson R. H., Sato S., Nagao M., Sugimura T., Thorgeirsson S. S. Use of the 32P-postlabeling method to detect DNA adducts of 2-amino-3-methylimidazolo[4,5-f]quinoline (IQ) in monkeys fed IQ: identification of the N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-IQ adduct. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Oct;9(10):1739–1743. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.10.1739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimura T. New environmental carcinogens in daily life. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Jun;9(6):205–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimura T. Studies on environmental chemical carcinogenesis in Japan. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):312–318. doi: 10.1126/science.3088728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Wakabayashi K., Nagao M., Yamamoto M., Masui T., Goto T., Kinae N., Tomita I., Sugimura T. Quantification of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline (IQ) and 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline (MeIQx) in beef extracts by liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection (LCEC). Carcinogenesis. 1985 Aug;6(8):1195–1199. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.8.1195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda H., Asamoto M., Ogiso T., Inoue T., Ito N., Nagao M. Dose-dependent induction of liver and thyroid neoplastic lesions by short-term administration of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline combined with partial hepatectomy followed by phenobarbital or low dose 3'-methyl-4-dimethylaminoazobenzene promotion. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1988 Jun;79(6):691–697. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1988.tb02224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turteltaub K. W., Felton J. S., Gledhill B. L., Vogel J. S., Southon J. R., Caffee M. W., Finkel R. C., Nelson D. E., Proctor I. D., Davis J. C. Accelerator mass spectrometry in biomedical dosimetry: relationship between low-level exposure and covalent binding of heterocyclic amine carcinogens to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5288–5292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiyama H., Wakabayashi K., Hirose M., Itoh H., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Presence of carcinogenic heterocyclic amines in urine of healthy volunteers eating normal diet, but not of inpatients receiving parenteral alimentation. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Aug;12(8):1417–1422. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.8.1417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Kern S. E., Preisinger A. C., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., White R., Smits A. M., Bos J. L. Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):525–532. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi K., Nagao M., Esumi H., Sugimura T. Food-derived mutagens and carcinogens. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 1;52(7 Suppl):2092s–2098s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Adachi M., Kato S., Nakagama H., Ochiai M., Wakabayashi K., Sato S., Nagao M., Sugimura T. DNA adducts formed by 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline in rat liver: dose-response on chronic administration. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1990 May;81(5):470–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1990.tb02593.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazoe Y., Abu-Zeid M., Yamauchi K., Kato R. Metabolic activation of pyrolysate arylamines by human liver microsomes; possible involvement of a P-488-H type cytochrome P-450. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1988 Nov;79(11):1159–1167. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1988.tb01540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota J., Wada M., Shimosato Y., Terada M., Sugimura T. Loss of heterozygosity on chromosomes 3, 13, and 17 in small-cell carcinoma and on chromosome 3 in adenocarcinoma of the lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9252–9256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. M., Wakabayashi K., Liu Z. C., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Mutagenic and carcinogenic heterocyclic amines in Chinese cooked foods. Mutat Res. 1988 Sep;201(1):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(88)90124-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


