Abstract
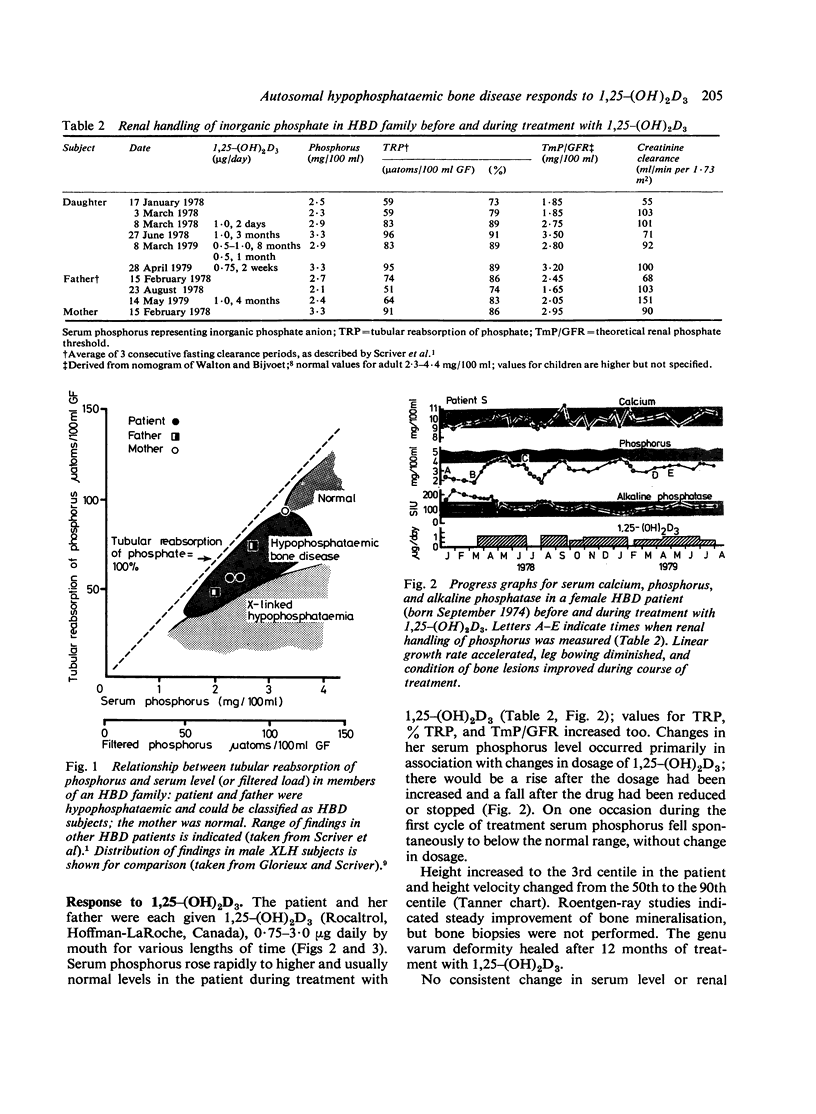
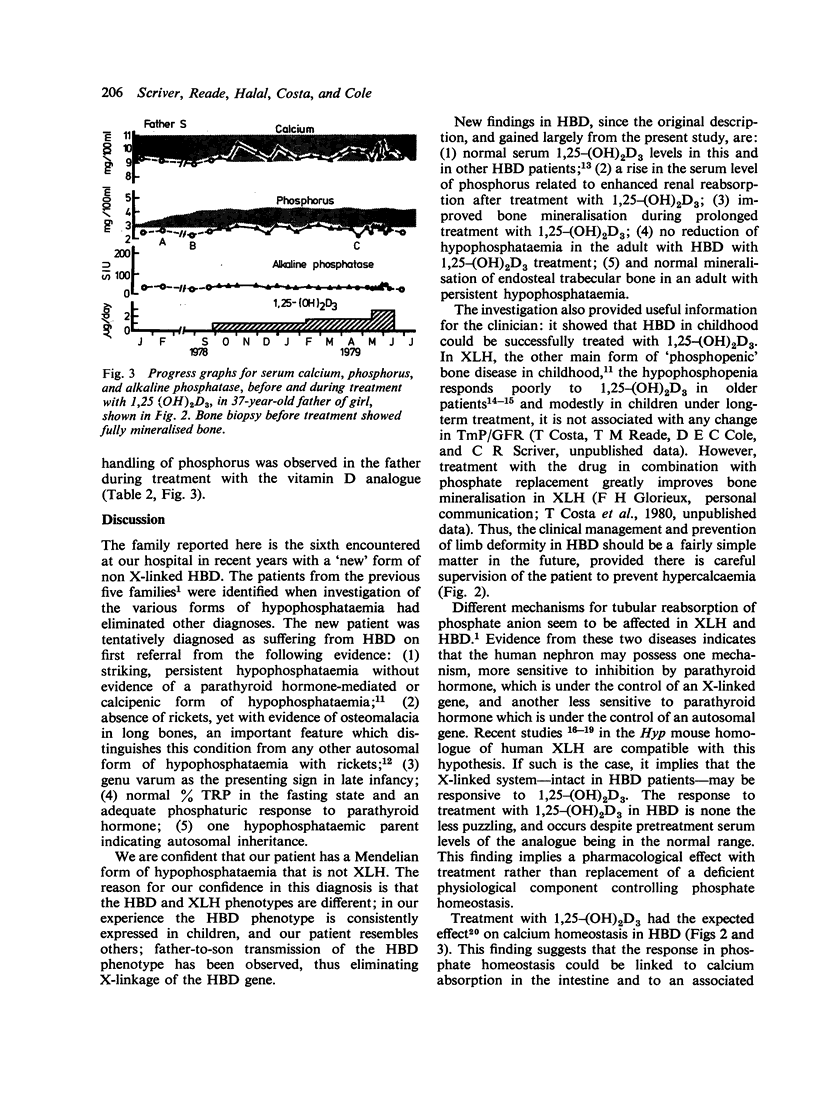
We diagnosed non X-linked hypophosphataemic bone disease in a 38-month-old girl. Findings included: genu varum, shortened stature, fasting hypophosphataemia (2.3-2.5 mg/100 ml; 0.74-0.81 mmol/l), diminished theoretical renal threshold for phosphate (TmP/GFR), and osteomalacia without rickets. One patient (the father) had fasting hypophosphataemia (2.3-2.7 mg/100 ml; 0.74-0.87 mmol/l) and low TmP/GFR without osteomalacia or shortened stature. Treatment of the girl with 1,25-(OH)2D3 (1 microgram a day) raised the level of serum phosphorus, improved tubular reabsorption of phosphate, and healed the bone deformity; this combination of responses is not present in X-linked hypophosphataemia. There was no correction of hypophosphataemia or TmP/GFR with 1,25-(OH)2D3 treatment (1-3 micrograms a day) in the father.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnaud C. D., Tsao H. S., Littledike T. Radioimmunoassay of human parathyroid hormone in serum. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):21–34. doi: 10.1172/JCI106476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickman A. S., Coburn J. W., Kurokawa K., Bethune J. E., Harrison H. E., Norman A. W. Actions of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol in patients with hypophosphatemic, vitamin-D-resistant rickets. N Engl J Med. 1973 Sep 6;289(10):495–498. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197309062891002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowgill L. D., Goldfarb S., Lau K., Slatopolsky E., Agus Z. S. Evidence for an intrinsic renal tubular defect in mice with genetic hypophosphatemic rickets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;63(6):1203–1210. doi: 10.1172/JCI109415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca H. F. The vitamin D system in the regulation of calcium and phosphorus metabolism. Nutr Rev. 1979 Jun;37(6):161–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1979.tb06660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent C. E. A study of the behaviour of some sixty amino-acids and other ninhydrin-reacting substances on phenol-;collidine' filter-paper chromatograms, with notes as to the occurrence of some of them in biological fluids. Biochem J. 1948;43(2):169–180. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eicher E. M., Southard J. L., Scriver C. R., Glorieux F. H. Hypophosphatemia: mouse model for human familial hypophosphatemic (vitamin D-resistant) rickets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4667–4671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisman J. A., Hamstra A. J., Kream B. E., DeLuca H. F. A sensitive, precise, and convenient method for determination of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D in human plasma. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Sep;176(1):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBERG B. G., WINTERS R. W., GRAHAM J. B. The normal range of serum inorganic phosphorus and its utility as a discriminant in the diagnosis of congenital hypophosphatemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1960 Mar;20:364–379. doi: 10.1210/jcem-20-3-364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorieux F. H., Holick M. F., Scriver C. R., DeLuca H. F. X-linked hypophosphataemic rickets: Inadequate therapeutic response to 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. Lancet. 1973 Aug 11;2(7824):287–289. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90793-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorieux F., Scriver C. R. Loss of a parathyroid hormone-sensitive component of phosphate transport in X-linked hypophosphatemia. Science. 1972 Mar 3;175(4025):997–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4025.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scriver C. R., MacDonald W., Reade T., Glorieux R. H., Nogrady B. Hypophosphatemic nonrachitic bone disease: an entity distinct from X-linked hypophosphatemia in the renal defect, bone involvement, and inheritance. Am J Med Genet. 1977;1(1):101–117. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320010111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scriver C. R., Reade T. M., DeLuca H. F., Hamstra A. J. Serum 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels in normal subjects and in patients with hereditary rickets or bone disease. N Engl J Med. 1978 Nov 2;299(18):976–979. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811022991803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scriver C. R. Rickets and the pathogenesis of impaired tubular transport of phosphate and other solutes. Am J Med. 1974 Jul;57(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90766-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenenhouse H. S., Scriver C. R. Renal adaptation to phosphate deprivation in the Hyp mouse with X-linked hypophosphatemia. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):938–944. doi: 10.1139/o79-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenenhouse H. S., Scriver C. R. The defect in transcellular transport of phosphate in the nephron is located in brush-border membranes in X-linked hypophosphatemia (Hyp mouse model). Can J Biochem. 1978 Jun;56(6):640–646. doi: 10.1139/o78-096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucci J. R., Perlstein R. S., Kopp L. E. The urine cyclic AMP response to parathyroid extract (PTE) administration in normal subjects and patients with parathyroid dysfunction. Metabolism. 1979 Aug;28(8):814–819. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton R. J., Bijvoet O. L. Nomogram for derivation of renal threshold phosphate concentration. Lancet. 1975 Aug 16;2(7929):309–310. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92736-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




