Abstract
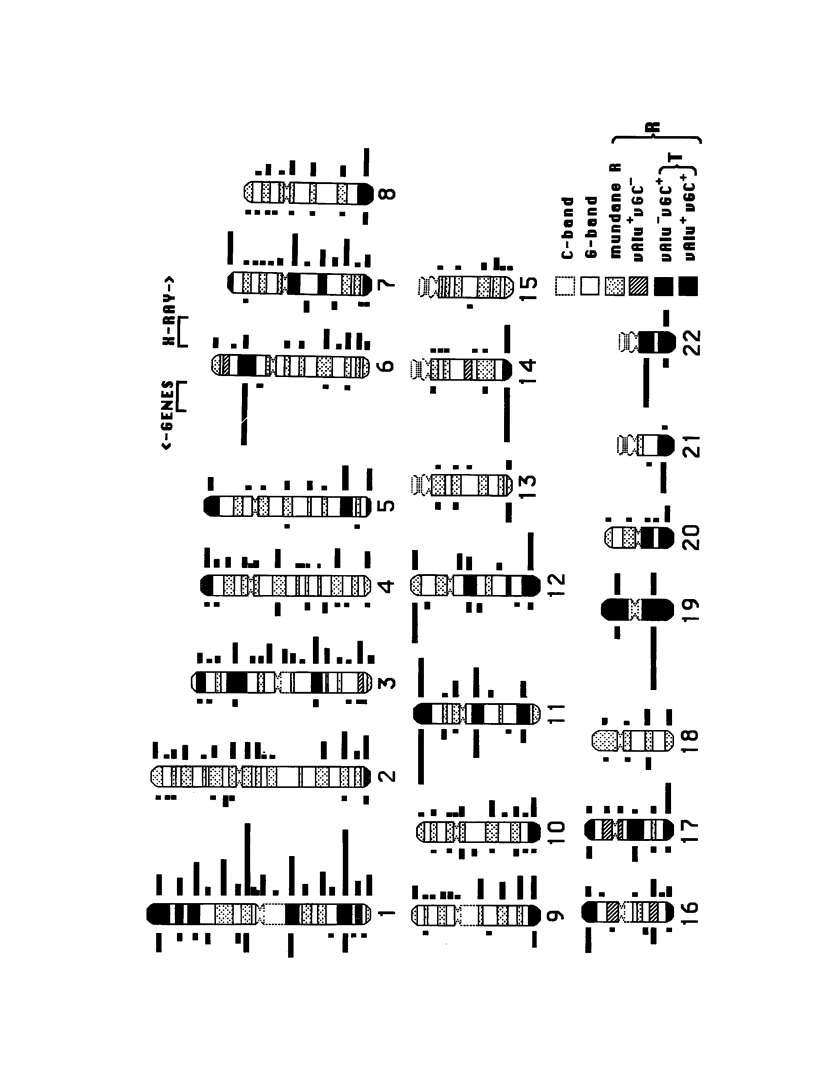
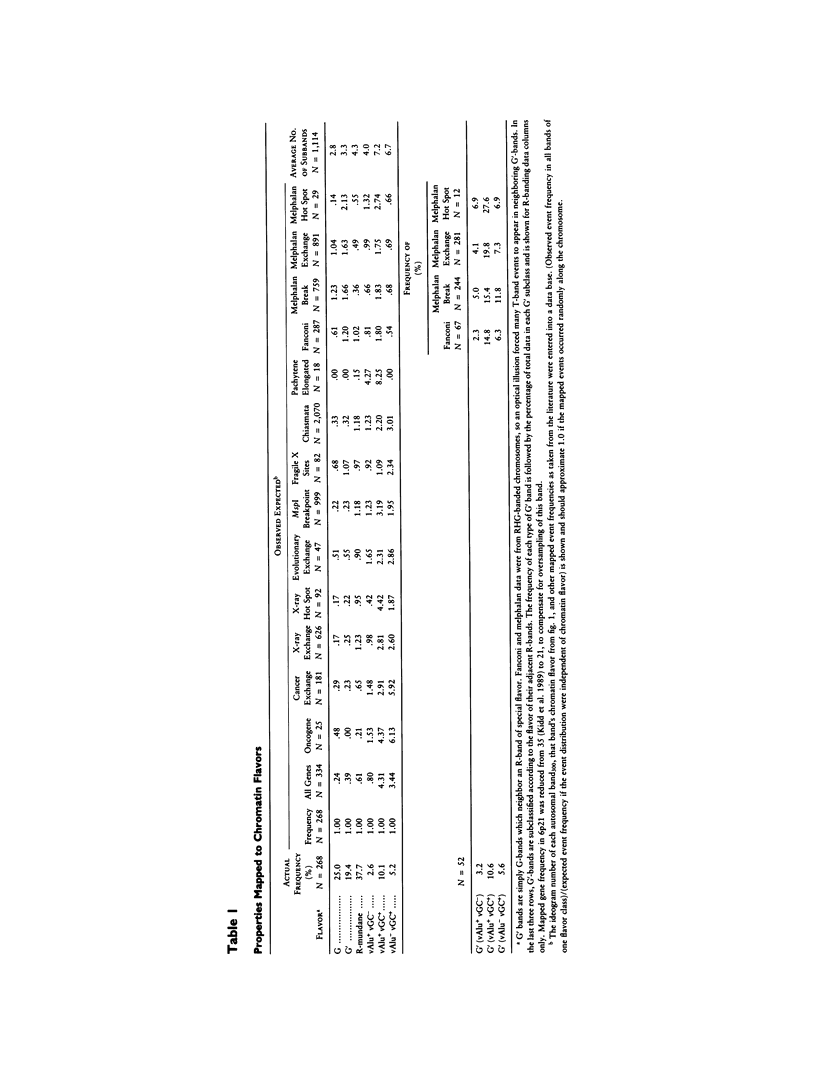
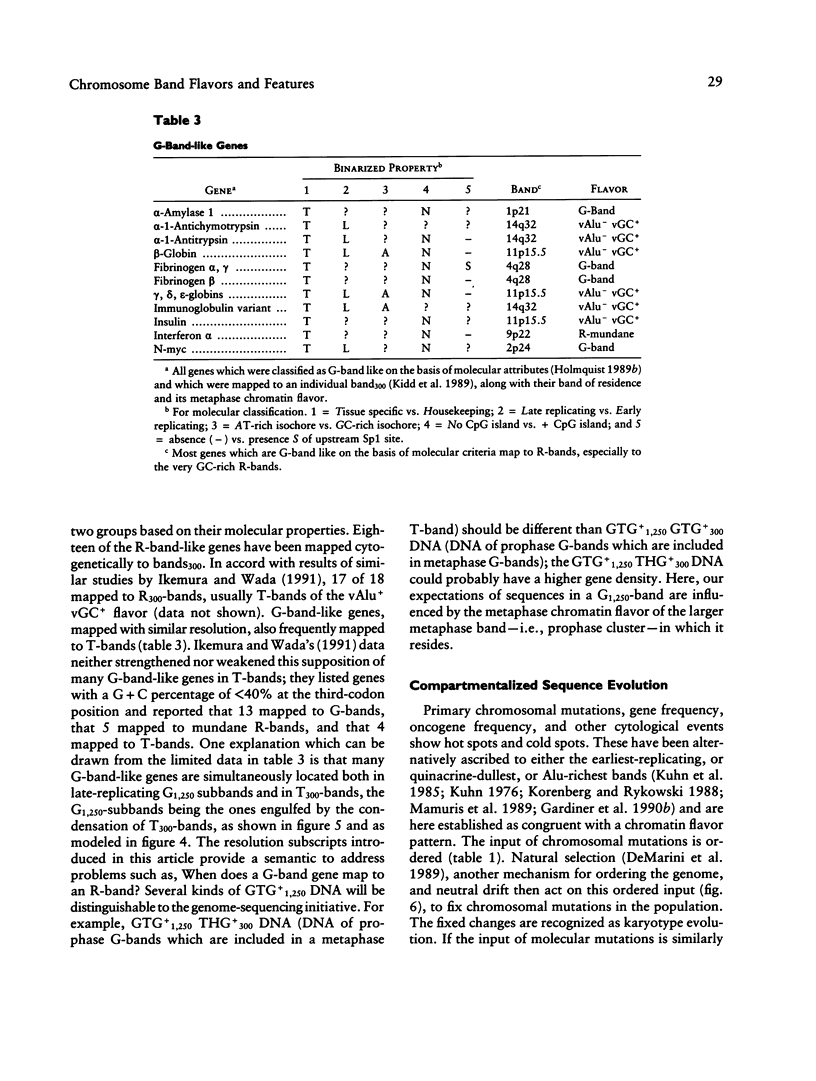
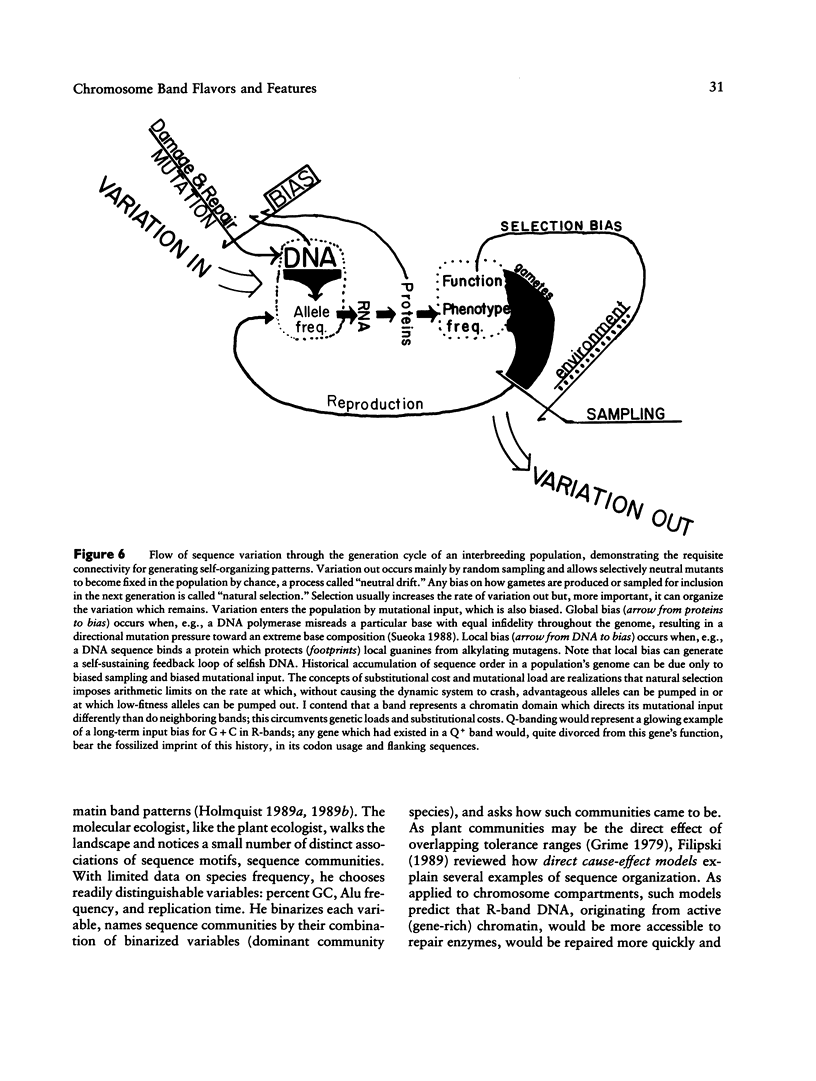
To show that the input pattern of chromosomal mutations is highly organized relative to the band patterns along human chromosomes, a new term, "metaphase chromatin flavor," is introduced. Five different flavors of euchromatic metaphase bands are cytologically identified along a human ideogram. These are G-bands and, based upon combinations of extreme Alu richness and GC richness, four different R-band flavors. The two flavors with extremely GC-rich components, traditionally called "T-bands," represent only 15% of all bands. However, they contain 65% of mapped genes, 19 of 25 mapped oncogenes, most cancer-associated rearrangements, evolutionary rearrangements, meiotic chiasmata, and X-ray-induced breaks. Flavors with extremely Alu-rich flavors are also involved in melphalan-induced rearrangements, pachytene stretching, and mitotic chiasmata. Frequencies of CpG islands, CCGCCC boxes, retroposon families, and genes are characteristic to each chromatin flavor and will facilitate alignment of genome sequences onto ideograms of chromatin flavor. The influence of chromatin flavor on the evolution of a gene's sequence is so strong that one can infer the flavor of the band in which a gene resides from the sequence of the gene itself. Correlation coefficients for many pairs of mapped genetic variables, while globally high, are quite low within bands of one flavor, implicating a concerted mode of evolution for bands of one chromatin flavor.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambros P. F., Sumner A. T. Correlation of pachytene chromomeres and metaphase bands of human chromosomes, and distinctive properties of telomeric regions. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;44(4):223–228. doi: 10.1159/000132375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley T. Prediction of mammalian meiotic synaptic and recombinational behavior of inversion heterozygotes based on mitotic breakpoint data and the possible evolutionary consequences. Genetica. 1990;83(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00774683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrios L., Miró R., Caballín M. R., Fuster C., Guedea F., Subias A., Egozcue J. Cytogenetic effects of radiotherapy. Breakpoint distribution in induced chromosome aberrations. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1989 Aug;41(1):61–70. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(89)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Bernardi G. Compositional constraints and genome evolution. J Mol Evol. 1986;24(1-2):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF02099946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Mouchiroud D., Gautier C., Bernardi G. Compositional patterns in vertebrate genomes: conservation and change in evolution. J Mol Evol. 1988 Dec;28(1-2):7–18. doi: 10.1007/BF02143493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Olofsson B., Filipski J., Zerial M., Salinas J., Cuny G., Meunier-Rotival M., Rodier F. The mosaic genome of warm-blooded vertebrates. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):953–958. doi: 10.1126/science.4001930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickmore W. A., Sumner A. T. Mammalian chromosome banding--an expression of genome organization. Trends Genet. 1989 May;5(5):144–148. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobrow M., Madan K. The effects of various banding procedures on human chromosomes, studied with acridine orange. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1973;12(3):143–156. doi: 10.1159/000130449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. C., Jiricny J. A specific mismatch repair event protects mammalian cells from loss of 5-methylcytosine. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):945–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90521-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckton K. E. Identification with G and R banding of the position of breakage points induced in human chromosomes by in vitro x-irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1976 May;29(5):475–488. doi: 10.1080/09553007614550571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister M., Monaco A. P., Gillard E. F., van Ommen G. J., Affara N. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Kunkel L. M., Lehrach H. A 10-megabase physical map of human Xp21, including the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Genomics. 1988 Apr;2(3):189–202. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuny G., Soriano P., Macaya G., Bernardi G. The major components of the mouse and human genomes. 1. Preparation, basic properties and compositional heterogeneity. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(2):227–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05227.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarini D. M., Brockman H. E., de Serres F. J., Evans H. H., Stankowski L. F., Jr, Hsie A. W. Specific-locus mutations induced in eukaryotes (especially mammalian cells) by radiation and chemicals: a perspective. Mutat Res. 1989 Jan;220(1):11–29. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(89)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):111–117. doi: 10.1038/299111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouin R., Lemieux N., Richer C. L. High-resolution R-banding at the 1250-band level. 1. Technical considerations on cell synchronization and R-banding (RHG and RBG). Cytobios. 1988;56(225):107–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouin R., Richer C. L. Analysis of high-resolution R-bands, obtained by heat-denaturation and Giemsa staining, on human prophase chromosomes. Can J Genet Cytol. 1985 Feb;27(1):83–91. doi: 10.1139/g85-014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubos C., Pequignot E. V., Dutrillaux B. Localization of gamma-rays induced chromatid breaks using a three consecutive staining technique. Mutat Res. 1978 Jan;49(1):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(78)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B., Couturier J., Richer C. L., Viegas-Péquignot E. Sequence of DNA replication in 277 R- and Q-bands of human chromosomes using a BrdU treatment. Chromosoma. 1976 Oct 12;58(1):51–61. doi: 10.1007/BF00293440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B., Couturier J., Viegas-Péquignot E., Schaison G. Localization chromatid breaks in Fanconi's anemia, using three consecutive stains. Hum Genet. 1977 Jun 10;37(1):65–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00293773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B., Covic M. Etude de facteurs influençant la dénaturation thermique ménagée des chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Mar 30;85(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90224-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B., Lejeune J. Sur une nouvelle technique d'analyse du caryotype humain. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1971 May 17;272(20):2638–2640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B. Nouveau système de marquage chromosomique: Les bandes. Chromosoma. 1973 Apr 27;41(4):395–402. doi: 10.1007/BF00396497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
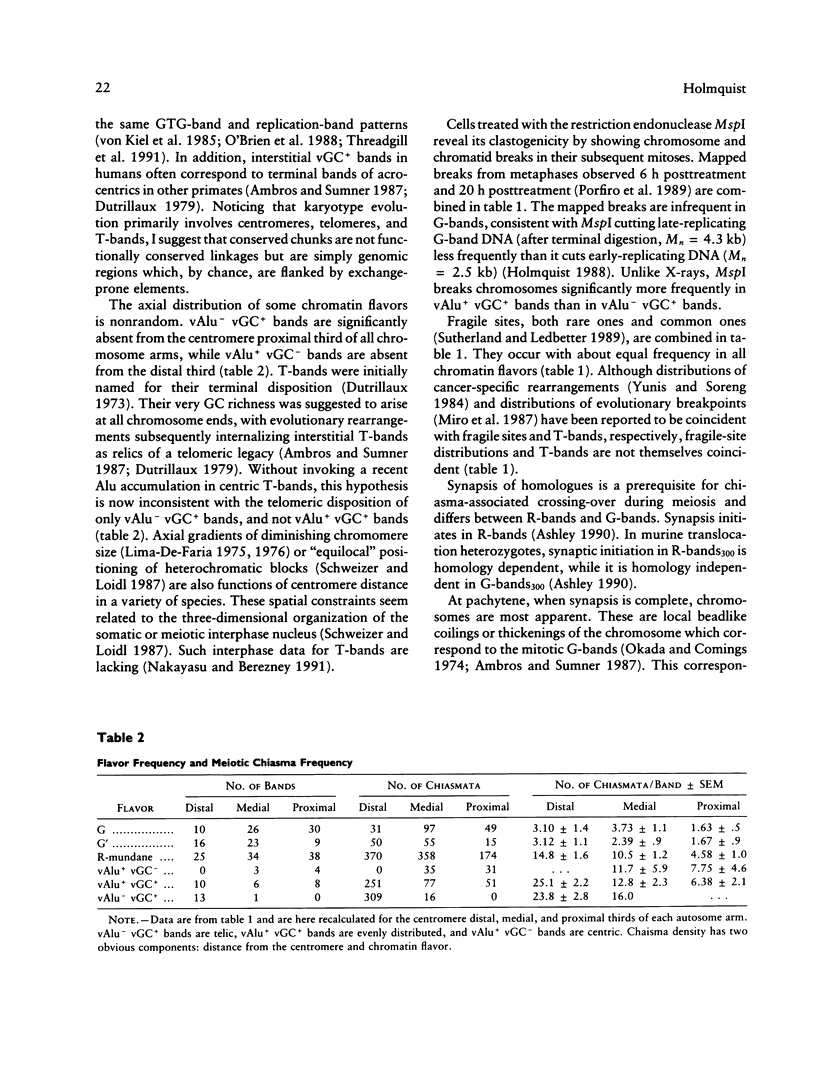
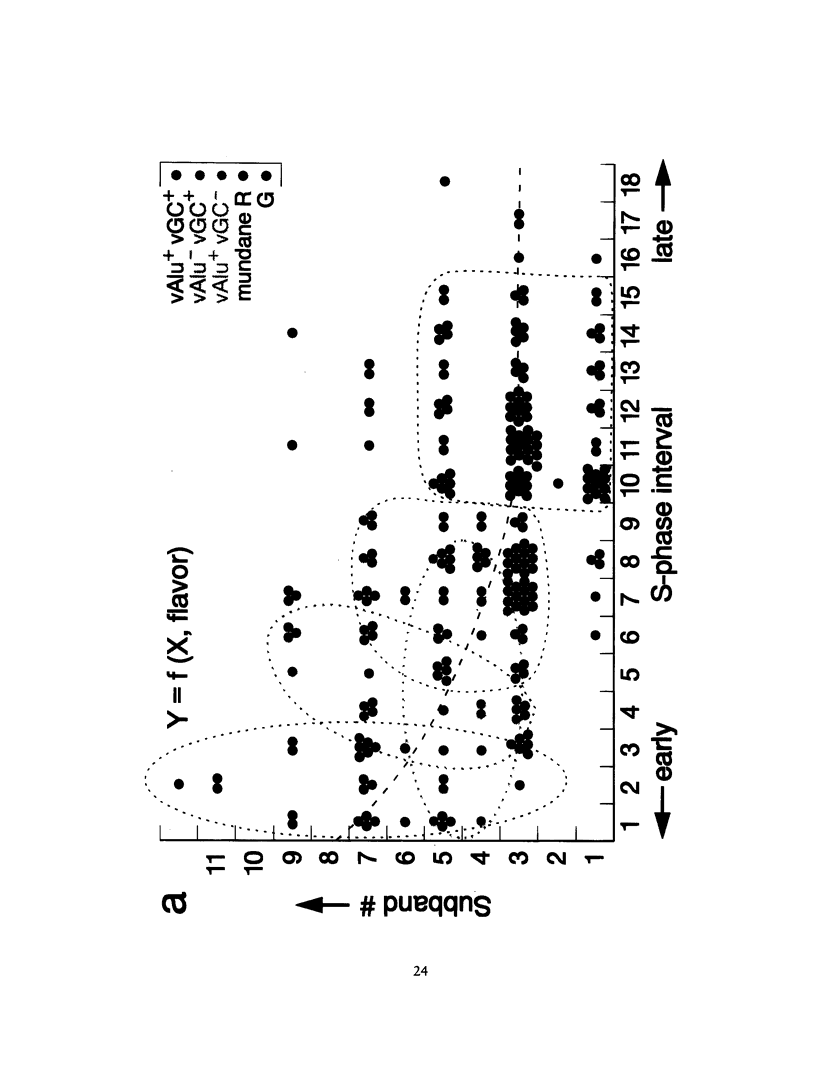
- Fang J. S., Jagiello G. M. An analysis of the chromomere map and chiasmata characteristics of human diplotene spermatocytes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;47(1-2):52–57. doi: 10.1159/000132505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipski J. Why the rate of silent codon substitutions is variable within a vertebrate's genome. J Theor Biol. 1988 Sep 17;134(2):159–164. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(88)80199-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
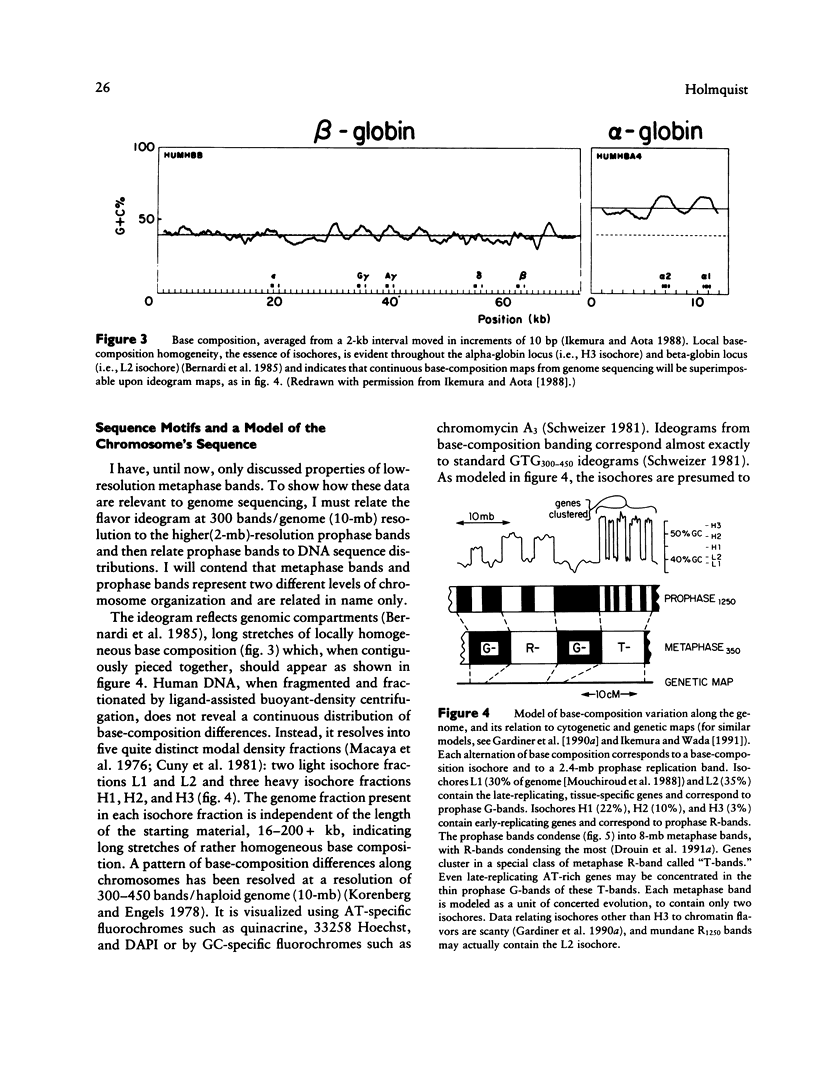
- Gardiner K., Aissani B., Bernardi G. A compositional map of human chromosome 21. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1853–1858. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08310.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Horisberger M., Kraus J., Tantravahi U., Korenberg J., Rao V., Reddy S., Patterson D. Analysis of human chromosome 21: correlation of physical and cytogenetic maps; gene and CpG island distributions. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):25–34. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08076.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. A., Holmquist G. P., Gray M. C., Caston L. A., Nag A. Replication timing of genes and middle repetitive sequences. Science. 1984 May 18;224(4650):686–692. doi: 10.1126/science.6719109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heim S., Mitelman F. Nineteen of 26 cellular oncogenes precisely localized in the human genome map to one of the 83 bands involved in primary cancer-specific rearrangements. Hum Genet. 1987 Jan;75(1):70–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00273843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg M., Jonasson J. Preferential location of x-ray induced chromosome breakage in the R-bands of human chromosomes. Hereditas. 1973;74(1):57–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1973.tb01104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist G. P., Caston L. A. Replication time of interspersed repetitive DNA sequences in hamsters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 13;868(2-3):164–177. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(86)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
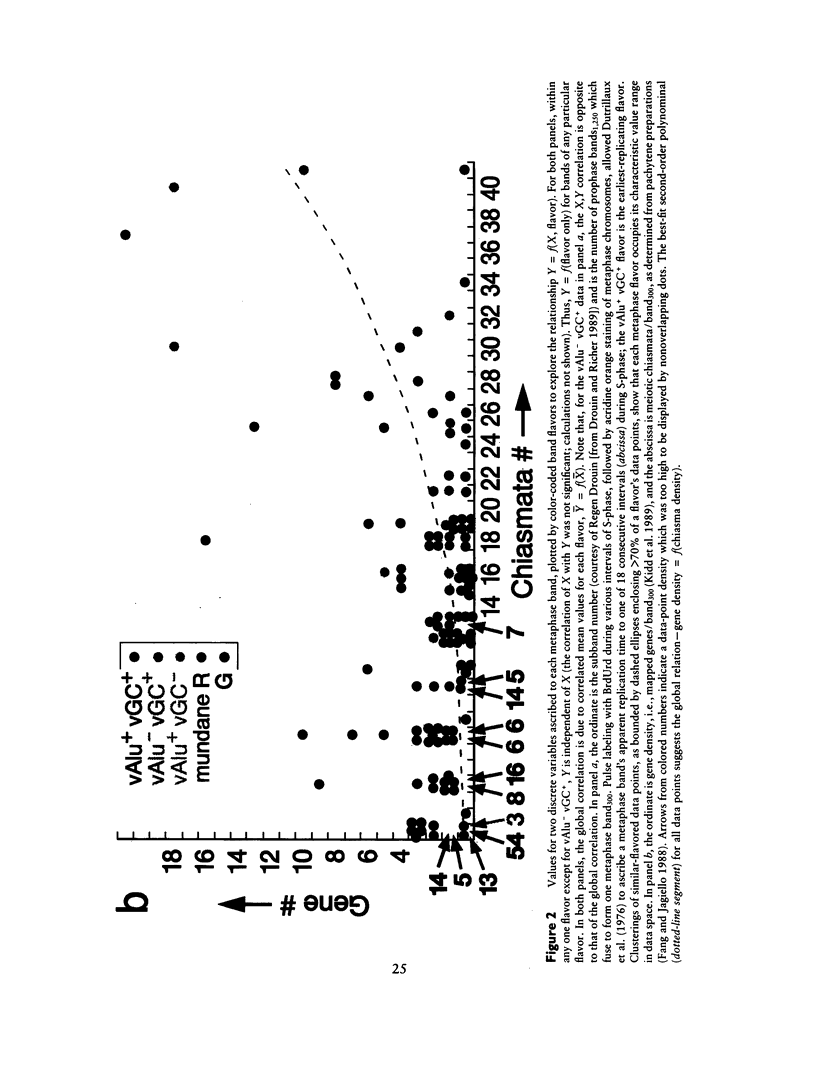
- Ikemura T., Aota S. Global variation in G+C content along vertebrate genome DNA. Possible correlation with chromosome band structures. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 5;203(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Wada K., Aota S. Giant G+C% mosaic structures of the human genome found by arrangement of GenBank human DNA sequences according to genetic positions. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90273-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Wada K. Evident diversity of codon usage patterns of human genes with respect to chromosome banding patterns and chromosome numbers; relation between nucleotide sequence data and cytogenetic data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4333–4339. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd K. K., Bowcock A. M., Schmidtke J., Track R. K., Ricciuti F., Hutchings G., Bale A., Pearson P., Willard H. F., Gelernter J. Report of the DNA committee and catalogs of cloned and mapped genes and DNA polymorphisms. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):622–947. doi: 10.1159/000132810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kootstra A., Lew L. K., Nairn R. S., MacLeod M. C. Preferential modification of GC boxes by benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-diol-9,10-epoxide. Mol Carcinog. 1989;1(4):239–244. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940010406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Rykowski M. C. Human genome organization: Alu, lines, and the molecular structure of metaphase chromosome bands. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90159-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn E. M. Localization by Q-banding of mitotic chiasmata in cases of Bloom's syndrome. Chromosoma. 1976 Aug 4;57(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00292945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn E. M., Therman E., Denniston C. Mitotic chiasmata, gene density, and oncogenes. Hum Genet. 1985;70(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF00389448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie D. A., Hultén M. A. Further studies on chiasma distribution and interference in the human male. Ann Hum Genet. 1985 Jul;49(Pt 3):203–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1985.tb01694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux N., Drouin R., Richer C. L. High-resolution dynamic and morphological G-bandings (GBG and GTG): a comparative study. Hum Genet. 1990 Aug;85(3):261–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00206742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima-de-Faria A. The relation between chromomeres, replicons, operons, transcription units, genes, viruses and palindromes. Hereditas. 1975;81(2):249–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1975.tb01039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciani J. M., Guichaoua M. R., Cau P., Devictor B., Salagnon N. Differential elongation of autosomal pachytene bivalents related to their DNA content in human spermatocytes. Chromosoma. 1988;97(1):19–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00331791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macaya G., Thiery J. P., Bernardi G. An approach to the organization of eukaryotic genomes at a macromolecular level. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov;108(1):237–254. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamuris Z., Prieur M., Dutrillaux B., Aurias A. The chemotherapeutic drug melphalan induces breakage of chromosomes regions rearranged in secondary leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1989 Jan;37(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(89)90076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. A view of interphase chromosomes. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1533–1540. doi: 10.1126/science.2274784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Ward D. C. Chromosomal and nuclear distribution of the HindIII 1.9-kb human DNA repeat segment. Chromosoma. 1984;91(1):28–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00286482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miró R., Clemente I. C., Fuster C., Egozcue J. Fragile sites, chromosome evolution, and human neoplasia. Hum Genet. 1987 Apr;75(4):345–349. doi: 10.1007/BF00284105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouchiroud D., Gautier C., Bernardi G. The compositional distribution of coding sequences and DNA molecules in humans and murids. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(4):311–320. doi: 10.1007/BF02101193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayasu H., Berezney R. Mapping replicational sites in the eucaryotic cell nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;108(1):1–11. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien S. J., Seuánez H. N., Womack J. E. Mammalian genome organization: an evolutionary view. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:323–351. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odum E. P. The strategy of ecosystem development. Science. 1969 Apr 18;164(3877):262–270. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3877.262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Dover G. A. Population genetics of multigene families that are dispersed into two or more chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4079–4083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada T. A., Comings D. E. Mechanisms of chromosome banding. III. Similarity between G-bands of mitotic chromosomes and chromomeres of meiotic chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1974;48(1):65–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00284867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivero O. A., Huitfeldt H., Poirier M. C. Chromosome site-specific immunohistochemical detection of DNA adducts in N-acetoxy-2-acetylaminofluorene--exposed Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Carcinog. 1990;3(1):37–43. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940030109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin P., Bernardi G. Directional fixation of mutations in vertebrate evolution. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(4):301–310. doi: 10.1007/BF02101148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer G. P., Drouin R., Riggs A. D., Holmquist G. P. In vivo mapping of a DNA adduct at nucleotide resolution: detection of pyrimidine (6-4) pyrimidone photoproducts by ligation-mediated polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porfirio B., Tedeschi B., Vernole P., Caporossi D., Nicoletti B. The distribution of MspI-induced breaks in human lymphocyte chromosomes and its relationship to common fragile sites. Mutat Res. 1989 Aug;213(2):117–124. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(89)90142-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage J. R. Assignment of aberration breakpoints in banded chromosomes. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):513–514. doi: 10.1038/270513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaaper R. M., Radman M. The extreme mutator effect of Escherichia coli mutD5 results from saturation of mismatch repair by excessive DNA replication errors. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3511–3516. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08516.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer D. Counterstain-enhanced chromosome banding. Hum Genet. 1981;57(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Meunier-Rotival M., Bernardi G. The distribution of interspersed repeats is nonuniform and conserved in the mouse and human genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1816–1820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sueoka N. Directional mutation pressure and neutral molecular evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2653–2657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threadgill D. S., Kraus J. P., Krawetz S. A., Womack J. E. Evidence for the evolutionary origin of human chromosome 21 from comparative gene mapping in the cow and mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):154–158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. M., Kaneko Y., Mitelman F. Report of the committee on structural chromosome changes in neoplasia. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):533–562. doi: 10.1159/000132807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venema J., Mullenders L. H., Natarajan A. T., van Zeeland A. A., Mayne L. V. The genetic defect in Cockayne syndrome is associated with a defect in repair of UV-induced DNA damage in transcriptionally active DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4707–4711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienberg J., Jauch A., Stanyon R., Cremer T. Molecular cytotaxonomy of primates by chromosomal in situ suppression hybridization. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe K. H., Sharp P. M., Li W. H. Mutation rates differ among regions of the mammalian genome. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):283–285. doi: 10.1038/337283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J. Mid-prophase human chromosomes. The attainment of 2000 bands. Hum Genet. 1981;56(3):293–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00274682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J., Soreng A. L. Constitutive fragile sites and cancer. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1199–1204. doi: 10.1126/science.6239375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial M., Salinas J., Filipski J., Bernardi G. Gene distribution and nucleotide sequence organization in the human genome. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 3;160(3):479–485. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerkandl E. Polite DNA: functional density and functional compatibility in genomes. J Mol Evol. 1986;24(1-2):12–27. doi: 10.1007/BF02099947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeeland A. A., Vrieling H., van Rooijen M. L., Venema J., Zdzienicka M. Z., Simons J. W., Mullenders L. H., Lohman P. H. Influence of DNA excision repair on UV-induced mutation spectra in Chinese hamster cells. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;340A:249–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kiel K., Hameister H., Somssich I. E., Adolph S. Early replication banding reveals a strongly conserved functional pattern in mammalian chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1985;93(1):69–76. doi: 10.1007/BF01259448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]