Abstract
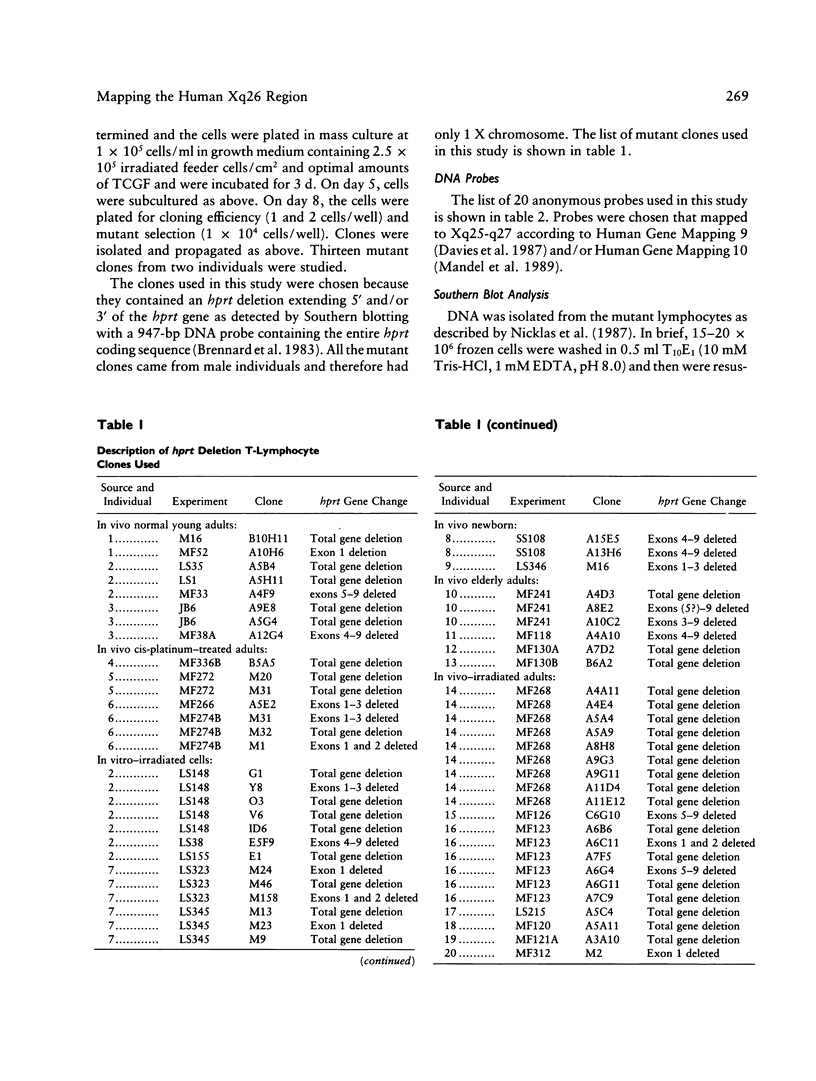
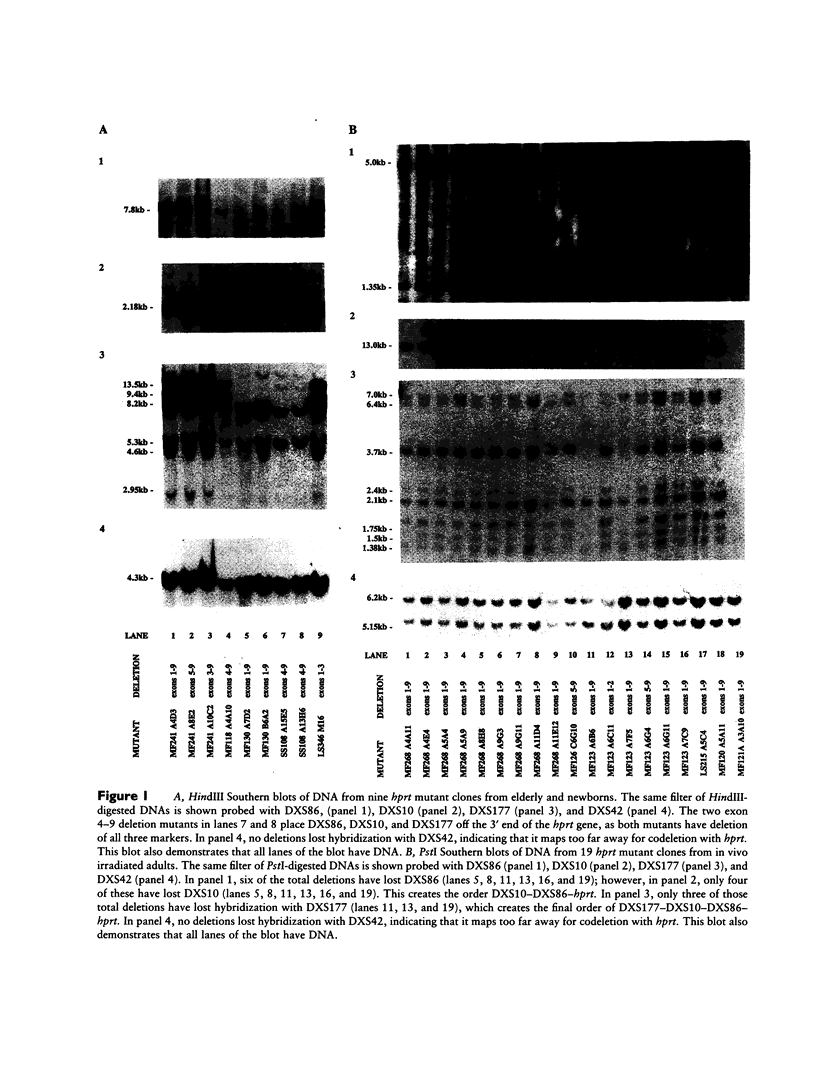
The Xq26-q27 region of the X chromosome is interesting, as an unusually large number of genes and anonymous RFLP probes have been mapped in this area. A number of studies have used classical linkage analysis in families to map this region. Here, we use mutant human T-lymphocyte clones known to be deleted for all or part of the hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (hprt) gene, to order anonymous probes known to map to Xq26. Fifty-seven T-cell clones were studied, including 44 derived from in vivo mutation and 13 from in vitro irradiated T-lymphocyte cultures. Twenty anonymous probes (DXS10, DXS11, DXS19, DXS37, DXS42, DXS51, DXS53, DXS59, DXS79, DXS86, DXS92, DXS99, DXS100d, DXS102, DXS107, DXS144, DXS172, DXS174, DXS177, and DNF1) were tested for codeletion with the hprt gene by Southern blotting methods. Five of these probes (DXS10, DXS53, DXS79, DXS86 and DXS177) showed codeletion with hprt in some mutants. The mutants established the following unambiguous ordering of the probes relative to the hprt gene: DXS53-DXS79-5'hprt3'-DXS86-DXS10-DXS177 . The centromere appears to map proximal to DXS53. These mappings order several closely linked but previously unordered probes. In addition, these studies indicate that rather large deletions of the functionally haploid X chromosome can occur while still retaining T-cell viability.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertini R. J., Castle K. L., Borcherding W. R. T-cell cloning to detect the mutant 6-thioguanine-resistant lymphocytes present in human peripheral blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6617–6621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albertini R. J., Sullivan L. M., Berman J. K., Greene C. J., Stewart J. A., Silveira J. M., O'Neill J. P. Mutagenicity monitoring in humans by autoradiographic assay for mutant T lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;204(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(88)90043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anson D. S., Blake D. J., Winship P. R., Birnbaum D., Brownlee G. G. Nullisomic deletion of the mcf.2 transforming gene in two haemophilia B patients. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2795–2799. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03134.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arveiler B., Oberlé I., Vincent A., Hofker M. H., Pearson P. L., Mandel J. L. Genetic mapping of the Xq27-q28 region: new RFLP markers useful for diagnostic applications in fragile-X and hemophilia-B families. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):380–389. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balazs I., Purrello M., Kurnit D. M., Grzeschik K. H., Siniscalco M. Isolation and characterization of human random cDNA clones homologous to DNA from the X chromosome. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Jul;10(4):385–397. doi: 10.1007/BF01535634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs B. A., Nussbaum R. L. Two anonymous X-specific human sequences detecting restriction fragment length polymorphisms in region Xq26----qter. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Nov;10(6):607–613. doi: 10.1007/BF01535226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley W. E., Gareau J. L., Seifert A. M., Messing K. Molecular characterization of 15 rearrangements among 90 human in vivo somatic mutants shows that deletions predominate. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):956–960. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennand J., Konecki D. S., Caskey C. T. Expression of human and Chinese hamster hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase cDNA recombinants in cultured Lesch-Nyhan and Chinese hamster fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9593–9596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. T., Ye W., Gross A. C., Chan C. B., Dobkin C. S., Jenkins E. C. Multipoint linkage of 9 anonymous probes to HPRT, factor 9, and fragile X. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):551–566. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerino G., Grzeschik K. H., Jaye M., De La Salle H., Tolstoshev P., Lecocq J. P., Heilig R., Mandel J. L. Regional localization on the human X chromosome and polymorphism of the coagulation factor IX gene (hemophilia B locus). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):498–502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J., Green M. H., James S. E., Henderson L., Cole H. A further assessment of factors influencing measurements of thioguanine-resistant mutant frequency in circulating T-lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;204(3):493–507. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(88)90044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davatelis G., Siniscalco M., Szabo P. An anonymous single copy X-chromosome clone DXS92, from Xq26-27, identifies two frequent RFLPs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7540–7540. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Mandel J. L., Weissenbach J., Fellous M. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of the X and Y chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;46(1-4):277–315. doi: 10.1159/000132481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempsey J. L., Seshadri R. S., Morley A. A. Increased mutation frequency following treatment with cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 1985 Jun;45(6):2873–2877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., White R. The genetic linkage map of the human X chromosome. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):753–758. doi: 10.1126/science.4059909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feil R., Palmieri G., d'Urso M., Heilig R., Oberlé I., Mandel J. L. Physical and genetic mapping of polymorphic loci in Xq28 (DXS15, DXS52, and DXS134): analysis of a cosmid clone and a yeast artificial chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):720–728. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraud F., Ayme S., Mattei J. F., Mattei M. G. Constitutional chromosomal breakage. Hum Genet. 1976 Oct 28;34(2):125–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00278880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakoda M., Akiyama M., Kyoizumi S., Awa A. A., Yamakido M., Otake M. Increased somatic cell mutant frequency in atomic bomb survivors. Mutat Res. 1988 Sep;201(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(88)90109-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakoda M., Hirai Y., Kyoizumi S., Akiyama M. Molecular analyses of in vivo hprt mutant T cells from atomic bomb survivors. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1989;13(1):25–33. doi: 10.1002/em.2850130103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey J., Judge C., Wiener S. Familial X-linked mental retardation with an X chromosome abnormality. J Med Genet. 1977 Feb;14(1):46–50. doi: 10.1136/jmg.14.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L., Cole H., Cole J., James S. E., Green M. Detection of somatic mutations in man: evaluation of the microtitre cloning assay for T-lymphocytes. Mutagenesis. 1986 May;1(3):195–200. doi: 10.1093/mutage/1.3.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. J., Turmel C., Noolandi J., Neumann P. E., Lalande M. Construction of the physical map for three loci in chromosome band 13q14: comparison to the genetic map. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3415–3419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Bergen A. A., Skraastad M. I., Carpenter N. J., Veenema H., Connor J. M., Bakker E., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Efficient isolation of X chromosome-specific single-copy probes from a cosmid library of a human X/hamster hybrid-cell line: mapping of new probes close to the locus for X-linked mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Apr;40(4):312–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Skraastad M. I., Bergen A. A., Wapenaar M. C., Bakker E., Millington-Ward A., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. The X chromosome shows less genetic variation at restriction sites than the autosomes. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;39(4):438–451. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden J. J., Wang H. S., White B. N. The fragile-X syndrome, IV. Progress towards the identification of linked restriction fragment length variants (RFLVs). Am J Med Genet. 1984 Jan;17(1):259–273. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320170118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenwrick S., Gitschier J. A contiguous, 3-Mb physical map of Xq28 extending from the colorblindness locus to DXS15. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Dec;45(6):873–882. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesko J. G., Nussbaum R. L. RFLP locus DXS42 is proximal to the locus for hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Nov;39(5):669–670. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little R. D., Porta G., Carle G. F., Schlessinger D., D'Urso M. Yeast artificial chromosomes with 200- to 800-kilobase inserts of human DNA containing HLA, V kappa, 5S, and Xq24-Xq28 sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1598–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüdecke H. J., Senger G., Claussen U., Horsthemke B. Construction and characterization of band-specific DNA libraries. Hum Genet. 1990 May;84(6):512–516. doi: 10.1007/BF00210800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Arveiler B., Camerino G., Hanauer A., Heilig R., Koenig M., Oberlé I. Genetic mapping of the human X chromosome: linkage analysis of the q26-q28 region that includes the fragile X locus and isolation of expressed sequences. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):195–203. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Willard H. F., Nussbaum R. L., Romeo G., Puck J. M., Davies K. E. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of the X chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):384–437. doi: 10.1159/000132801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinniss M. J., Falta M. T., Sullivan L. M., Albertini R. J. In vivo hprt mutant frequencies in T-cells of normal human newborns. Mutat Res. 1990 Feb;240(2):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(90)90015-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinniss M. J., Nicklas J. A., Albertini R. J. Molecular analyses of in vivo hprt mutations in human T-lymphocytes: IV. Studies in newborns. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1989;14(4):229–237. doi: 10.1002/em.2850140404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing K., Ferraris J., Bradley W. E., Swartz J., Seifert A. M. Mutant frequency of radiotherapy technicians appears to be associated with recent dose of ionizing radiation. Health Phys. 1989 Oct;57(4):537–544. doi: 10.1097/00004032-198910000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley A. A., Trainor K. J., Seshadri R., Ryall R. G. Measurement of in vivo mutations in human lymphocytes. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):155–156. doi: 10.1038/302155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulley J., Turner G., Bain S., Sutherland G. R. Linkage between the fragile X and F9, DXS52 (St14), DXS98 (4D-8) and DXS105 (cX55.7). Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):567–580. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan L. M., Phillips M. A., Forster-Gibson C. J., Beckett J., Partington M. W., Simpson N. E., Holden J. J., White B. N. Genetic mapping of DNA segments relative to the locus for the fragile-X syndrome at Xq27.3. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):463–472. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan L., Holden J. J., White B. N. A DNA marker closely linked to the factor IX (haemophilia B) gene. Hum Genet. 1987 Apr;75(4):381–383. doi: 10.1007/BF00284113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. D., Kidd J. R., Breg W. R., Ruddle F. H., Kidd K. K. An anonymous single copy X-chromosome clone, DXS79, from Xq26-Xq28, identifies a moderately frequent RFLP [HGM8 provisional no. DXS79]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):3015–3015. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. D., Ruddle F. H. Isolation and regional mapping of random X sequences from distal human X chromosome. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Sep;11(5):433–444. doi: 10.1007/BF01534837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen C., Mattei M. G., Rey J. A., Baeteman M. A., Mattei J. F., Jordan B. R. Cytogenetic and physical mapping in the region of the X chromosome surrounding the fragile site. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):601–611. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklas J. A., Falta M. T., Hunter T. C., O'Neill J. P., Jacobson-Kram D., Williams J. R., Albertini R. J. Molecular analysis of in vivo hprt mutations in human T lymphocytes. V. Effects of total body irradiation secondary to radioimmunoglobulin therapy (RIT) Mutagenesis. 1990 Sep;5(5):461–468. doi: 10.1093/mutage/5.5.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklas J. A., Hunter T. C., O'Neill J. P., Albertini R. J. Molecular analyses of in vivo hprt mutations in human T-lymphocytes. III. Longitudinal study of hprt gene structural alterations and T-cell clonal origins. Mutat Res. 1989 Dec;215(2):147–160. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(89)90178-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklas J. A., Hunter T. C., Sullivan L. M., Berman J. K., O'Neill J. P., Albertini R. J. Molecular analyses of in vivo hprt mutations in human T-lymphocytes. I. Studies of low frequency 'spontaneous' mutants by Southern blots. Mutagenesis. 1987 Sep;2(5):341–347. doi: 10.1093/mutage/2.5.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Lewis R. A., Lesko J. G., Ferrell R. Choroideremia is linked to the restriction fragment length polymorphism DXYS1 at XQ13-21. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):473–481. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill J. P., Hunter T. C., Sullivan L. M., Nicklas J. A., Albertini R. J. Southern-blot analyses of human T-lymphocyte mutants induced in vitro by gamma-irradiation. Mutat Res. 1990 Feb;240(2):143–149. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(90)90018-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill J. P., McGinniss M. J., Berman J. K., Sullivan L. M., Nicklas J. A., Albertini R. J. Refinement of a T-lymphocyte cloning assay to quantify the in vivo thioguanine-resistant mutant frequency in humans. Mutagenesis. 1987 Mar;2(2):87–94. doi: 10.1093/mutage/2.2.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill J. P., Sullivan L. M., Albertini R. J. In vitro induction, expression and selection of thioguanine-resistant mutants with human T-lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1990 Feb;240(2):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(90)90017-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill J. P., Sullivan L. M., Booker J. K., Pornelos B. S., Falta M. T., Greene C. J., Albertini R. J. Longitudinal study of the in vivo hprt mutant frequency in human T-lymphocytes as determined by a cell cloning assay. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1989;13(4):289–293. doi: 10.1002/em.2850130403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Camerino G., Kloepfer C., Moisan J. P., Grzeschik K. H., Hellkuhl B., Hors-Cayla M. C., Van Cong N., Weil D., Mandel J. L. Characterization of a set of X-linked sequences and of a panel of somatic cell hybrids useful for the regional mapping of the human X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1986 Jan;72(1):43–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00278816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Camerino G., Wrogemann K., Arveiler B., Hanauer A., Raimondi E., Mandel J. L. Multipoint genetic mapping of the Xq26-q28 region in families with fragile X mental retardation and in normal families reveals tight linkage of markers in q26-q27. Hum Genet. 1987 Sep;77(1):60–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00284716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai G. S., Sprenkle J. A., Do T. T., Mareni C. E., Migeon B. R. Localization of loci for hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and biochemical evidence of nonrandom X chromosome expression from studies of a human X-autosome translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2810–2813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson M., Bell M., Schwartz C., Davies K. Pulsed-field gel mapping studies in the vicinity of the fragile site at Xq27.3. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):581–591. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly D. S., Lewis R. A., Ledbetter D. H., Nussbaum R. L. Tightly linked flanking markers for the Lowe oculocerebrorenal syndrome, with application to carrier assessment. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 May;42(5):748–755. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly D. S., Lewis R. A., Nussbaum R. L. Genetic and physical mapping of Xq24-q26 markers flanking the Lowe oculocerebrorenal syndrome. Genomics. 1990 Sep;8(1):62–70. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90226-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert A. M., Bradley W. E., Messing K. Exposure of nuclear medicine patients to ionizing radiation is associated with rises in HPRT- mutant frequency in peripheral T-lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1987 May;191(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(87)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiloh Y., Litvak G., Ziv Y., Lehner T., Sandkuyl L., Hildesheimer M., Buchris V., Cremers F. P., Szabo P., White B. N. Genetic mapping of X-linked albinism-deafness syndrome (ADFN) to Xq26.3-q27.I. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jul;47(1):20–27. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver D. N., Lewis R. A., Nussbaum R. L. Mapping the Lowe oculocerebrorenal syndrome to Xq24-q26 by use of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):282–285. doi: 10.1172/JCI112795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J. C., Grierson H. L., Sullivan J. L., Nussbaum R. L., Purtilo D. T., Sylla B. S., Lenoir G. M., Reilly D. S., White B. N., Milunsky A. Linkage analysis of seven kindreds with the X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome (XLP) confirms that the XLP locus is near DXS42 and DXS37. Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;82(4):354–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00273997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J. C., Sullivan J. L., Milunsky A. Mapping the mutation causing the X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome in relation to restriction fragment length polymorphisms on Xq. Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;82(4):349–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00273996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylla B. S., Wang Q., Hayoz D., Lathrop G. M., Lenoir G. M. Multipoint linkage mapping of the Xq25-q26 region in a family affected by the X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. Clin Genet. 1989 Dec;36(6):459–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1989.tb03377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tates A. D., Bernini L. F., Natarajan A. T., Ploem J. S., Verwoerd N. P., Cole J., Green M. H., Arlett C. F., Norris P. N. Detection of somatic mutants in man: HPRT mutations in lymphocytes and hemoglobin mutations in erythrocytes. Mutat Res. 1989 Jul;213(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(89)90033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. R., Morley A. A., Haliandros M., Kutlaca R., Sanderson B. J. In vivo somatic mutations in human lymphocytes frequently result from major gene alterations. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):343–345. doi: 10.1038/315343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Gedeon A., Mulley J., Sutherland G., Rae J., Power K., Arthur I. Börjeson-Forssman-Lehmann syndrome: clinical manifestations and gene localization to Xq26-27. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Dec;34(4):463–469. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320340402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada M., Little R. D., Abidi F., Porta G., Labella T., Cooper T., Della Valle G., D'Urso M., Schlessinger D. Human Xq24-Xq28: approaches to mapping with yeast artificial chromosomes. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jan;46(1):95–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadelius C., Fagerholm P., Pettersson U., Annerén G. Lowe oculocerebrorenal syndrome: DNA-based linkage of the gene to Xq24-q26, using tightly linked flanking markers and the correlation to lens examination in carrier diagnosis. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Feb;44(2):241–247. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Davies K. E., Cooke H. J., Pearson P. L., Williamson R., Bhattacharya S., Zimmer J., Ropers H. H. Toward a complete linkage map of the human X chromosome: regional assignment of 16 cloned single-copy DNA sequences employing a panel of somatic cell hybrids. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):265–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]