Abstract
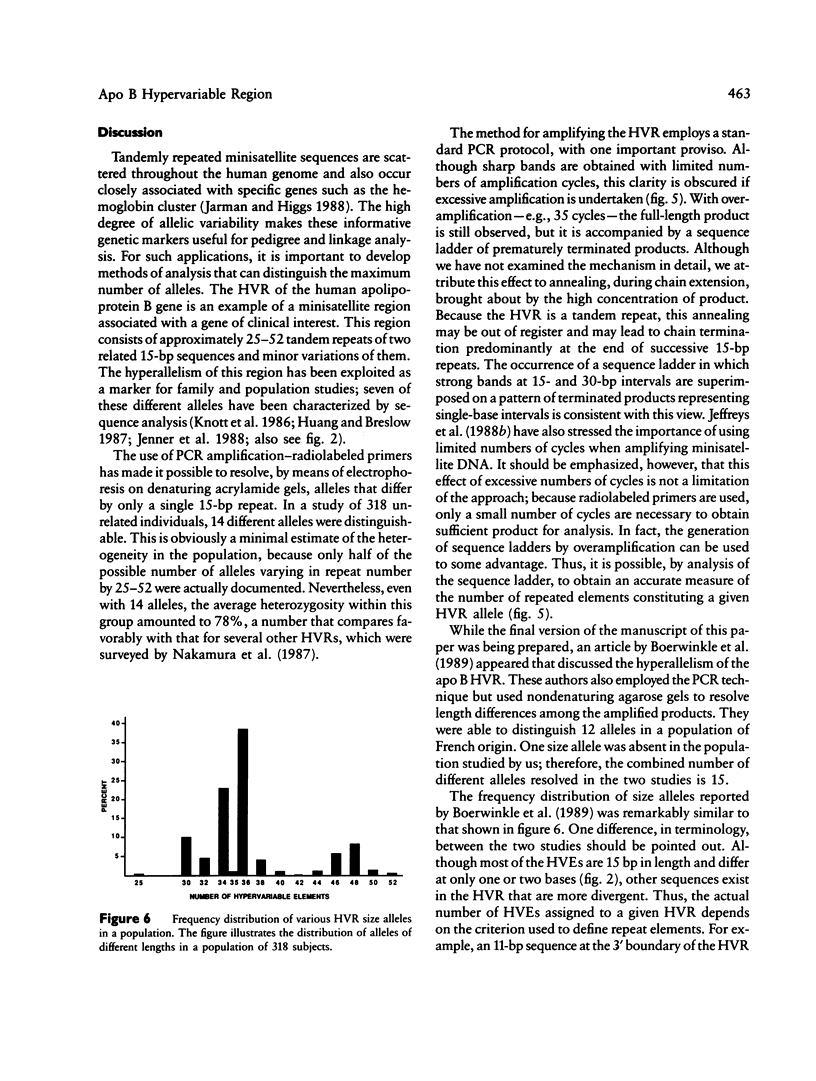
A hypervariable region occurs immediately 3' of the human apolipoprotein B gene. Several allelic variants of this tandemly repeated sequence can be resolved by genomic blotting. Higher resolution among size variants may be obtained by polymerase-chain-reaction amplification of this region followed by electrophoresis in a denaturing acrylamide gel. Fourteen different alleles containing 25-52 repeats of the basic 15-bp unit were distinguished in a population study of 318 unrelated individuals. This approach should be applicable to pedigree and linkage analysis with the apolipoprotein B gene or other tandemly repeated sequence elements.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali S., Wallace R. B. Intrinsic polymorphism of variable number tandem repeat loci in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8487–8496. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Selby M. J., Rutter W. J. The highly polymorphic region near the human insulin gene is composed of simple tandemly repeating sequences. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):31–35. doi: 10.1038/295031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg K. DNA polymorphism at the apolipoprotein B locus is associated with lipoprotein level. Clin Genet. 1986 Dec;30(6):515–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb01920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackhart B. D., Ludwig E. M., Pierotti V. R., Caiati L., Onasch M. A., Wallis S. C., Powell L., Pease R., Knott T. J., Chu M. L. Structure of the human apolipoprotein B gene. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15364–15367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Xiong W. J., Fourest E., Chan L. Rapid typing of tandemly repeated hypervariable loci by the polymerase chain reaction: application to the apolipoprotein B 3' hypervariable region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):212–216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegele R. A., Huang L. S., Herbert P. N., Blum C. B., Buring J. E., Hennekens C. H., Breslow J. L. Apolipoprotein B-gene DNA polymorphisms associated with myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 11;315(24):1509–1515. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612113152403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. S., Breslow J. L. A unique AT-rich hypervariable minisatellite 3' to the ApoB gene defines a high information restriction fragment length polymorphism. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):8952–8955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarman A. P., Higgs D. R. A new hypervariable marker for the human alpha-globin gene cluster. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Sep;43(3):249–256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarman A. P., Nicholls R. D., Weatherall D. J., Clegg J. B., Higgs D. R. Molecular characterisation of a hypervariable region downstream of the human alpha-globin gene cluster. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1857–1863. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Royle N. J., Wilson V., Wong Z. Spontaneous mutation rates to new length alleles at tandem-repetitive hypervariable loci in human DNA. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):278–281. doi: 10.1038/332278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Neumann R., Keyte J. Amplification of human minisatellites by the polymerase chain reaction: towards DNA fingerprinting of single cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):10953–10971. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.10953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Hypervariable 'minisatellite' regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):67–73. doi: 10.1038/314067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenner K., Sidoli A., Ball M., Rodriguez J. R., Pagani F., Giudici G., Vergani C., Mann J., Baralle F. E., Shoulders C. C. Characterization of genetic markers in the 3' end of the apo B gene and their use in family and population studies. Atherosclerosis. 1988 Jan;69(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(88)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott T. J., Wallis S. C., Pease R. J., Powell L. M., Scott J. A hypervariable region 3' to the human apolipoprotein B gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9215–9216. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft R., Tardiff J., Krauter K. S., Leinwand L. A. Using mini-prep plasmid DNA for sequencing double stranded templates with Sequenase. Biotechniques. 1988 Jun;6(6):544-6, 549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig E. H., Blackhart B. D., Pierotti V. R., Caiati L., Fortier C., Knott T., Scott J., Mahley R. W., Levy-Wilson B., McCarthy B. J. DNA sequence of the human apolipoprotein B gene. DNA. 1987 Aug;6(4):363–372. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusis A. J. Genetic factors affecting blood lipoproteins: the candidate gene approach. J Lipid Res. 1988 Apr;29(4):397–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Leppert M., O'Connell P., Wolff R., Holm T., Culver M., Martin C., Fujimoto E., Hoff M., Kumlin E. Variable number of tandem repeat (VNTR) markers for human gene mapping. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1616–1622. doi: 10.1126/science.3029872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapacz J., Hasler-Rapacz J., Taylor K. M., Checovich W. J., Attie A. D. Lipoprotein mutations in pigs are associated with elevated plasma cholesterol and atherosclerosis. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1573–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.3787263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soria L. F., Ludwig E. H., Clarke H. R., Vega G. L., Grundy S. M., McCarthy B. J. Association between a specific apolipoprotein B mutation and familial defective apolipoprotein B-100. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):587–591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker N. G., Cheah K. S., Griffin J. R., Pope F. M., Solomon E. A highly polymorphic region 3' to the human type II collagen gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4613–4622. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Newhouse Y. M., Young S. G., Arnold K. S., Krauss R. M., Vega G. L., Grundy S. M., Mahley R. W. Familial defective apolipoprotein B-100: enhanced binding of monoclonal antibody MB47 to abnormal low density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9758–9762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]