Abstract
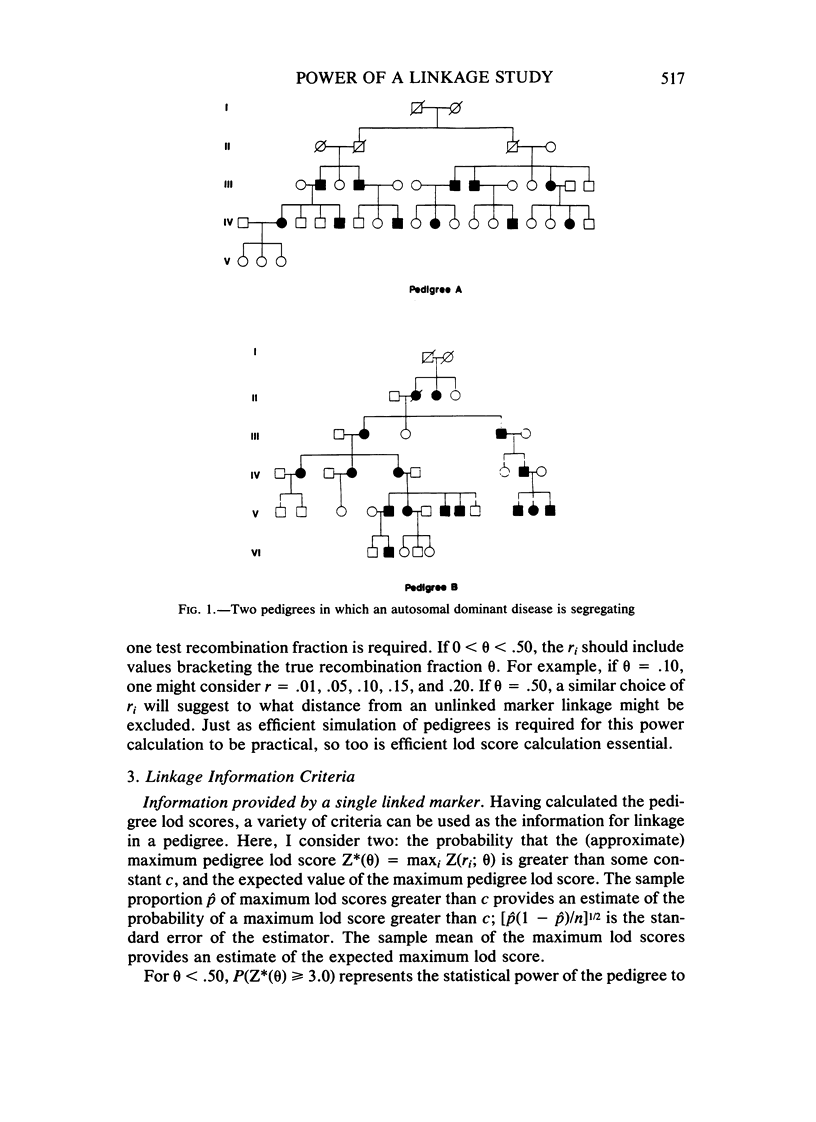
I describe a simulation method to estimate the power to detect linkage given a set of pedigrees of known structure and for which family history data may be available. This method can be applied to autosomal and X-linked dominant diseases; depending on the pedigrees under consideration, it will often be applicable for autosomal and X-linked recessive diseases. This power calculation can most usefully be undertaken after family history data are gathered, but prior to examination and testing of pedigree members to obtain marker information. Of key importance, the power calculation is straightforward to carry out and not too time-consuming; it is practical even on a microcomputer. The result of the power calculation is an objective answer to the question: Will my families be sufficient to demonstrate linkage?
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chotai J. On the lod score method in linkage analysis. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 Oct;48(Pt 4):359–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb00849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C., Bonney G. E. Sampling considerations in the design and analysis of family studies. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1984;147:349–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C., Lange K. The prior probability of autosomal linkage. Ann Hum Genet. 1975 Jan;38(3):341–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1975.tb00619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Boehnke M. How many polymorphic genes will it take to span the human genome? Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Nov;34(6):842–845. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. Sequential tests for the detection of linkage. Am J Hum Genet. 1955 Sep;7(3):277–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. A computer program for linkage analysis of general human pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet. 1976 Sep;28(5):528–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renwick J. H. The mapping of human chromosomes. Annu Rev Genet. 1971;5:81–120. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.05.120171.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick M. H., Bishop D. T., Cannings C., Hasstedt S. J. The impact of RFLPs on human gene mapping. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1984;147:271–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


