Abstract
Advances in our understanding of the physiology of many quantitative phenotypes combined with better measurement abilities is providing a means for pursuing a measured genotype approach to partitioning the phenotypic variance into the contribution of separate loci. The standard estimate of the contribution of a single locus to the phenotypic variance applied recently in the human genetics literature is a biased statistic. We compare the biased estimates from several published studies with biased corrected estimates to illustrate the general problem.
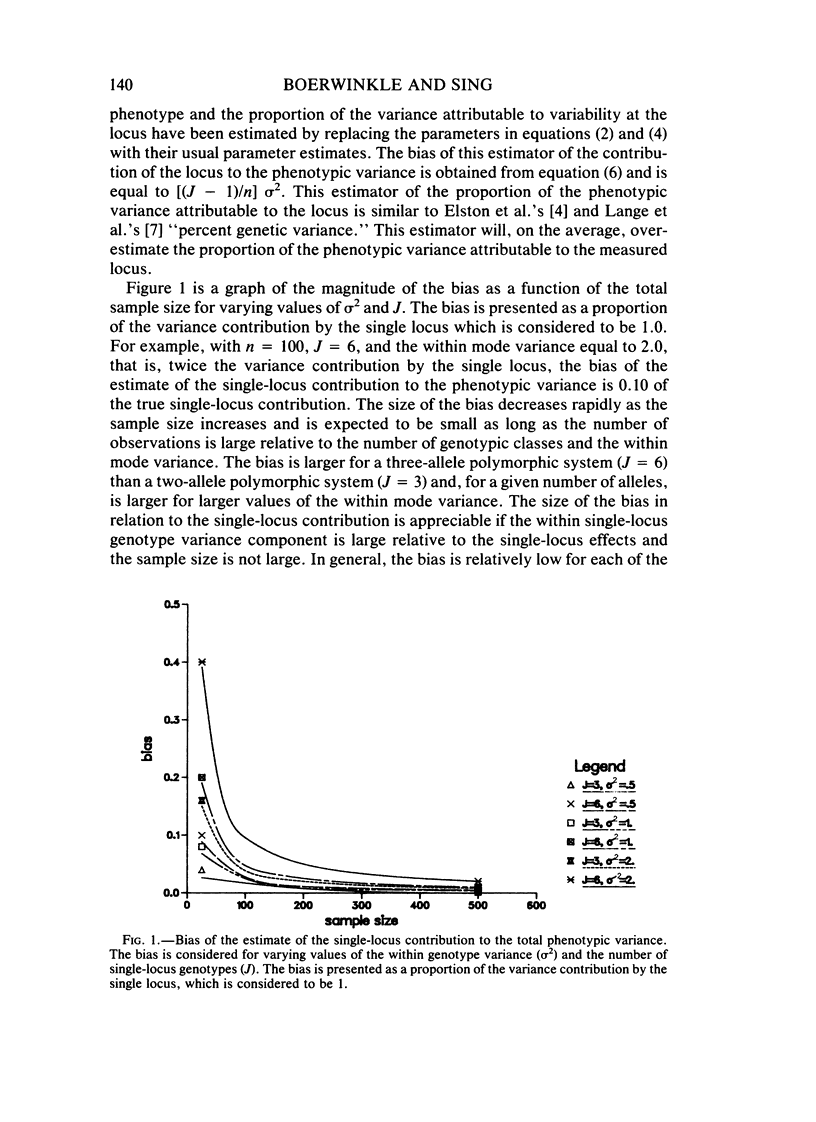
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boerwinkle E., Chakraborty R., Sing C. F. The use of measured genotype information in the analysis of quantitative phenotypes in man. I. Models and analytical methods. Ann Hum Genet. 1986 May;50(Pt 2):181–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1986.tb01037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daiger S. P., Miller M., Chakraborty R. Heritability of quantitative variation at the group-specific component (Gc) locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):663–676. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner A. The analysis of intraclass correlation in multiple samples. Ann Hum Genet. 1985 Jan;49(Pt 1):75–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1985.tb01677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C., Namboodiri K. K., Nino H. V., Pollitzer W. S. Studies on blood and urine glucose in Seminole Indians: indications for segregation of a major gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Jan;26(1):13–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold R. J., Maag U. R., Neal J. L., Scriver C. R. The use of biochemical data in screening for mutant alleles and in genetic counselling. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 Jan;37(3):315–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanis C. L., Chakraborty R., Hewett-Emmett D. How much of variability in apolipoprotein AII concentrations is explained by polymorphism adjacent to apo-AII gene? Lancet. 1985 Jun 8;1(8441):1339–1340. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92838-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper J. L., Tait B. D., Propert D. N., Mathews J. D. Genetic analysis of systolic blood pressure in Melbourne families. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1982 May-Jun;9(3):247–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1982.tb00802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalouel J. M., Darlu P., Henrotte J. G., Rao D. C. Genetic regulation of plasma and red blood cell magnesium concentration in man. II. Segregation analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Sep;35(5):938–950. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Spence M. A., Frank M. B. Application of the lod method to the detection of linkage between a quantitative trait and a qualitative marker: a simulation experiment. Am J Hum Genet. 1976 Mar;28(2):167–173. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis W. H. Common polymorphism of peptidase A. Electrohoretic variants associated with quantitative variation of red cell levels. Ann Hum Genet. 1973 Jan;36(3):267–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1973.tb00589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel H. J., Kladetzky R. G., Assmann G. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and coronary artery disease. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Jul-Aug;3(4):310–315. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.4.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll P. P., Sing C. F., Williams R. R., Mao S. J., Kottke B. A. The genetic determination of plasma apolipoprotein A-I levels measured by radioimmunoassay: a study of high-risk pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Mar;38(3):361–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENCER N., HOPKINSON D. A., HARRIS H. QUANTITATIVE DIFFERENCES AND GENE DOSAGE IN THE HUMAN RED CELL ACID PHOSPHATASE POLYMORPHISM. Nature. 1964 Jan 18;201:299–300. doi: 10.1038/201299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sing C. F., Davignon J. Role of the apolipoprotein E polymorphism in determining normal plasma lipid and lipoprotein variation. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):268–285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


