Abstract
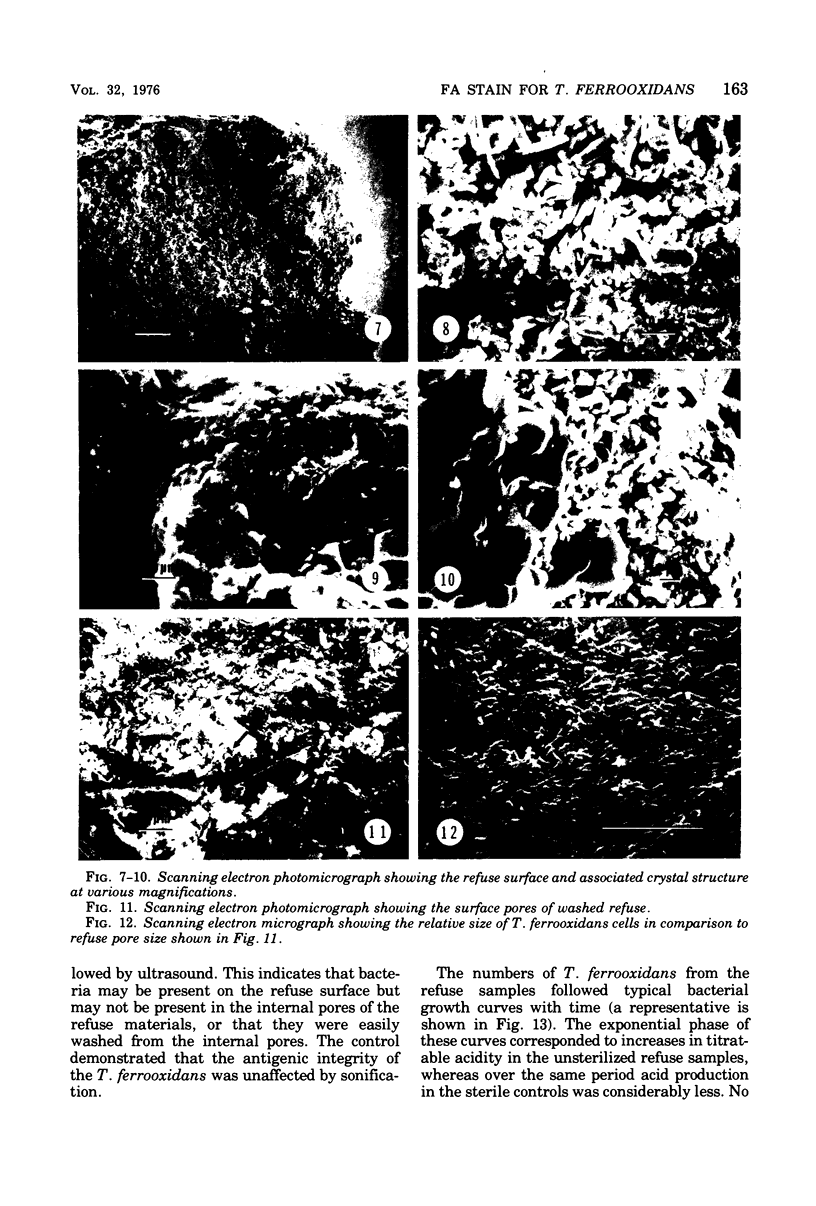
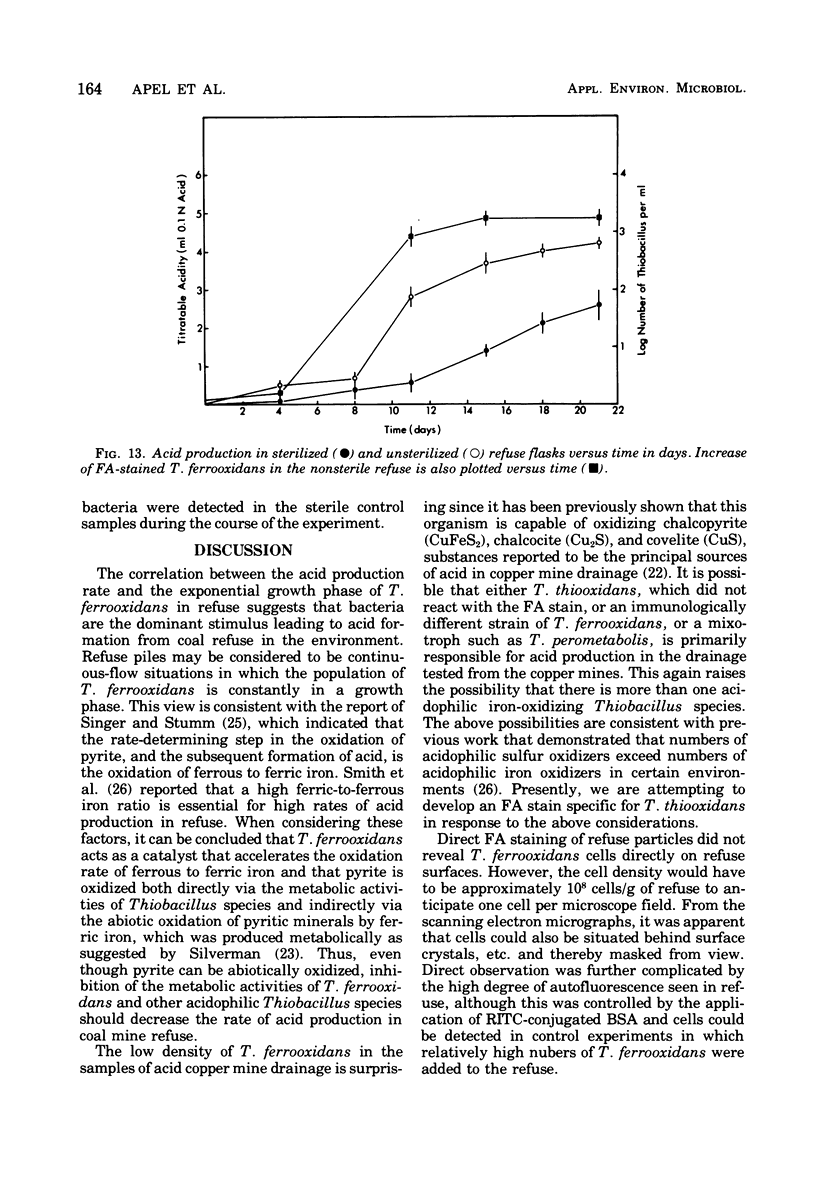
An indirect fluorescent antibody (FA) staining technique was developed for the rapid detection of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. The specificity of the FA stain for T. ferrooxidans was demonstrated with both laboratory and environmental samples. Coal refuse examined by scanning electron microscopy exhibited a rough, porous surface, which was characteristically covered by water-soluble crystals. Significant numbers of T. ferrooxidans were detected in the refuse pores. A positive correlation between numbers of T. ferrooxidans and acid production in coal refuse in the laboratory was demonstrated with the FA technique.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAUMSTARK J. S., LAFFIN R. J., BARDAWIL W. A. A PREPARATIVE METHOD FOR THE SEPARATION OF 7S GAMMA GLOBULIN FROM HUMAN SERUM. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Dec;108:514–522. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90436-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belly R. T., Brock T. D. Ecology of iron-oxidizing bacteria in pyritic materials associated with coal. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):726–732. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.726-732.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlool B. B., Brock T. D. Immunofluorescence approach to the study of the ecology of Thermoplasma acidophilum in coal refuse material. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jul;28(1):11–16. doi: 10.1128/am.28.1.11-16.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Nonspecific staining: its control in immunofluorescence examination of soil. Science. 1968 Nov 29;162(3857):1012–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3857.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugan P. R., MacMillan C. B., Pfister R. M. Aerobic heterotrophic bacteria indigenous to pH 2.8 acid mine water: microscopic examination of acid streamers. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):973–981. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.973-981.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Autecological study of the chemoautotroph Nitrobacter by immunofluorescence. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):124–129. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.124-129.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Schmidt E. L. Autoradiography and immunofluorescence combined for autecological study of single cell activity with Nitrobacter as a model system. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Oct;30(4):676–684. doi: 10.1128/am.30.4.676-684.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry R. A., Johnson R. C., Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Detection of Leptospira in soil and water by immunofluorescence staining. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):953–956. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.953-956.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Evison L. M. A fluorescent antibody technique for the enumeration of faecal streptococci in water. J Appl Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;38(1):63–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1975.tb00502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT E. L., BANKOLE R. O. Detection of Aspergillus flavus in soil by immunofluorescent staining. Science. 1962 Jun 1;136(3518):776–777. doi: 10.1126/science.136.3518.776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERMAN M. P., LUNDGREN D. G. Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. II. Manometric studies. J Bacteriol. 1959 Sep;78:326–331. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.3.326-331.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. L., Biesbrock J. A., Bohlool B. B., Marx D. H. Study of mycorrhizae by means of fluorescent antibody. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Feb;20(2):137–139. doi: 10.1139/m74-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver M., Torma A. E. Oxidation of metal sulfides by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans grown on different substrates. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Feb;20(2):141–147. doi: 10.1139/m74-023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M. P. Mechanism of bacterial pyrite oxidation. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1046–1051. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1046-1051.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer P. C., Stumm W. Acidic mine drainage: the rate-determining step. Science. 1970 Feb 20;167(3921):1121–1123. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3921.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttle J. H., Dugan P. R., Macmillan C. B., Randles C. I. Microbial dissimilatory sulfur cycle in acid mine water. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):594–602. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.594-602.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttle J. H., Randles C. I., Dugan P. R. Activity of microorganisms in acid mine water. I. Influence of acid water on aerobic heterotrophs of a normal stream. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1495–1503. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1495-1503.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]