Abstract
The catabolism of 131I and 125I paired labelled Fc fragments of myeloma proteins and of H chain disease proteins of different heavy chain subclasses was studied in men and monkeys. In contrast to the previously demonstrated catabolic heterogeneity of intact γG immunoglobulins, the Fc fragments and H chain disease proteins of all subclasses tested were catabolized at a similar rate. These data suggest that structures not present on the Fc fragments are responsible for the faster turnover rate of γG3 immunoglobulins and for the differences in half-lives of myeloma proteins within a given subclass.
The catabolic features of the H chain disease proteins differed from those of intact γG. Although the whole body half-lives of the two proteins were similar, the fractional turnover rate of the H chain disease proteins was higher than that of γG, on the average 8% of the intravascular pool/day as compared to 4% for γG. One-half to 1% of the intravascular pool of the H chain disease protein and less than 0·1% of the γG was excreted into the urine. An average of 24% of the H chain disease proteins and 44% of the γG equilibrated into the intravascular compartment.
Full text
PDF


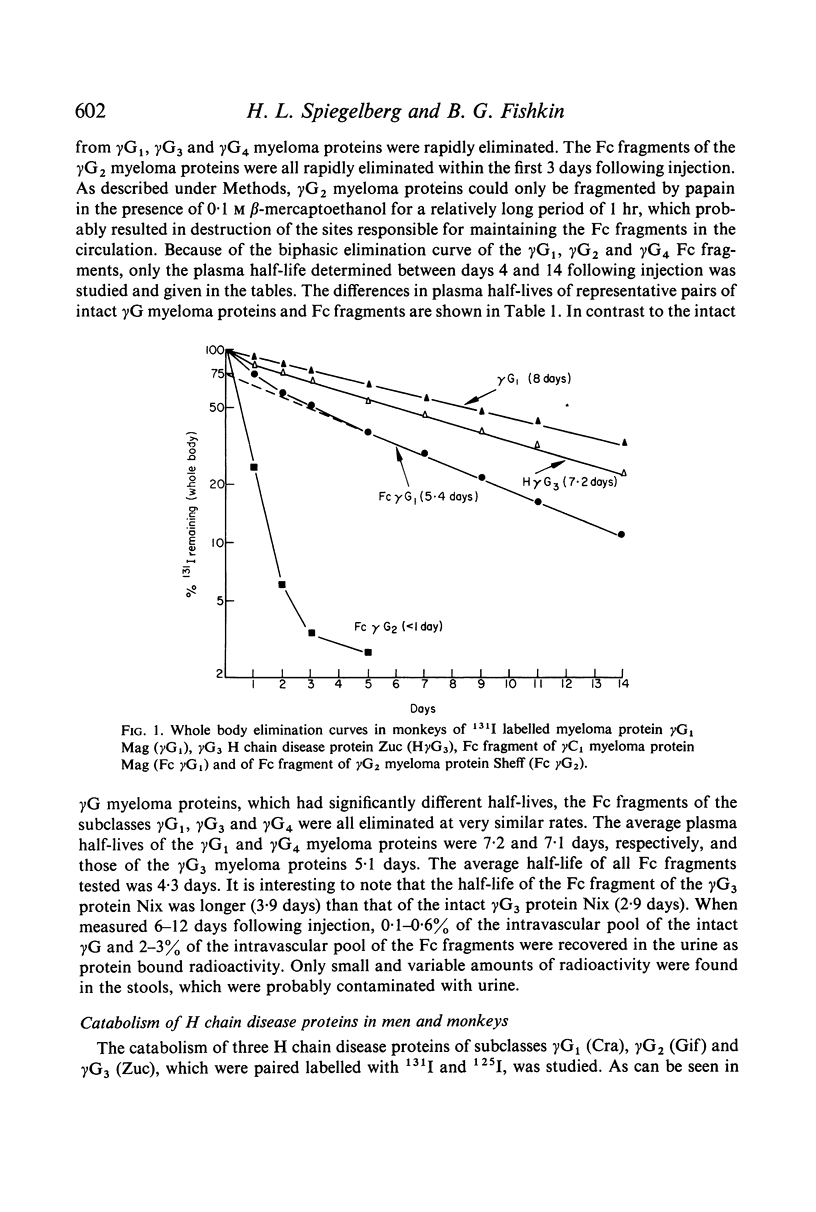
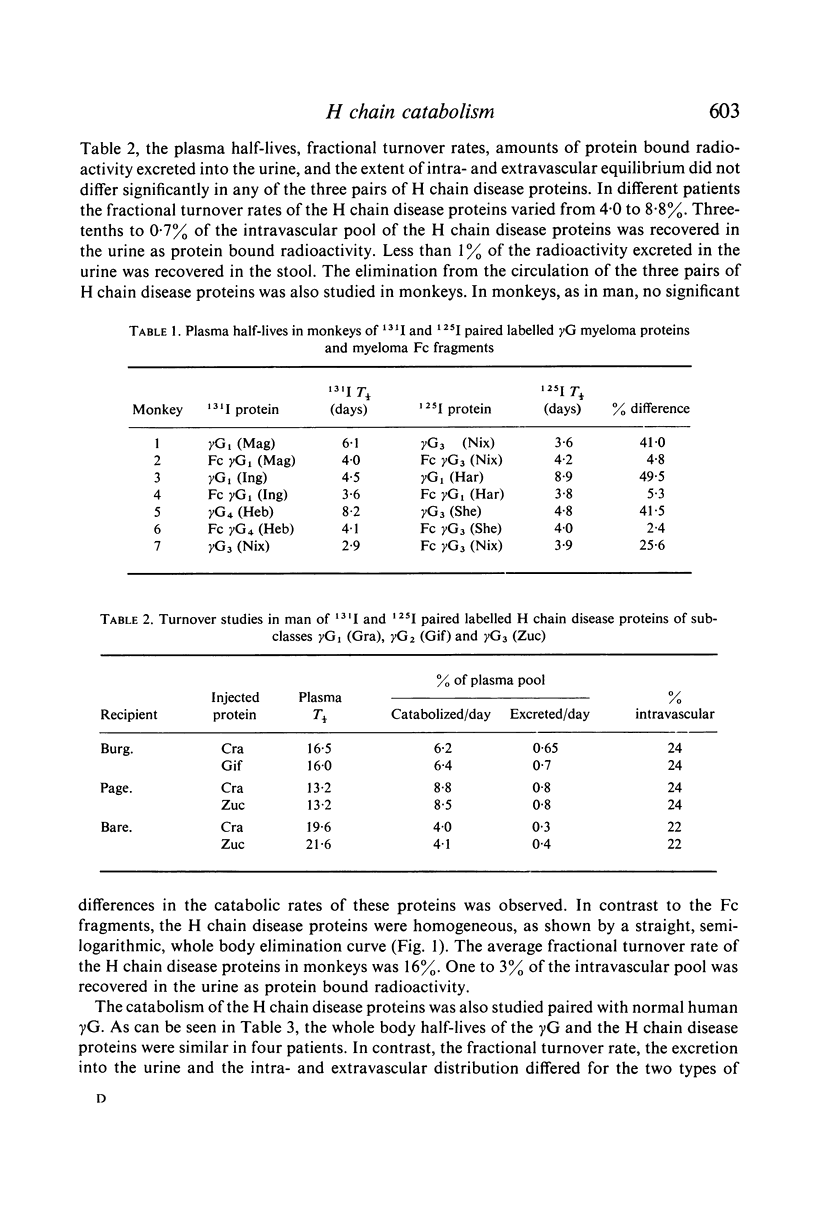
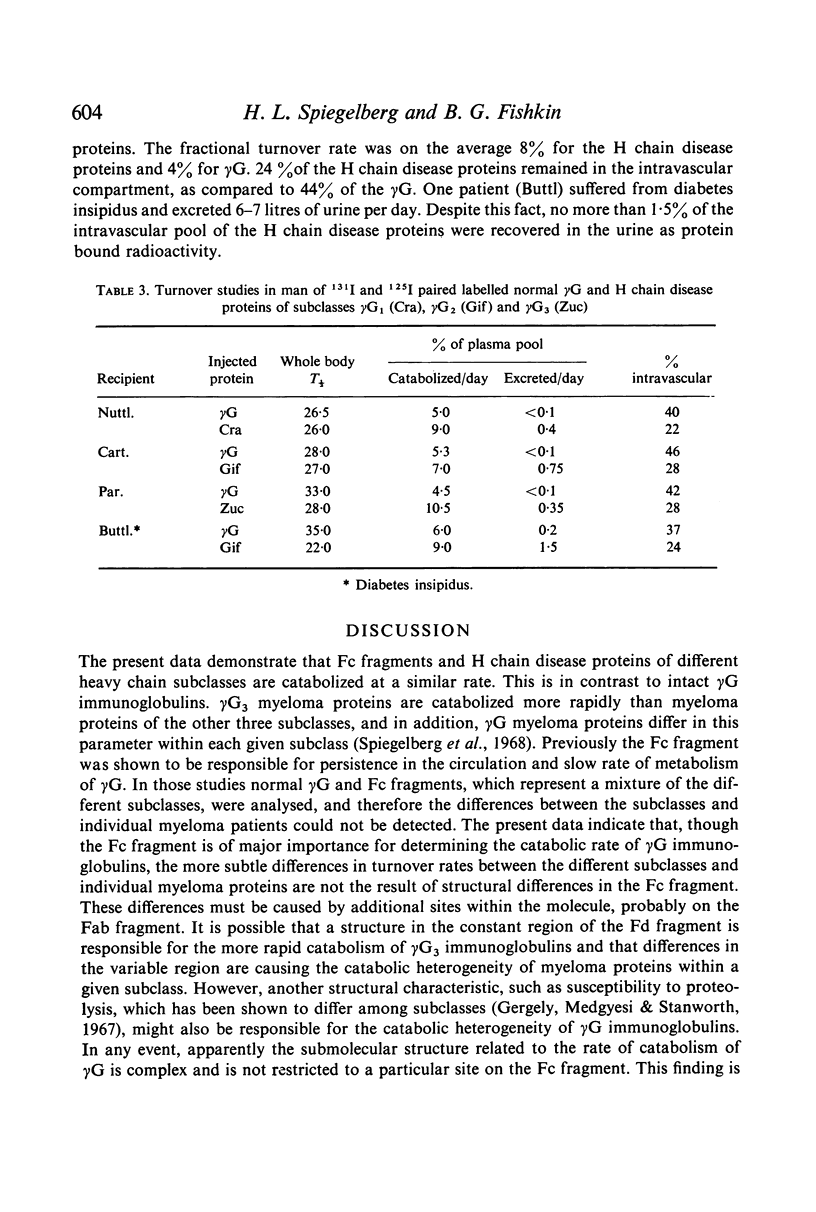



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ein D., Buell D. N., Fahey J. L. Biosynthetic and structural studies of a heavy chain disease protein. J Clin Invest. 1969 Apr;48(4):785–793. doi: 10.1172/JCI106036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ein D., Waldmann T. A. Metabolic studies of a heavy chain disease protein. J Immunol. 1969 Aug;103(2):345–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN E. C., LOWENSTEIN J., BIGELOW B., MELTZER M. HEAVY CHAIN DISEASE- A NEW DISORDER OF SERUM GAMMA-GLOBULINS : REPORT OF THE FIRST CASE. Am J Med. 1964 Sep;37:332–350. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90191-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Milstein C. Partial deletion in the heavy chain disease protein ZUC. Nature. 1969 Nov 8;224(5219):597–599. doi: 10.1038/224597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERKE J. R., HANEY T. A., PAGANO J. F., FERRARI A. Automation of the microbiological assay of antibiotics with an autoanalyzer instrumental system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jul 22;87:782–791. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb23235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey H. M., Kunkel H. G. Heavy-chain subclasses of human gamma-G-globulin. Peptide and immunochemical relationships. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2326–2334. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Salmon S., Fudenberg H. Biologic activities of aggregated gamma-globulin. 8. Aggregated immunoglobulins of different classes. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):82–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Terry W. D., Waldmann T. A. Metabolic properties of IgG subclasses in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):673–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI106279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSSERMAN E. F., TAKATSUKI K. PLASMA CELL MYELOMA: GAMMA GLOBULIN SYNTHESIS AND STRUCTURE. A REVIEW OF BIOCHEMICAL AND CLINICAL DATA, WITH THE DESCRIPTION OF A NEWLY-RECOGNIZED AND RELATED SYNDROME, "H-GAMMA-2-CHAIN (FRANKLIN'S) DISEASE. Medicine (Baltimore) 1963 Nov;42:357–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prahl J. W. N- and C-terminal sequences of a heavy chain disease protein and its genetic implications. Nature. 1967 Sep 23;215(5108):1386–1387. doi: 10.1038/2151386a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIEGELBERG H. L., WEIGLE W. O. THE CATABOLISM OF HOMOLOGOUS AND HETEROLOGOUS 7S GAMMA GLOBULIN FRAGMENTS. J Exp Med. 1965 Mar 1;121:323–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.3.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Fishkin B. G., Grey H. M. Catabolism of human gammaG-immunoglobulins of different heavy chain subclasses. I. Catabolism of gammaG-myeloma proteins in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Oct;47(10):2323–2330. doi: 10.1172/JCI105917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Grey H. M. Catabolism of human gamma-G immunoglobulins of different heavy chain subclasses. II. Catabolism of gamma-G myeloma proteins in heterologous species. J Immunol. 1968 Oct;101(4):711–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Weigle W. O. Studies on the catabolism of gamma- G subunits and chains. J Immunol. 1965 Dec;95(6):1034–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Weigle W. O. The production of antisera to human gammaGlobulin subclasses in rabbits using immunological unresponsiveness. J Immunol. 1968 Aug;101(2):377–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry W. D. Skin-sensitizing activity related to gamma- polypeptide chain characteristics of human IgG. J Immunol. 1965 Dec;95(6):1041–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIGLE W. O., DIXON F. J. The antibody response of lymph node cells transferred to tolerant recipients. J Immunol. 1959 Jun;82(6):516–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Strober W. Metabolism of immunoglobulins. Prog Allergy. 1969;13:1–110. doi: 10.1159/000385919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J., Tee D. E. Catabolism of gamma G-globulin and myeloma proteins of the subclasses gamma G1 and gamma G2 in a healthy volunteer. Immunology. 1970 Apr;18(4):537–543. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


