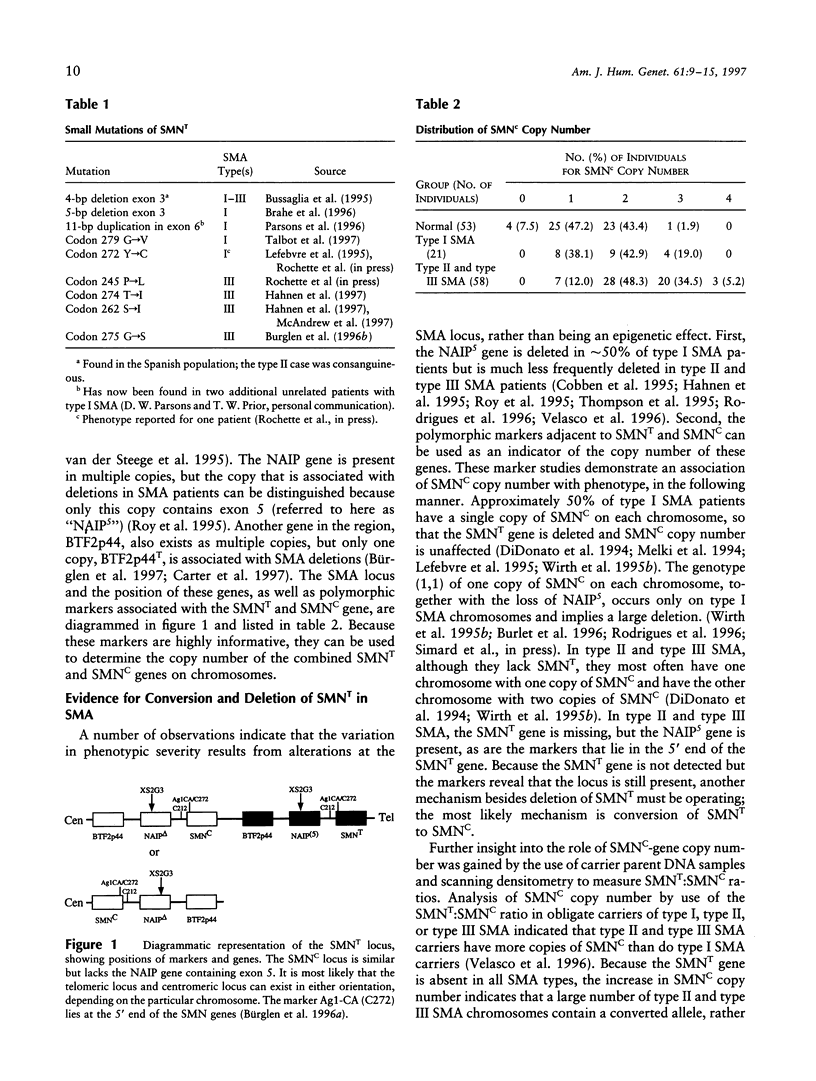
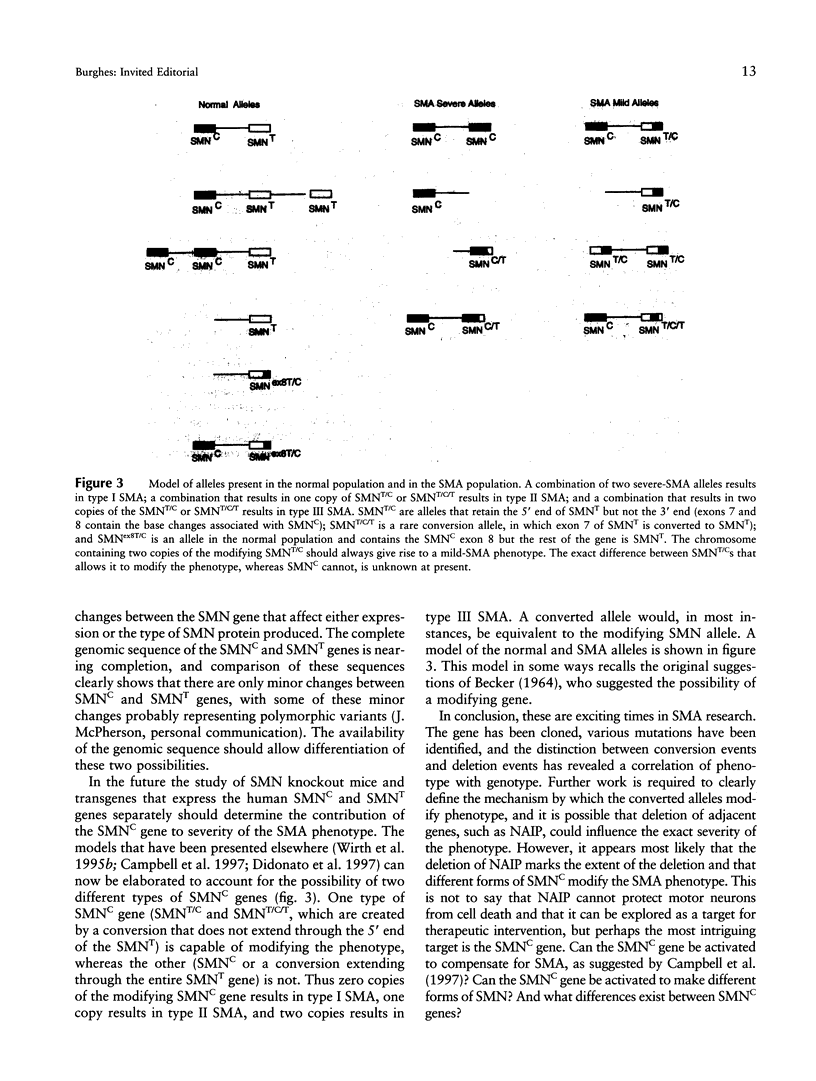
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKER P. E. ATROPHIA MUSCULORUM SPINALIS PSEUDOMYOPATHICA. HEREDITAERE NEUROGENE PROXIMALE AMYOTROPHIE VON KUGELBERG UND WELANDER. Z Mensch Vererb Konstitutionsl. 1963 Dec 17;37:193–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahe C., Clermont O., Zappata S., Tiziano F., Melki J., Neri G. Frameshift mutation in the survival motor neuron gene in a severe case of SMA type I. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Dec;5(12):1971–1976. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.12.1971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahe C., Velonà I., van der Steege G., Zappata S., van de Veen A. Y., Osinga J., Tops C. M., Fodde R., Khan P. M., Buys C. H. Mapping of two new markers within the smallest interval harboring the spinal muscular atrophy locus by family and radiation hybrid analysis. Hum Genet. 1994 May;93(5):494–501. doi: 10.1007/BF00202811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzustowicz L. M., Lehner T., Castilla L. H., Penchaszadeh G. K., Wilhelmsen K. C., Daniels R., Davies K. E., Leppert M., Ziter F., Wood D. Genetic mapping of chronic childhood-onset spinal muscular atrophy to chromosome 5q11.2-13.3. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):540–541. doi: 10.1038/344540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghes A. H., Ingraham S. E., Kóte-Jarai Z., Rosenfeld S., Herta N., Nadkarni N., DiDonato C. J., Carpten J., Hurko O., Florence J. Linkage mapping of the spinal muscular atrophy gene. Hum Genet. 1994 Mar;93(3):305–312. doi: 10.1007/BF00212028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghes A. H., Ingraham S. E., McLean M., Thompson T. G., McPherson J. D., Kote-Jarai Z., Carpten J. D., DiDonato C. J., Ikeda J. E., Surh L. A multicopy dinucleotide marker that maps close to the spinal muscular atrophy gene. Genomics. 1994 May 15;21(2):394–402. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlet P., Bürglen L., Clermont O., Lefebvre S., Viollet L., Munnich A., Melki J. Large scale deletions of the 5q13 region are specific to Werdnig-Hoffmann disease. J Med Genet. 1996 Apr;33(4):281–283. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.4.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussaglia E., Clermont O., Tizzano E., Lefebvre S., Bürglen L., Cruaud C., Urtizberea J. A., Colomer J., Munnich A., Baiget M. A frame-shift deletion in the survival motor neuron gene in Spanish spinal muscular atrophy patients. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):335–337. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglen L., Lefebvre S., Clermont O., Burlet P., Viollet L., Cruaud C., Munnich A., Melki J. Structure and organization of the human survival motor neurone (SMN) gene. Genomics. 1996 Mar 15;32(3):479–482. doi: 10.1006/geno.1996.0147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglen L., Seroz T., Miniou P., Lefebvre S., Burlet P., Munnich A., Pequignot E. V., Egly J. M., Melki J. The gene encoding p44, a subunit of the transcription factor TFIIH, is involved in large-scale deletions associated with Werdnig-Hoffmann disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1997 Jan;60(1):72–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell L., Potter A., Ignatius J., Dubowitz V., Davies K. Genomic variation and gene conversion in spinal muscular atrophy: implications for disease process and clinical phenotype. Am J Hum Genet. 1997 Jul;61(1):40–50. doi: 10.1086/513886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpten J. D., DiDonato C. J., Ingraham S. E., Wagner-McPherson C., Nieuwenhuijsen B. W., Wasmuth J. J., Burghes A. H. A YAC contig of the region containing the spinal muscular atrophy gene (SMA): identification of an unstable region. Genomics. 1994 Nov 15;24(2):351–356. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter T. A., Bönnemann C. G., Wang C. H., Obici S., Parano E., De Fatima Bonaldo M., Ross B. M., Penchaszadeh G. K., Mackenzie A., Soares M. B. A multicopy transcription-repair gene, BTF2p44, maps to the SMA region and demonstrates SMA associated deletions. Hum Mol Genet. 1997 Feb;6(2):229–236. doi: 10.1093/hmg/6.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobben J. M., van der Steege G., Grootscholten P., de Visser M., Scheffer H., Buys C. H. Deletions of the survival motor neuron gene in unaffected siblings of patients with spinal muscular atrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Oct;57(4):805–808. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriendt K., Lammens M., Schollen E., Van Hole C., Dom R., Devlieger H., Cassiman J. J., Fryns J. P., Matthijs G. Clinical and molecular genetic features of congenital spinal muscular atrophy. Ann Neurol. 1996 Nov;40(5):731–738. doi: 10.1002/ana.410400509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDonato C. J., Ingraham S. E., Mendell J. R., Prior T. W., Lenard S., Moxley R. T., 3rd, Florence J., Burghes A. H. Deletion and conversion in spinal muscular atrophy patients: is there a relationship to severity? Ann Neurol. 1997 Feb;41(2):230–237. doi: 10.1002/ana.410410214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDonato C. J., Morgan K., Carpten J. D., Fuerst P., Ingraham S. E., Prescott G., McPherson J. D., Wirth B., Zerres K., Hurko O. Association between Ag1-CA alleles and severity of autosomal recessive proximal spinal muscular atrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Dec;55(6):1218–1229. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis M. J., Morrison K. E., Campbell L., Grewal P. K., Christodoulou Z., Daniels R. J., Monaco A. P., Frischauf A. M., McPherson J., Wasmuth J. A contig of non-chimaeric YACs containing the spinal muscular atrophy gene in 5q13. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1161–1167. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahnen E., Forkert R., Marke C., Rudnik-Schöneborn S., Schönling J., Zerres K., Wirth B. Molecular analysis of candidate genes on chromosome 5q13 in autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy: evidence of homozygous deletions of the SMN gene in unaffected individuals. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Oct;4(10):1927–1933. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.10.1927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahnen E., Schönling J., Rudnik-Schöneborn S., Raschke H., Zerres K., Wirth B. Missense mutations in exon 6 of the survival motor neuron gene in patients with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). Hum Mol Genet. 1997 May;6(5):821–825. doi: 10.1093/hmg/6.5.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahnen E., Schönling J., Rudnik-Schöneborn S., Zerres K., Wirth B. Hybrid survival motor neuron genes in patients with autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy: new insights into molecular mechanisms responsible for the disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Nov;59(5):1057–1065. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleyn P. W., Wang C. H., Lien L. L., Vitale E., Pan J., Ross B. M., Grunn A., Palmer D. A., Warburton D., Brzustowicz L. M. Construction of a yeast artificial chromosome contig spanning the spinal muscular atrophy disease gene region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6801–6805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre S., Bürglen L., Reboullet S., Clermont O., Burlet P., Viollet L., Benichou B., Cruaud C., Millasseau P., Zeviani M. Identification and characterization of a spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene. Cell. 1995 Jan 13;80(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90460-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Q., Dreyfuss G. A novel nuclear structure containing the survival of motor neurons protein. EMBO J. 1996 Jul 15;15(14):3555–3565. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthijs G., Schollen E., Legius E., Devriendt K., Goemans N., Kayserili H., Apäk M. Y., Cassiman J. J. Unusual molecular findings in autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy. J Med Genet. 1996 Jun;33(6):469–474. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.6.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAndrew P. E., Parsons D. W., Simard L. R., Rochette C., Ray P. N., Mendell J. R., Prior T. W., Burghes A. H. Identification of proximal spinal muscular atrophy carriers and patients by analysis of SMNT and SMNC gene copy number. Am J Hum Genet. 1997 Jun;60(6):1411–1422. doi: 10.1086/515465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melki J., Abdelhak S., Sheth P., Bachelot M. F., Burlet P., Marcadet A., Aicardi J., Barois A., Carriere J. P., Fardeau M. Gene for chronic proximal spinal muscular atrophies maps to chromosome 5q. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):767–768. doi: 10.1038/344767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melki J., Lefebvre S., Burglen L., Burlet P., Clermont O., Millasseau P., Reboullet S., Bénichou B., Zeviani M., Le Paslier D. De novo and inherited deletions of the 5q13 region in spinal muscular atrophies. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1474–1477. doi: 10.1126/science.7910982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller B., Melki J., Burlet P., Clerget-Darpoux F. Proximal spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) types II and III in the same sibship are not caused by different alleles at the SMA locus on 5q. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 May;50(5):892–895. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons D. W., McAndrew P. E., Monani U. R., Mendell J. R., Burghes A. H., Prior T. W. An 11 base pair duplication in exon 6 of the SMN gene produces a type I spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) phenotype: further evidence for SMN as the primary SMA-determining gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Nov;5(11):1727–1732. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.11.1727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearn J. Classification of spinal muscular atrophies. Lancet. 1980 Apr 26;1(8174):919–922. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90847-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues N. R., Owen N., Talbot K., Ignatius J., Dubowitz V., Davies K. E. Deletions in the survival motor neuron gene on 5q13 in autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Apr;4(4):631–634. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.4.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues N. R., Owen N., Talbot K., Patel S., Muntoni F., Ignatius J., Dubowitz V., Davies K. E. Gene deletions in spinal muscular atrophy. J Med Genet. 1996 Feb;33(2):93–96. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.2.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy N., Mahadevan M. S., McLean M., Shutler G., Yaraghi Z., Farahani R., Baird S., Besner-Johnston A., Lefebvre C., Kang X. The gene for neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein is partially deleted in individuals with spinal muscular atrophy. Cell. 1995 Jan 13;80(1):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90461-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simard L. R., Vanasse M., Rochette C., Morgan K., Lemieux B., Melançon S. B., Labuda D. Linkage study of chronic childhood-onset spinal muscular atrophy (SMA): confirmation of close linkage to D5S39 in French Canadian families. Genomics. 1992 Sep;14(1):188–190. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot K., Ponting C. P., Theodosiou A. M., Rodrigues N. R., Surtees R., Mountford R., Davies K. E. Missense mutation clustering in the survival motor neuron gene: a role for a conserved tyrosine and glycine rich region of the protein in RNA metabolism? Hum Mol Genet. 1997 Mar;6(3):497–500. doi: 10.1093/hmg/6.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson T. G., DiDonato C. J., Simard L. R., Ingraham S. E., Burghes A. H., Crawford T. O., Rochette C., Mendell J. R., Wasmuth J. J. A novel cDNA detects homozygous microdeletions in greater than 50% of type I spinal muscular atrophy patients. Nat Genet. 1995 Jan;9(1):56–62. doi: 10.1038/ng0195-56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velasco E., Valero C., Valero A., Moreno F., Hernández-Chico C. Molecular analysis of the SMN and NAIP genes in Spanish spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) families and correlation between number of copies of cBCD541 and SMA phenotype. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Feb;5(2):257–263. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.2.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. H., Xu J., Carter T. A., Ross B. M., Dominski M. K., Bellcross C. A., Penchaszadeh G. K., Munsat T. L., Gilliam T. C. Characterization of survival motor neuron (SMNT) gene deletions in asymptomatic carriers of spinal muscular atrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Mar;5(3):359–365. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth B., Hahnen E., Morgan K., DiDonato C. J., Dadze A., Rudnik-Schöneborn S., Simard L. R., Zerres K., Burghes A. H. Allelic association and deletions in autosomal recessive proximal spinal muscular atrophy: association of marker genotype with disease severity and candidate cDNAs. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Aug;4(8):1273–1284. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.8.1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth B., Pick E., Leutner A., Dadze A., Voosen B., Knapp M., Piechaczek-Wappenschmidt B., Rudnik-Schöneborn S., Schönling J., Cox S. Large linkage analysis in 100 families with autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) and 11 CEPH families using 15 polymorphic loci in the region 5q11.2-q13.3. Genomics. 1994 Mar 1;20(1):84–93. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth B., el-Agwany A., Baasner A., Burghes A., Koch A., Dadze A., Piechaczeck-Wappenschmidt B., Rudnik-Schöneborn S., Zerres K., Schönling J. Mapping of the spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) gene to a 750-kb interval flanked by two new microsatellites. Eur J Hum Genet. 1995;3(1):56–60. doi: 10.1159/000472274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Steege G., Grootscholten P. M., Cobben J. M., Zappata S., Scheffer H., den Dunnen J. T., van Ommen G. J., Brahe C., Buys C. H. Apparent gene conversions involving the SMN gene in the region of the spinal muscular atrophy locus on chromosome 5. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Oct;59(4):834–838. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Steege G., Grootscholten P. M., van der Vlies P., Draaijers T. G., Osinga J., Cobben J. M., Scheffer H., Buys C. H. PCR-based DNA test to confirm clinical diagnosis of autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy. Lancet. 1995 Apr 15;345(8955):985–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


