Abstract
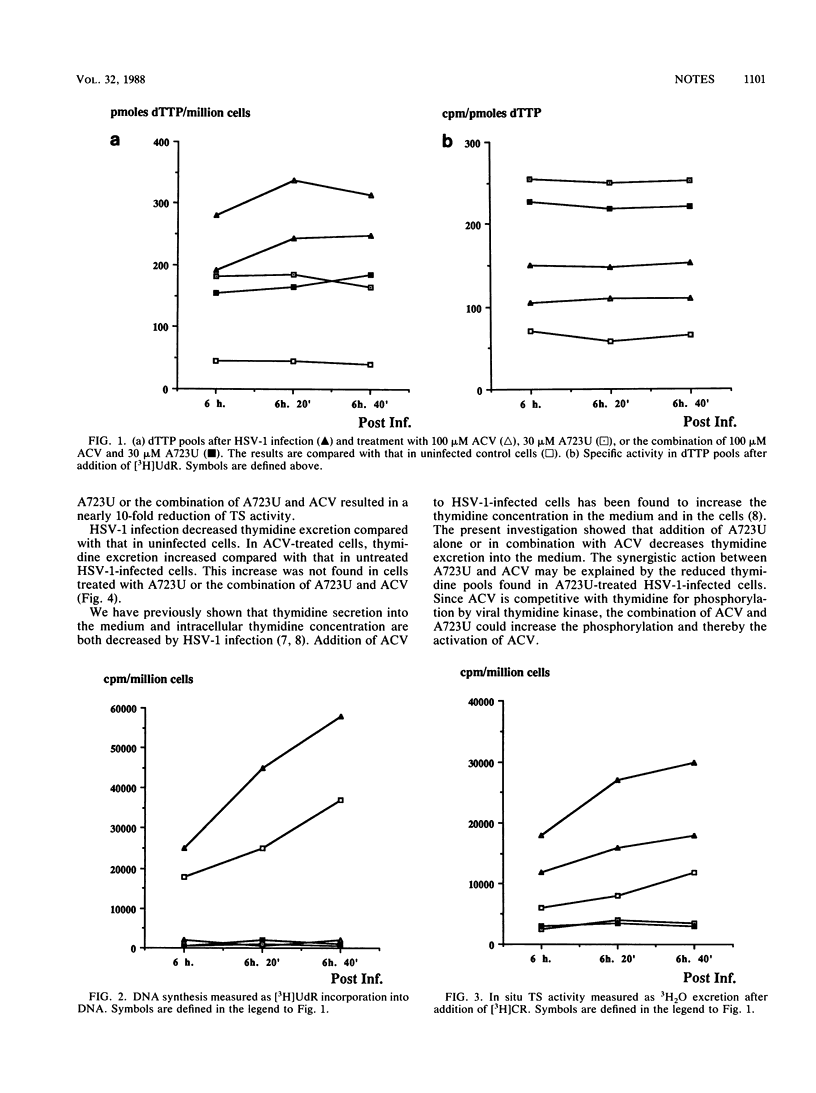
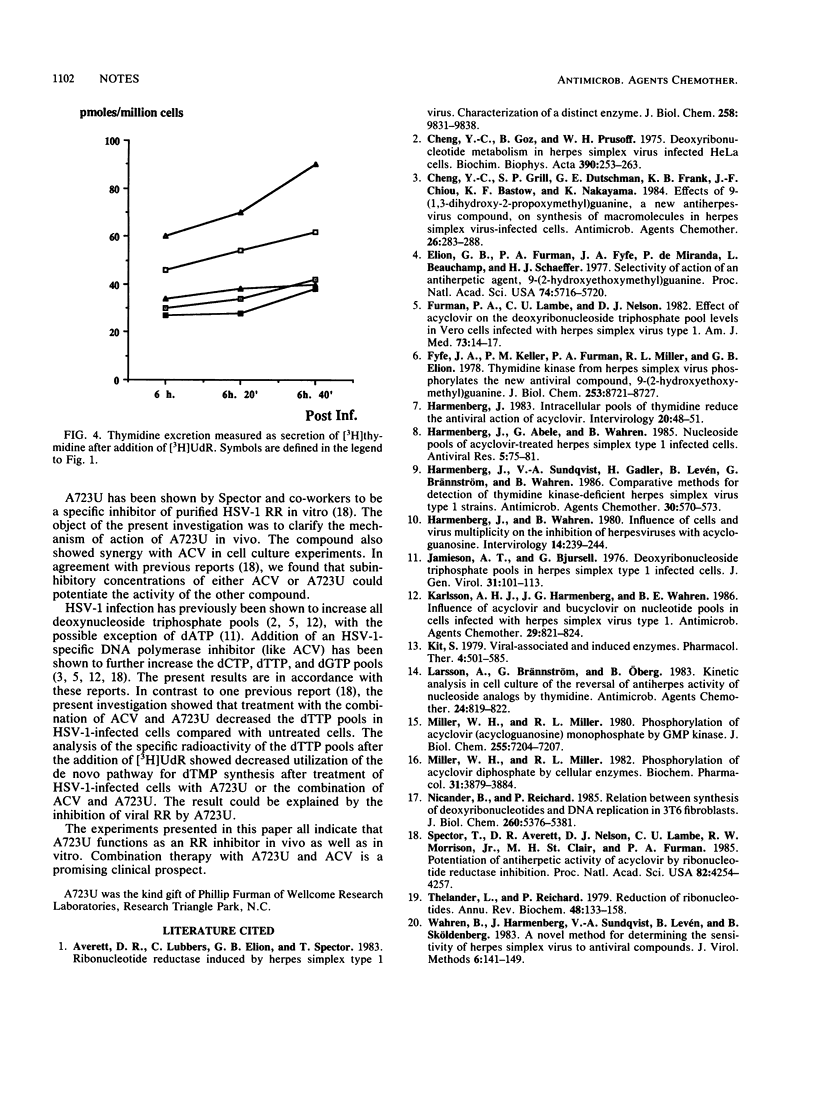
The pyrimidine metabolism of fibroblasts infected with herpes simplex virus type 1 was studied. Herpes simplex virus type 1 infection increased the dTTP pool and thymidylate synthetase activity but reduced thymidine excretion. Addition of acyclovir to infected cells increased thymidine excretion, the dTTP pool, and thymidylate synthetase activity. Addition of a virus-specific ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor (A723U) decreased all three. The synergy between the two compounds is discussed.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Averett D. R., Lubbers C., Elion G. B., Spector T. Ribonucleotide reductase induced by herpes simplex type 1 virus. Characterization of a distinct enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9831–9838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Goz B., Prusoff W. H. Deoxyribonucleotide metabolism in Herpes simplex virus infected HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 16;390(3):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Grill S. P., Dutschman G. E., Frank K. B., Chiou J. F., Bastow K. F., Nakayama K. Effects of 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine, a new antiherpesvirus compound, on synthesis of macromolecules in herpes simplex virus-infected cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Sep;26(3):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.3.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion G. B., Furman P. A., Fyfe J. A., de Miranda P., Beauchamp L., Schaeffer H. J. Selectivity of action of an antiherpetic agent, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5716–5720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., Lambe C. U., Nelson D. J. Effect of acyclovir on the deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate pool levels in Vero cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. Am J Med. 1982 Jul 20;73(1A):14–17. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe J. A., Keller P. M., Furman P. A., Miller R. L., Elion G. B. Thymidine kinase from herpes simplex virus phosphorylates the new antiviral compound, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8721–8727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmenberg J., Abele G., Wahren B. Nucleoside pools of acyclovir-treated herpes simplex type 1 infected cells. Antiviral Res. 1985 Apr;5(2):75–81. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(85)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmenberg J. Intracellular pools of thymidine reduce the antiviral action of acyclovir. Intervirology. 1983;20(1):48–51. doi: 10.1159/000149373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmenberg J., Sundqvist V. A., Gadler H., Levén B., Brännström G., Wahren B. Comparative methods for detection of thymidine kinase-deficient herpes simplex virus type 1 strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Oct;30(4):570–573. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.4.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmenberg J., Wahren B., Oberg B. Influence of cells and virus multiplicity on the inhibition of herpesviruses with acycloguanosine. Intervirology. 1980;14(5-6):239–244. doi: 10.1159/000149192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson A. T., Bjursell G. Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate pools in herpes simplex type 1 infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1976 Apr;31(1):101–113. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-1-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson A. H., Harmenberg J. G., Wahren B. E. Influence of acyclovir and bucyclovir on nucleotide pools in cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):821–824. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S. Viral-associated and induced enzymes. Pharmacol Ther B. 1979;4(3):501–585. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(79)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson A., Brännström G., Oberg B. Kinetic analysis in cell culture of the reversal of antiherpes activity of nucleoside analogs by thymidine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Nov;24(5):819–822. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.5.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. H., Miller R. L. Phosphorylation of acyclovir (acycloguanosine) monophosphate by GMP kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7204–7207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. H., Miller R. L. Phosphorylation of acyclovir diphosphate by cellular enzymes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 1;31(23):3879–3884. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicander B., Reichard P. Relations between synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides and DNA replication in 3T6 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5376–5381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T., Averett D. R., Nelson D. J., Lambe C. U., Morrison R. W., Jr, St Clair M. H., Furman P. A. Potentiation of antiherpetic activity of acyclovir by ribonucleotide reductase inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4254–4257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelander L., Reichard P. Reduction of ribonucleotides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:133–158. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren B., Harmenberg J., Sundqvist V. A., Levén B., Sköldenberg B. A novel method for determining the sensitivity of herpes simplex virus to antiviral compounds. J Virol Methods. 1983 Mar;6(3):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(83)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


