Abstract
1. Renin-like activity was found in rat submaxillary glands.
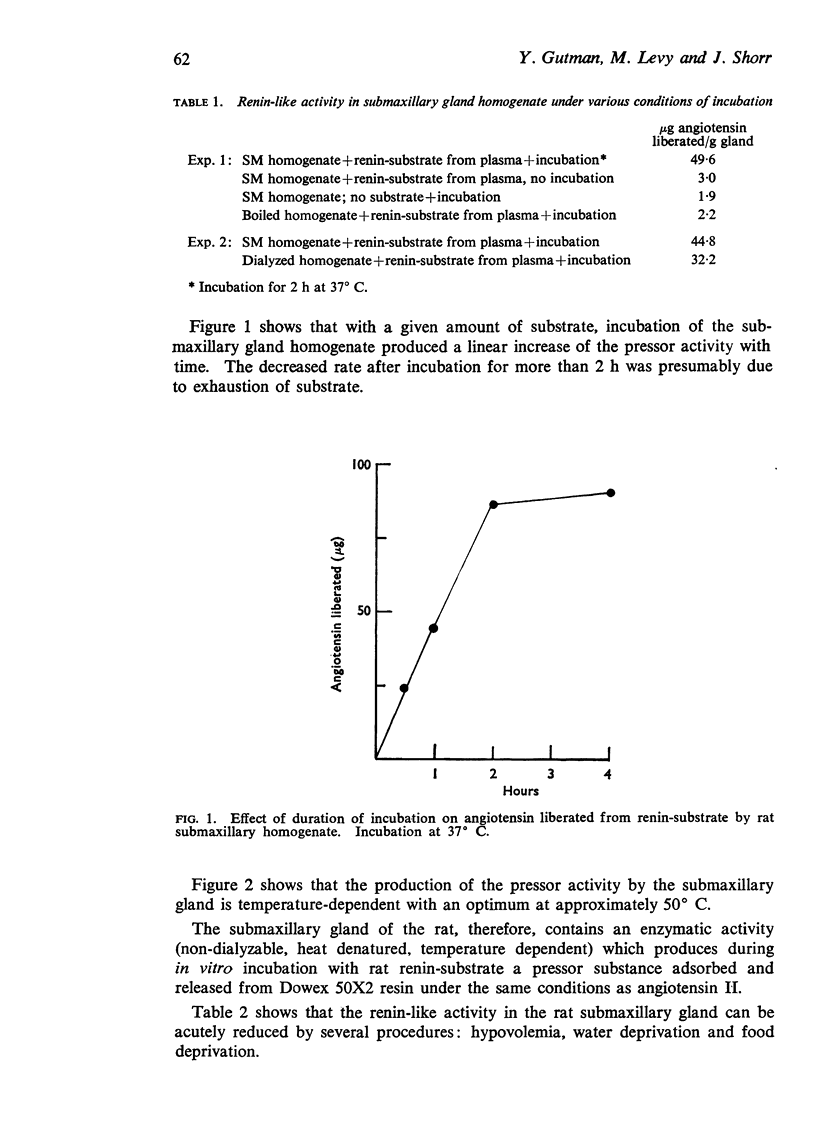
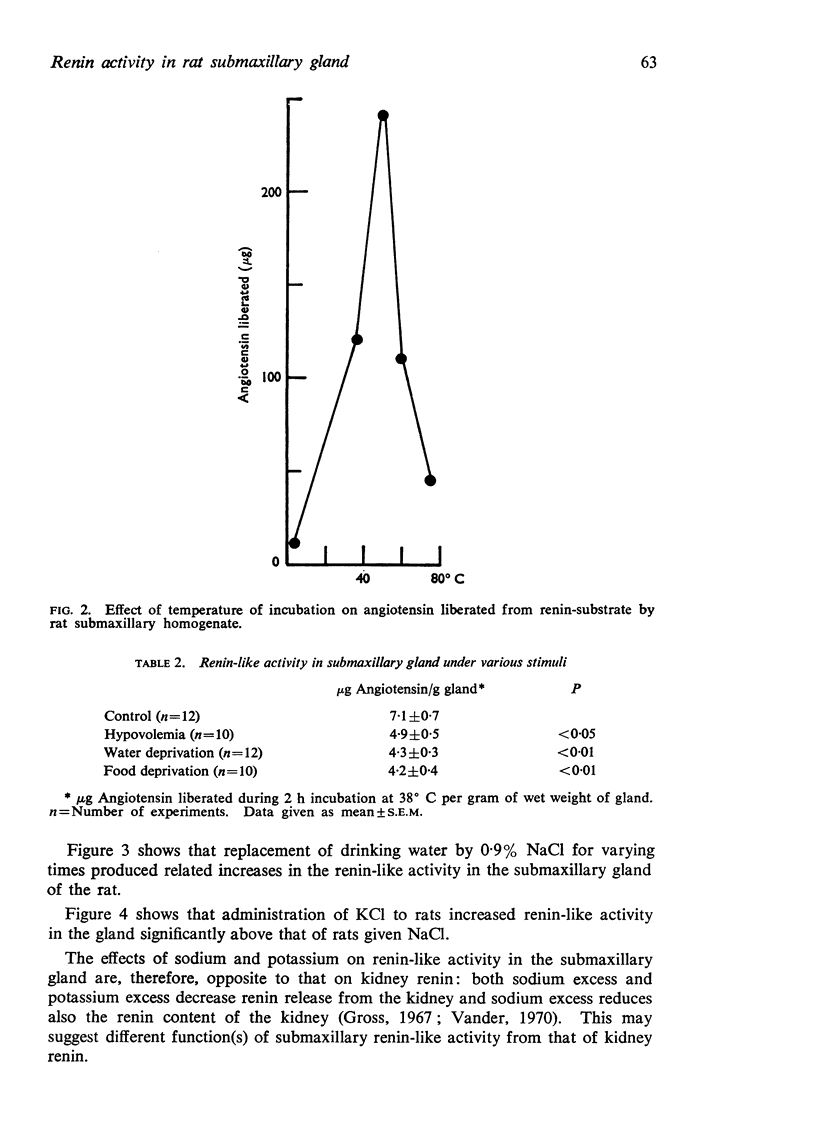
2. This activity was destroyed by boiling, was non-dialyzable and showed an optimum at approximately 50° C.
3. Renin-like activity in the submaxillary gland was not diminished 24 h after nephrectomy but was considerably reduced after ligature of the submaxillary duct.
4. Renin-like activity in the submaxillary gland was reduced following food-deprivation, water-deprivation or hypovolemia.
5. Renin-like activity in the rat submaxillary gland was increased after isoproterenol administration but not following pilocarpine.
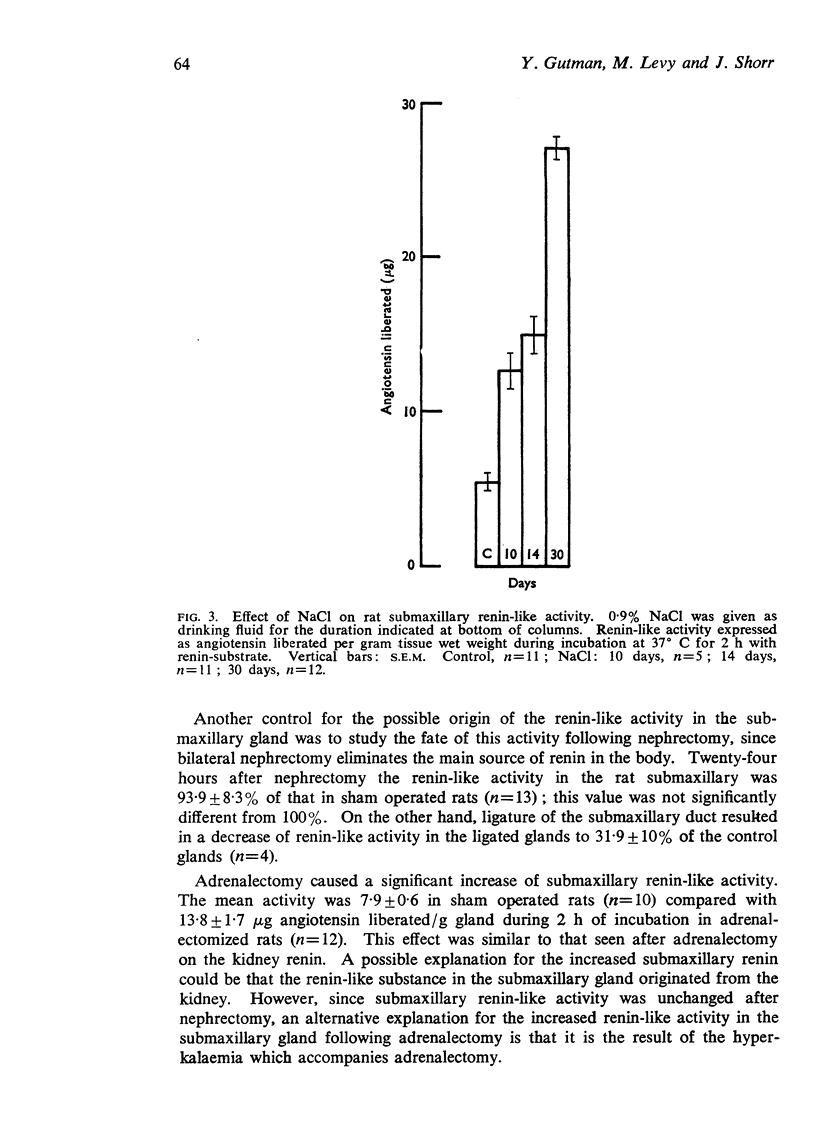
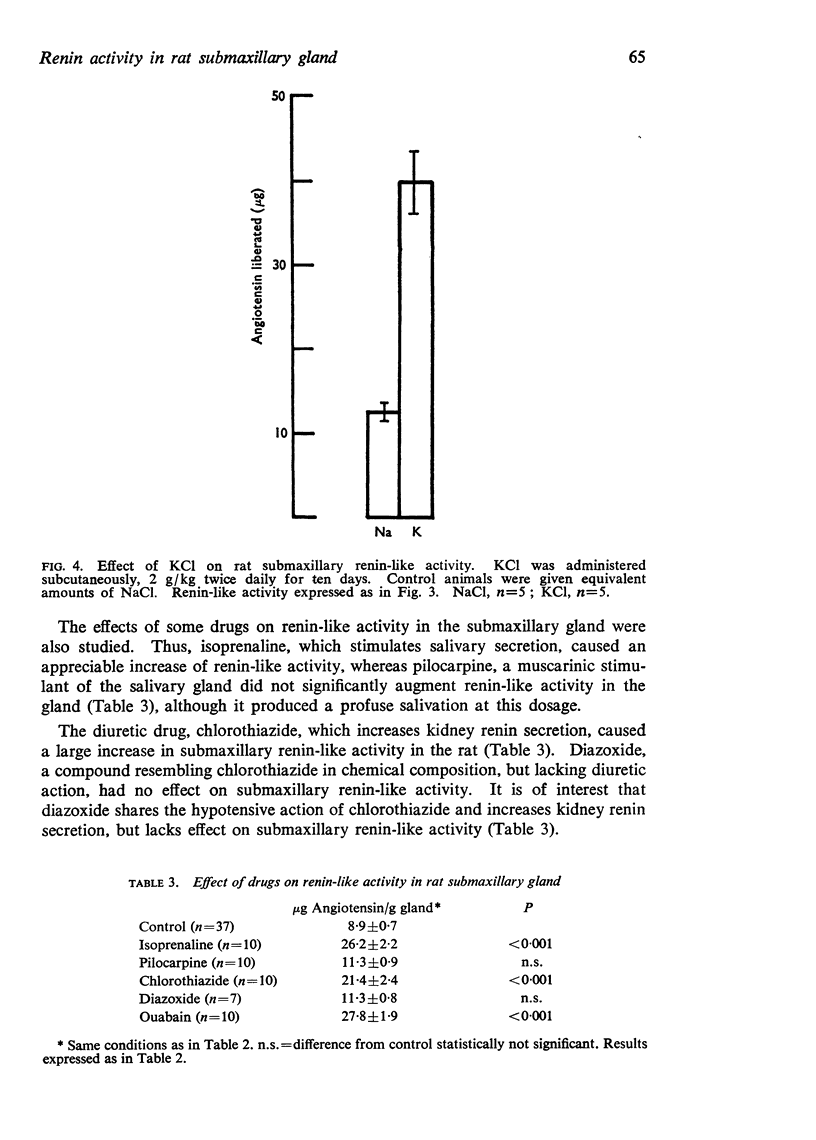
6. Renin-like activity in the rat submaxillary gland was increased considerably by administration of NaCl or KCl, as well as following adrenalectomy.
7. Chlorothiazide and ouabain increased submaxillary renin-like activity but diazoxide did not affect this activity.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boucher R., Ménard J., Genest J. A micromethod for measurement of renin in the plasma and kidney of rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1967 Sep;45(5):881–890. doi: 10.1139/y67-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carretero O. A., Bujak B., Houle J. A. Renin isozymes of extrarenal origin. Am J Physiol. 1971 May;220(5):1468–1472. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.5.1468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzsimons J. T., Simons B. J. The effect on drinking in the rat of intravenous infusion of angiotensin, given alone or in combination with other stimuli of thirst. J Physiol. 1969 Jul;203(1):45–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS F., SCHAECHTELIN G., ZIEGLER M., BERGER M. A RENIN-LIKE SUBSTANCE IN THE PLACENTA AND UTERUS OF THE RABBIT. Lancet. 1964 Apr 25;1(7339):914–916. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91637-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganten D., Minnich J. L., Granger P., Hayduk K., Brecht H. M., Barbeau A., Boucher R., Genest J. Angiotensin-forming enzyme in brain tissue. Science. 1971 Jul 2;173(3991):64–65. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3991.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman Y., Benzakein F. Relation of kidneys and adrenal glands to hypovolemic thirst. Isr J Med Sci. 1969 May-Jun;5(3):411–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman Y., Livneh P., Pietrokovski J. Role of salivary glands in response to thirst stimuli. Isr J Med Sci. 1970 Jul-Aug;6(4):573–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas E., Goldblatt H., Gipson E. C., Lewis L. Extraction, purification, and assay of human renin free of angiotensinase. Circ Res. 1966 Oct;19(4):739–749. doi: 10.1161/01.res.19.4.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainsworth F. R., Stricker E. M. Evaporative cooling in the rat: differences between salivary glands as thermoregulatory effectors. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1971 Jun;49(6):573–580. doi: 10.1139/y71-074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C., Unger H. J. Ein blutdrucksteigerndes Prinzip in der Glandula submaxillaris der Ratte. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol. 1969;264(3):257–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. W. Specificity of the renin-like enzyme of rabbit uterus. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(1):159–160. doi: 10.1042/bj1160159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeggs L. T., Lentz K. E., Kahn J. R., Dorer F. E., Levine M. Pseudorenin. A new angiotensin-forming enzyme. Circ Res. 1969 Oct;25(4):451–462. doi: 10.1161/01.res.25.4.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricker E. M. Extracellular fluid volume and thirst. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):232–238. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda T., DeBusk J., Grollman A. Physiologic role of reninlike constituent of submaxillary gland of the mouse. Am J Physiol. 1969 May;216(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.5.1194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Direct effects of potassium on renin secretion and renal function. Am J Physiol. 1970 Aug;219(2):455–459. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.2.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERLE E., VOGEL R., GOLDEL L. F. Uber ein blutdrucksteigerndes Prinzip in Extrakten aus der Glandula submaxillaris der weissen Maus. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1957;230(3):236–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


