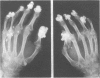
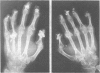
Abstract
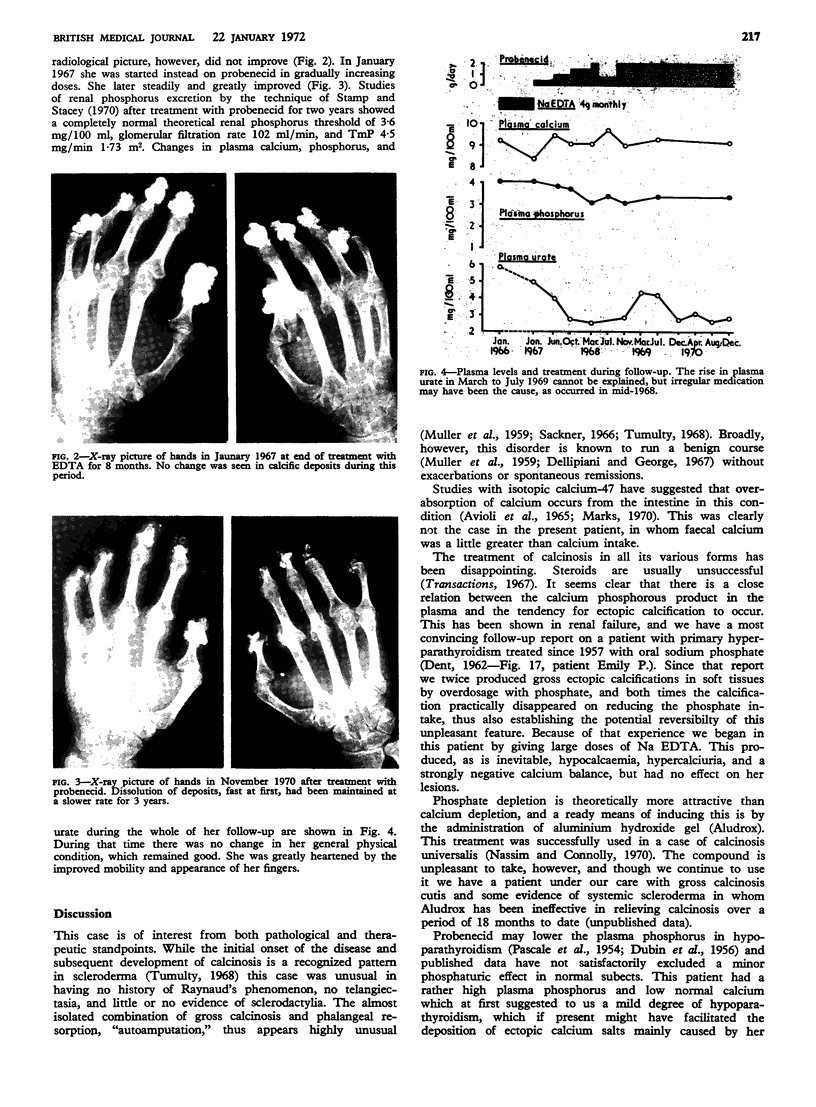
A 23-year-old woman presented with an 11-year history of peripheral joint pains and stiffness slowly progressing to the development of gross calcinosis circumscripta. She had no definite evidence of systemic scleroderma. She was first treated for one year with frequent intravenous sodium EDTA, which increased urinary calcium and enhanced negative calcium balance but did not lessen her calcinosis. She was then treated with probenecid up to 2 g daily and her calcinosis lessened steadily over three years. Plasma levels of both phosphorus and urate fell during this time.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVIOLI L. V., MCDONALD J. E., SINGER R. A., HENNEMAN P. H. A NEW ORAL ISOTOPIC TEST OF CALCIUM ABSORPTION. J Clin Invest. 1965 Jan;44:128–139. doi: 10.1172/JCI105119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRONSKY D., DUBIN A., KUSHNER D. S., PASCALE L. R. Hyperuricemia in hypoparathyroidism. Metabolism. 1956 Nov;5(6 Pt 1):703–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellipiani A. W., George M. Syndrome of sclerodactyly, calcinosis, Raynaud's phenomenon, and telangiectasia. Br Med J. 1967 Nov 11;4(5575):334–335. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5575.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis M. D., Russell R. G., Fleisch H. Diphosphonates inhibit formation of calcium phosphate crystals in vitro and pathological calcification in vivo. Science. 1969 Sep 19;165(3899):1264–1266. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3899.1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLER S. A., BRUNSTING L. A., WINKELMANN R. K. Calcinosis cutis: its relationship to scleroderma. AMA Arch Derm. 1959 Jul;80(1):15–21. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1959.01560190017002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassim J. R., Connolly C. K. Treatment of calcinosis universalis with aluminium hydroxide. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Feb;45(239):118–121. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.239.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PASCALE L. R., DUBIN A., HOFFMAN W. S. Influence of benemid on urinary excretion of phosphate in hypoparathyroidism. Metabolism. 1954 Sep;3(5):462–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPURR C. L., FORD R. V., MOYER J. H. The effect of probenecid (benemid) on phosphate excretion and other metabolic processes. Am J Med Sci. 1954 Sep;228(3):256–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi A., Berczi I., Selye H. Inhibition by salicylates of various calcifying connective tissue reactions. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1969 Jan;177(1):211–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamp T. C., Stacey T. E. Evaluation of theoretical renal phosphorus threshold as an index of renal phosphorus handling. Clin Sci. 1970 Oct;39(4):505–516. doi: 10.1042/cs0390505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tumulty P. A. Topics in clinical medicine. Clinical synopsis of scleroderma, simulator of other diseases. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1968 Apr;122(4):236–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]