Abstract
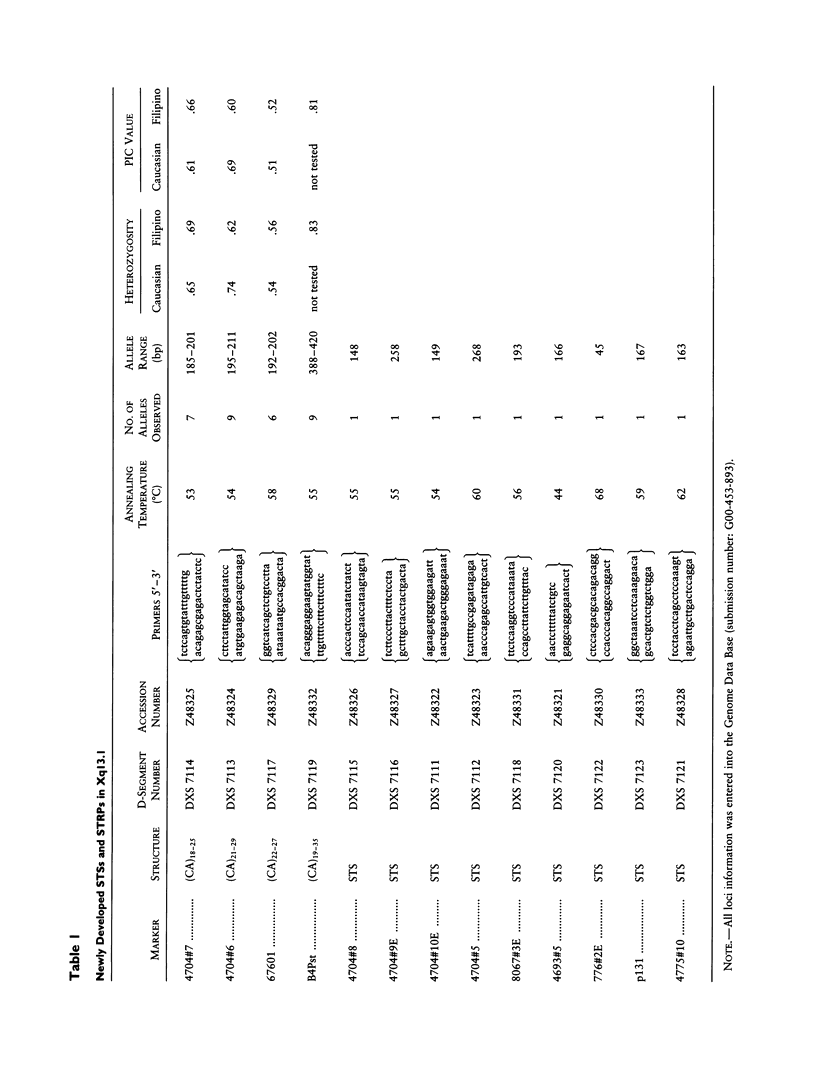
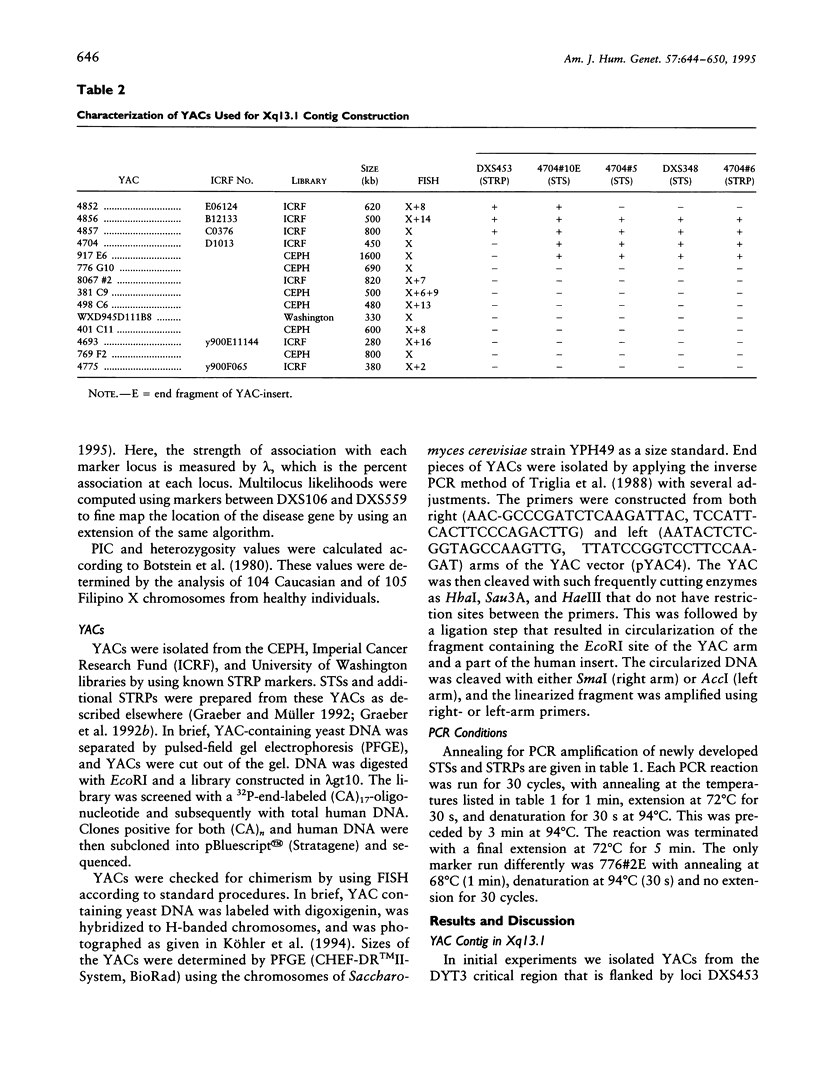
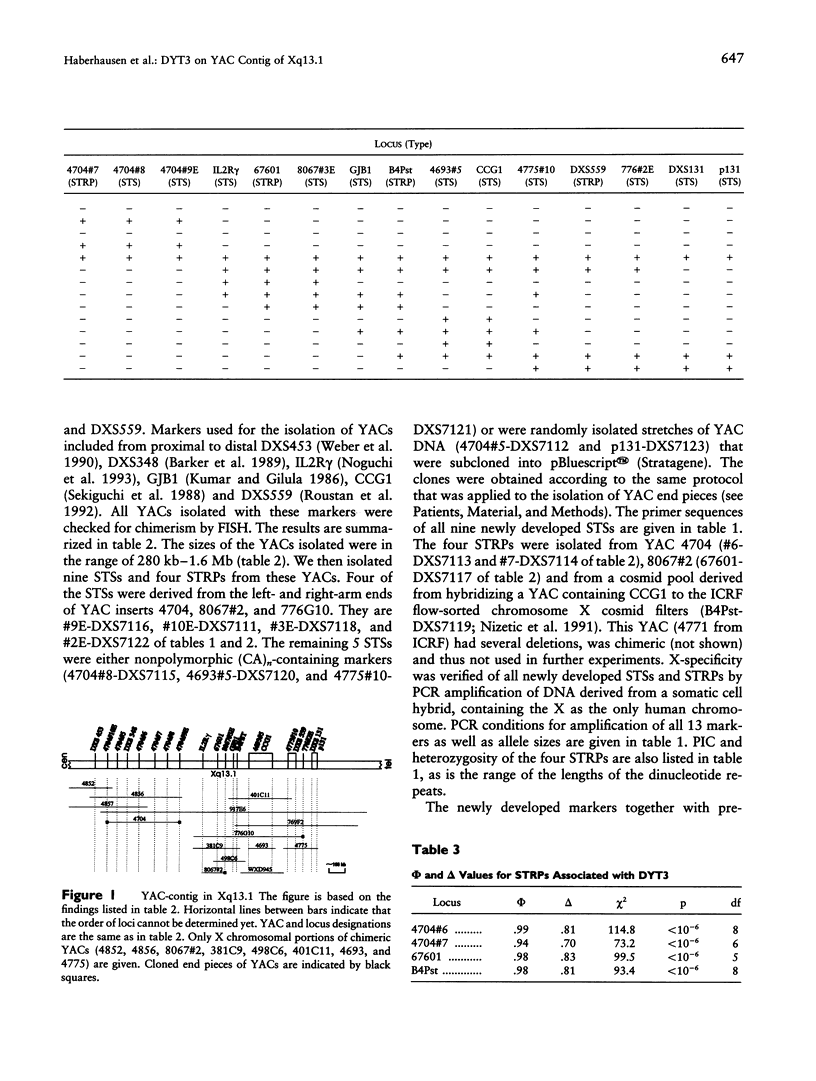
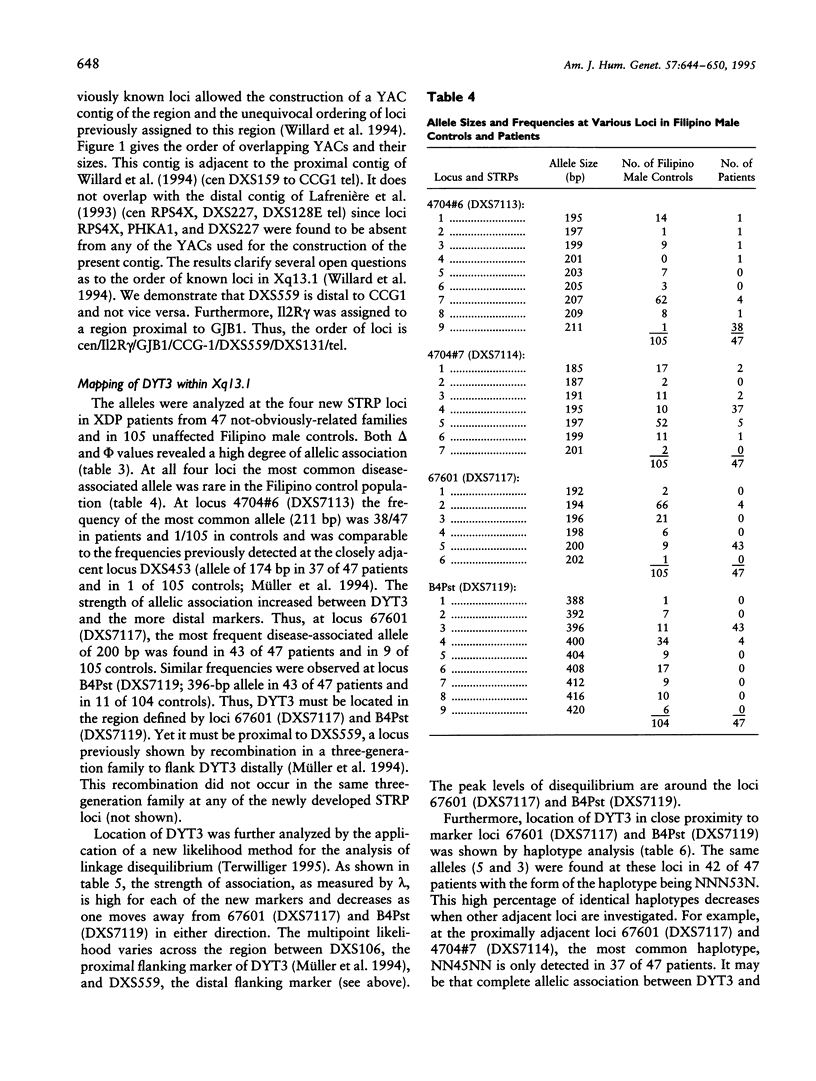
A YAC contig was constructed of Xq13.1 in order to sublocalize the X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism (XDP) syndrome locus, DYT3. The contig spans a region of approximately 1.8 Mb and includes loci DXS453/DXS348/IL2R gamma/GJB1/CCG1/DXS559. For the construction of the contig, nine sequence-tagged sites and four short tandem repeat polymorphisms (STRPs) were isolated. The STRPs, designated as 4704#6 (DXS7113), 4704#7 (DXS7114), 67601 (DXS7117), and B4Pst (DXS7119) were assigned to a region flanked by DXS348 proximally and by DXS559 distally. Their order was DXS348/4704 #6/4704 #7/67601/B4Pst/DXS559. They were applied to the analysis of allelic association and of haplotypes in 47 not-obviously-related XDP patients and in 105 Filipino male controls. The same haplotype was found at loci 67601 (DXS7117) and B4Pst (DXS7119) in 42 of 47 patients. This percentage of common haplotypes decreased at the adjacent loci. The findings, together with the previous demonstration of DXS559 being the distal flanking marker of DYT3, assign the disease locus to a small region in Xq13.1 defined by loci 67601 (DXS7117) and B4Pst (DXS7119). The location of DYT3 was born out by the application of a newly developed likelihood method for the analysis of linkage disequilibrium.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergoffen J., Scherer S. S., Wang S., Scott M. O., Bone L. J., Paul D. L., Chen K., Lensch M. W., Chance P. F., Fischbeck K. H. Connexin mutations in X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):2039–2042. doi: 10.1126/science.8266101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Buetow K. H., Antonarakis S. E., Waber P. G., Boehm C. D., Kazazian H. H. Nonuniform recombination within the human beta-globin gene cluster. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1239–1258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairweather N., Bell C., Cochrane S., Chelly J., Wang S., Mostacciuolo M. L., Monaco A. P., Haites N. E. Mutations in the connexin 32 gene in X-linked dominant Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMTX1) Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jan;3(1):29–34. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeber M. B., Kupke K. G., Müller U. Delineation of the dystonia-parkinsonism syndrome locus in Xq13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8245–8248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeber M. B., Monaco A. P., Chelly J., Müller U. Isolation of DNTR polymorphisms from yeast artificial chromosomes encompassing X chromosomal loci PGK1 and DXS56. Hum Genet. 1992 Nov;90(3):270–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00220077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeber M. B., Müller U. The X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism syndrome (XDP): clinical and molecular genetic analysis. Brain Pathol. 1992 Oct;2(4):287–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1992.tb00706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisatake K., Hasegawa S., Takada R., Nakatani Y., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. The p250 subunit of native TATA box-binding factor TFIID is the cell-cycle regulatory protein CCG1. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):179–181. doi: 10.1038/362179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I., Sistonen P., Weaver A., Lander E. Linkage disequilibrium mapping in isolated founder populations: diastrophic dysplasia in Finland. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):204–211. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar N. M., Gilula N. B. Cloning and characterization of human and rat liver cDNAs coding for a gap junction protein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):767–776. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupke K. G., Graeber M. B., Müller U. Dystonia-parkinsonism syndrome (XDP) locus: flanking markers in Xq12-q21.1. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Apr;50(4):808–815. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupke K. G., Lee L. V., Müller U. Assignment of the X-linked torsion dystonia gene to Xq21 by linkage analysis. Neurology. 1990 Sep;40(9):1438–1442. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.9.1438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler A., Hain J., Müller U. Familial half cryptic translocation t(9;17). J Med Genet. 1994 Sep;31(9):712–714. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.9.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafrenière R. G., Brown C. J., Rider S., Chelly J., Taillon-Miller P., Chinault A. C., Monaco A. P., Willard H. F. 2.6 Mb YAC contig of the human X inactivation center region in Xq13: physical linkage of the RPS4X, PHKA1, XIST and DXS128E genes. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1105–1115. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. V., Kupke K. G., Caballar-Gonzaga F., Hebron-Ortiz M., Müller U. The phenotype of the X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism syndrome. An assessment of 42 cases in the Philippines. Medicine (Baltimore) 1991 May;70(3):179–187. doi: 10.1097/00005792-199105000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Lin C., Srinidhi L., Bates G., Altherr M., Whaley W. L., Lehrach H., Wasmuth J., Gusella J. F. Complex patterns of linkage disequilibrium in the Huntington disease region. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):723–734. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Haberhausen G., Wagner T., Fairweather N. D., Chelly J., Monaco A. P. DXS106 and DXS559 flank the X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism syndrome locus (DYT3). Genomics. 1994 Sep 1;23(1):114–117. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nizetić D., Zehetner G., Monaco A. P., Gellen L., Young B. D., Lehrach H. Construction, arraying, and high-density screening of large insert libraries of human chromosomes X and 21: their potential use as reference libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3233–3237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi M., Yi H., Rosenblatt H. M., Filipovich A. H., Adelstein S., Modi W. S., McBride O. W., Leonard W. J. Interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain mutation results in X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency in humans. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90167-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roustan P., Curtis A. R., Kamakari S., Thiselton D., Lindsay S., Bhattacharya S. S. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the DXS559 locus. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Dec;1(9):778–778. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.9.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert S., Wang E. H., Tjian R. Cloning and expression of human TAFII250: a TBP-associated factor implicated in cell-cycle regulation. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):175–179. doi: 10.1038/362175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi T., Miyata T., Nishimoto T. Molecular cloning of the cDNA of human X chromosomal gene (CCG1) which complements the temperature-sensitive G1 mutants, tsBN462 and ts13, of the BHK cell line. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1683–1687. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02996.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger J. D. A powerful likelihood method for the analysis of linkage disequilibrium between trait loci and one or more polymorphic marker loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Mar;56(3):777–787. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triglia T., Peterson M. G., Kemp D. J. A procedure for in vitro amplification of DNA segments that lie outside the boundaries of known sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):8186–8186. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.8186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., Kwitek A. E., May P. E., Polymeropoulos M. H., Ledbetter S. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms at the DXS453, DXS454 and DXS458 loci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4037–4037. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


