Abstract
Mutants with enhanced β-lactam resistance were selected from strains of Enterobacter cloacae and E. aerogenes by using three antibiotics. High-level β-lactamase-producing mutants had similar degrees of increased resistance, enzyme substrate profiles, and isoelectric (pI) values irrespective of the selective agent. Reverse mutants from a resistant E. cloacae mutant regained the susceptibility pattern originally exhibited by the wild type, or were of enhanced susceptibility, and no longer expressed increased β-lactamase production. β-Lactamases of the mutants were similar in pI values to the wild-type enzyme. The increased resistance of the mutants therefore appeared to be accounted for by increased β-lactamase production.
Full text
PDF

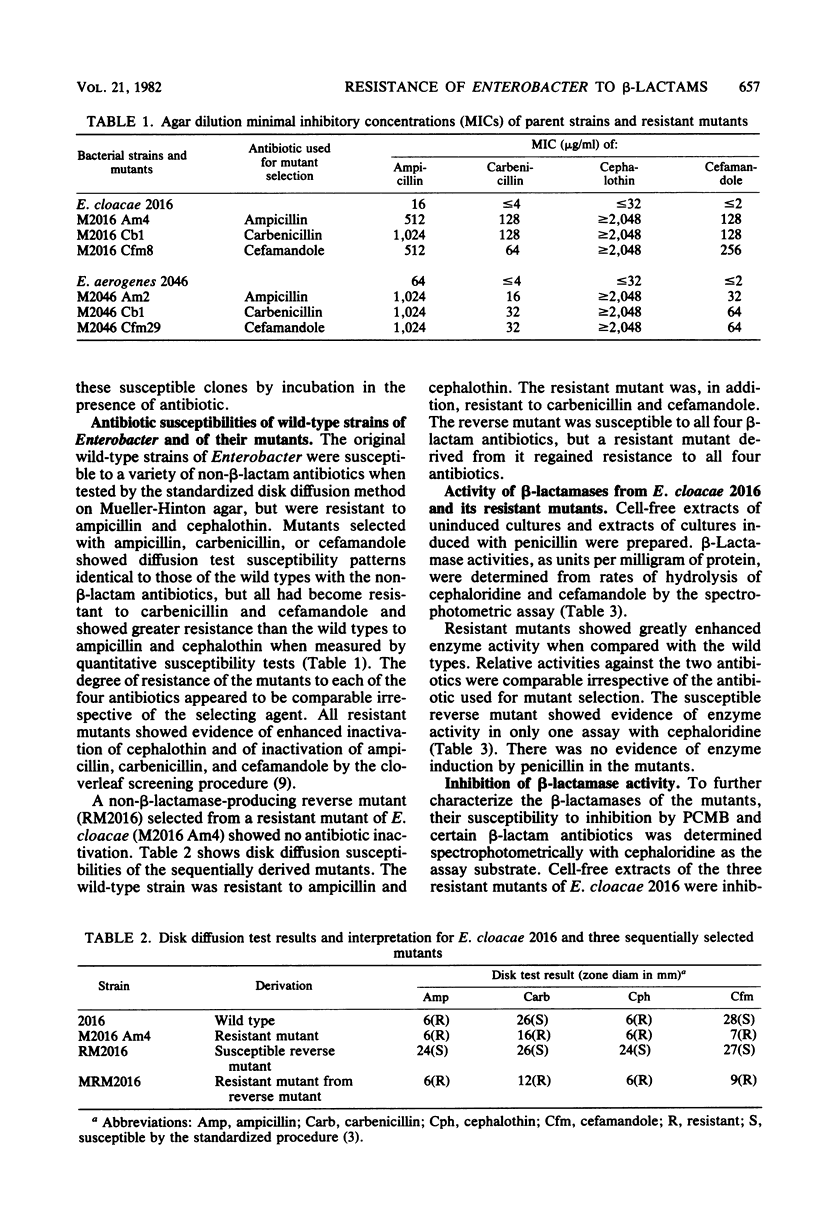
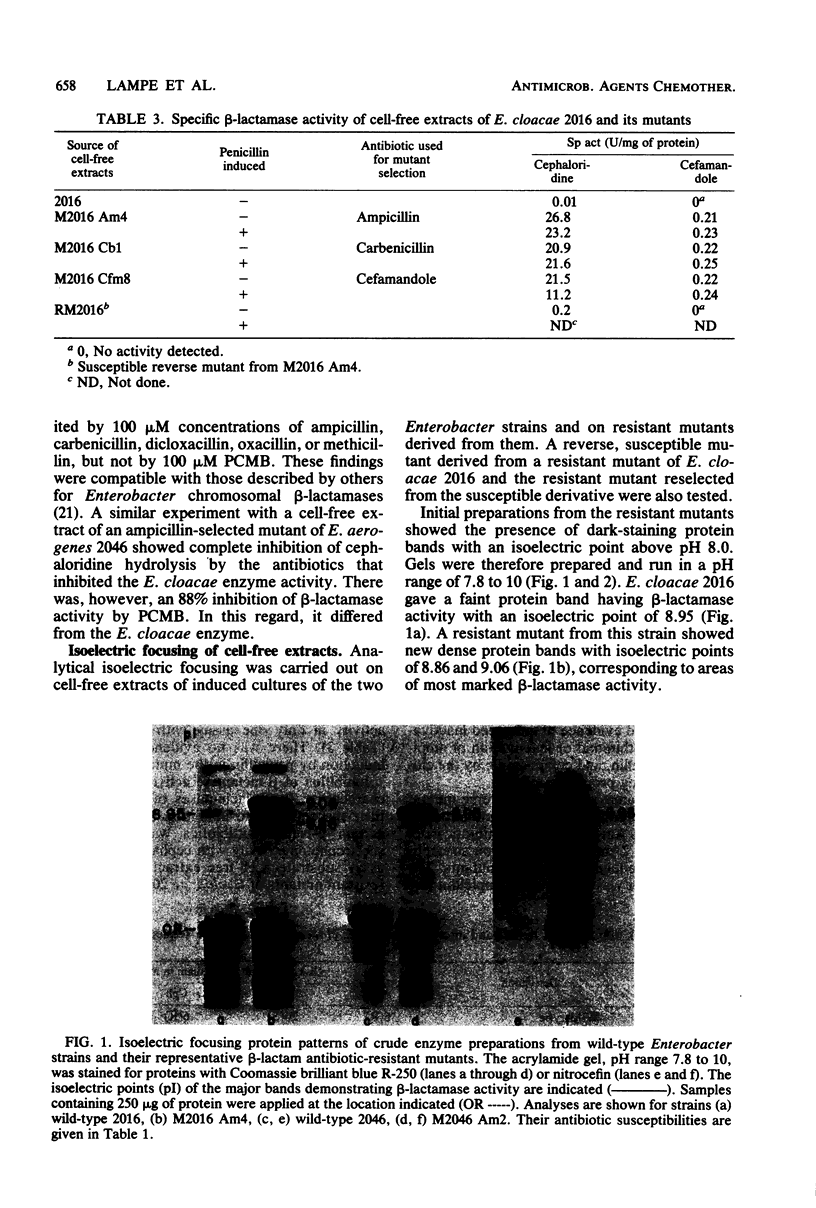


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan B. J., Kirk J., White T. T. Alteration of human pancreatic secretions by pancreatic and ampullary carcinoma. A computer-aided analysis of isoelectric focusing patterns. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Dec 29;85(4):1239–1246. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson H. M., Sherris J. C. Antibiotic sensitivity testing. Report of an international collaborative study. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;217(Suppl):1+–1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEMING P. C., GOLDNER M., GLASS D. G. Observations on the nature, distribution, and significance of cephalosporinase. Lancet. 1963 Jun 29;1(7296):1399–1401. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findell C. M., Sherris J. C. Susceptibility of Enterobacter to cefamandole: evidence for a high mutation rate to resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):970–974. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldner M., Glass D. G., Fleming P. C. Spontaneous mutant with loss of beta-lactamase in Aerobacter cloacae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):961–961. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.961-.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessey T. D. Inducible beta-lactamase in Enterobacter. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Nov;49(2):277–285. doi: 10.1099/00221287-49-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack G. W., Richmond M. H. A comparative study of eight distinct beta-lactamases synthesized by gram-negative bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Apr;61(1):43–61. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe M. F., Minshew B. H., Sherris J. C. In vitro response of Enterobacter to ampicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Oct;16(4):458–462. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.4.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami S., Yotsuji A., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Induction of beta-lactamase by various beta-lactam antibiotics in Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Sep;18(3):382–385. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.3.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Winshell E. B. Relation of beta-lactamase activity and cellular location to resistance of Enterobacter to penicillins and cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Feb;1(2):107–111. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.2.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Muggleton P. W., Ross G. W. Effects of beta-lactamase from gram-negative organisms on cephalosporins and penicillins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1968;8:57–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. L., Turner J. R., Mahoney D. F. Lack of correlation between beta-lactamase production and susceptibility to cefamandole or cefoxitin among spontaneous mutants of Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jan;15(1):14–19. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. W., O'Callaghan C. H. Beta-lactamase assays. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:69–85. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Emergence of resistance to cefamandole: possible role of cefoxitin-inducible beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jun;15(6):792–797. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.6.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Matthew M. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their role in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Jun;2(2):115–157. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterworth P. M., Emmerson A. M. Dissociated resistance among cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):497–503. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]