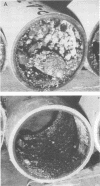
Abstract
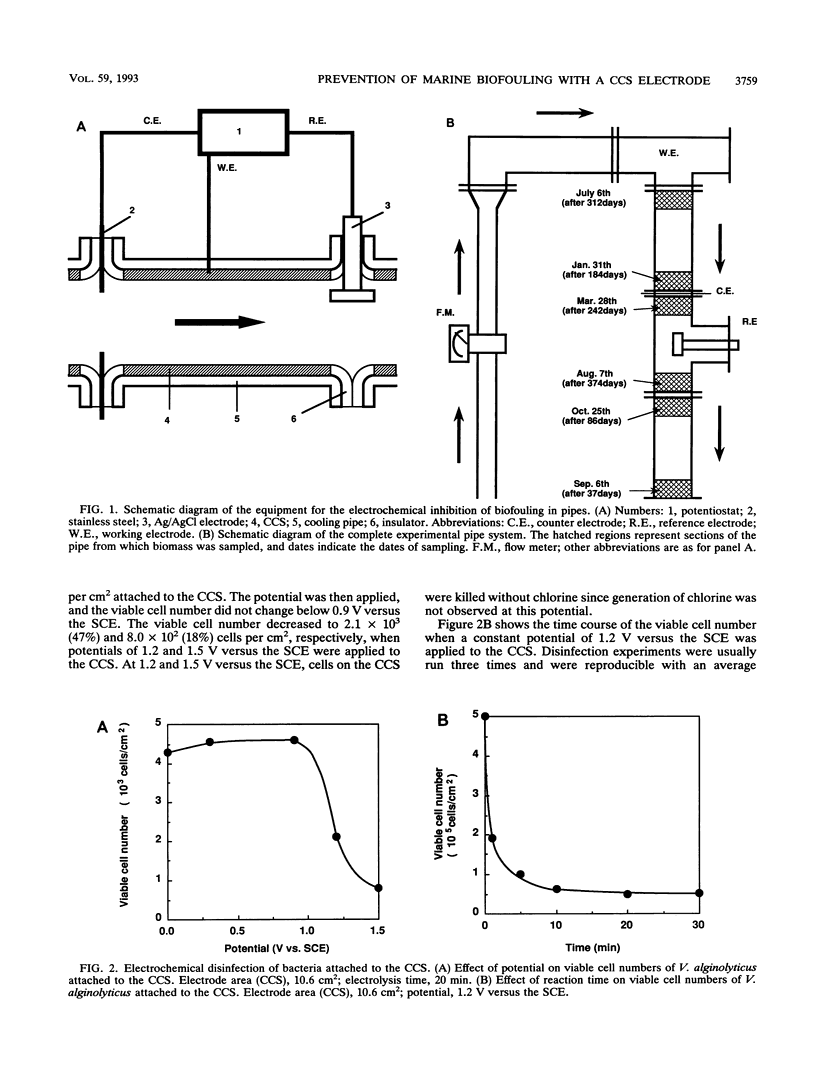
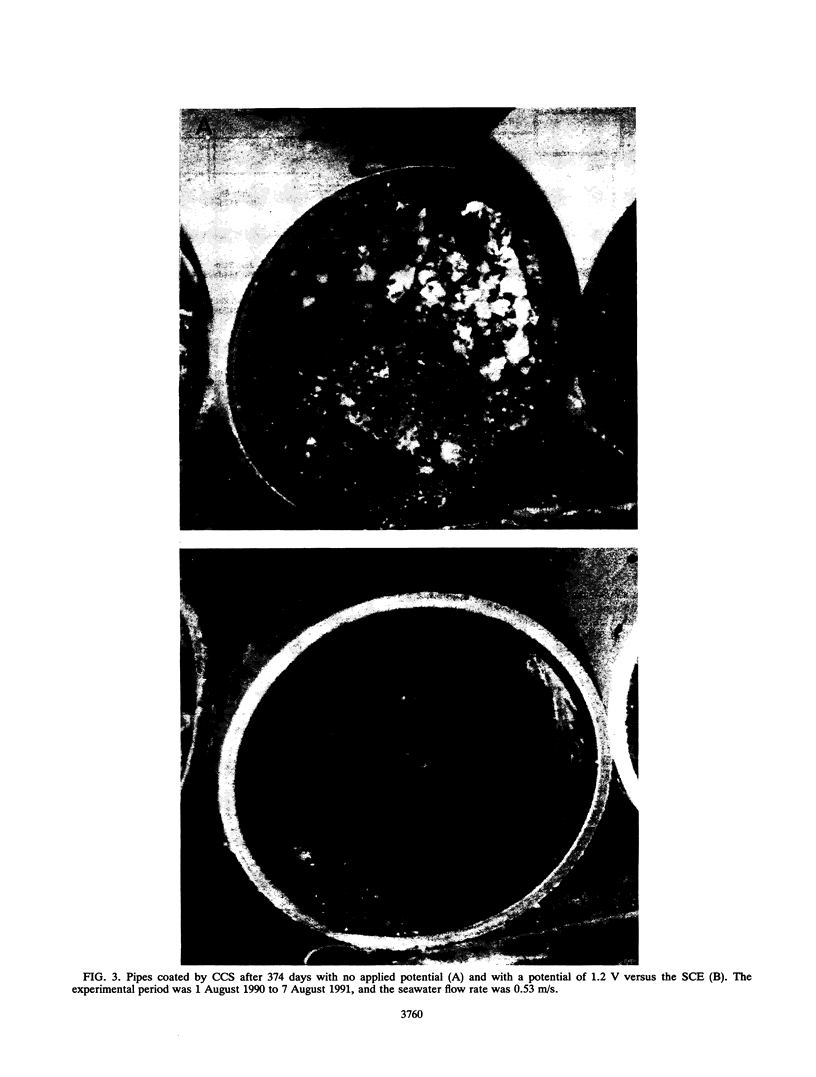
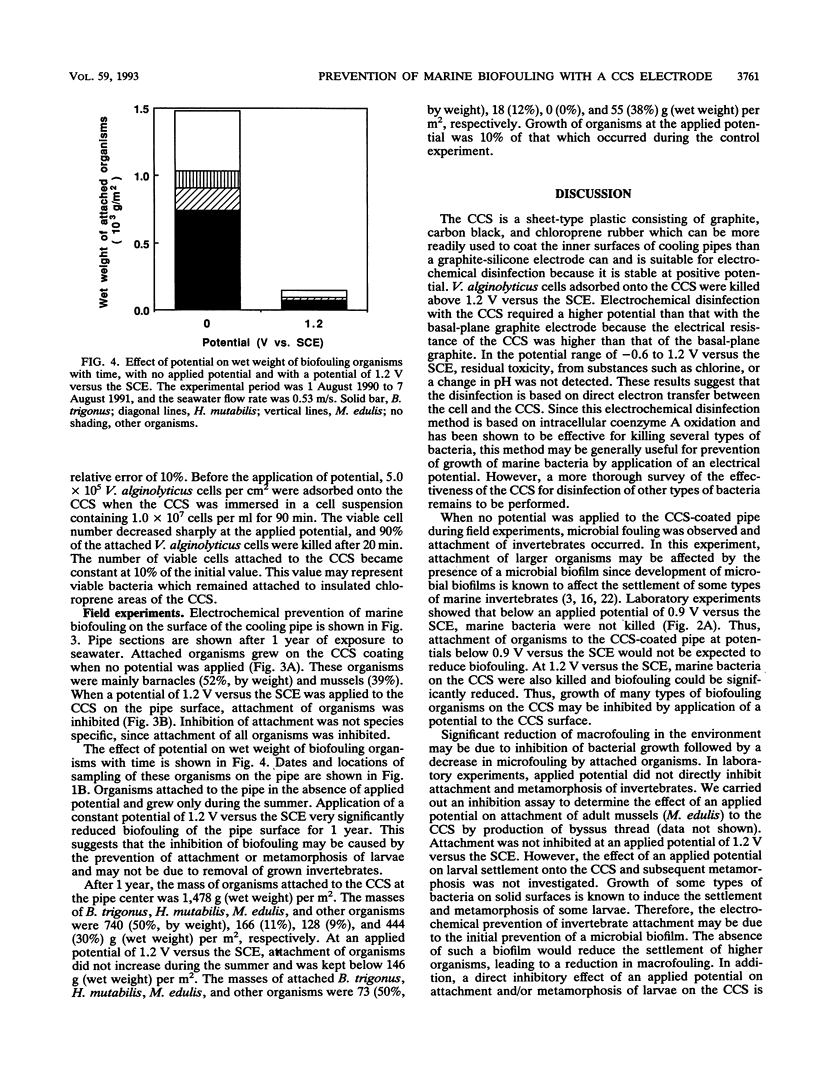
A carbon-chloroprene sheet (CCS) electrode was used for the electrochemical disinfection of the marine gram-negative bacterium Vibrio alginolyticus. When the electrode was incubated in seawater containing 105 cells per ml for 90 min, the amount of adsorbed cells was 4.5 × 103 cells per cm2. When a potential of 1.2 V versus a saturated calomel electrode was applied to the CCS for 20 min, 67% of adsorbed cells were killed. This disinfection was due to the direct electrochemical oxidation of cells and not to a change in pH or to the generation of toxic substances, such as chlorine. In a 1-year field experiment, marine biofouling of a CCS-coated cooling pipe caused by attachment of bacteria and invertebrates was considerably reduced by application of a potential of 1.2 V versus a saturated calomel electrode. Since this method requires low potential electrical energy, use of a CCS coating appears to be a suitable method for the clean prevention of marine biofouling.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger T. J., Spadaro J. A., Chapin S. E., Becker R. O. Electrically generated silver ions: quantitative effects on bacterial and mammalian cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Feb;9(2):357–358. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood-Sears V., Gordon A. S. Copper-induced production of copper-binding supernatant proteins by the marine bacterium Vibrio alginolyticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1327–1332. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1327-1332.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga T., Nakasono S., Masuda S. Electrochemical sterilization of bacteria absorbed on granular activated carbon. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Jun 15;72(3):255–259. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90471-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga T., Nakasono S., Takamuku T., Burgess J. G., Nakamura N., Sode K. Disinfection of drinking water by using a novel electrochemical reactor employing carbon-cloth electrodes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):686–689. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.686-689.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga T., Namba Y. Detection of microbial cells by cyclic voltammetry. Anal Chem. 1984 Apr;56(4):798–801. doi: 10.1021/ac00268a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]