Abstract
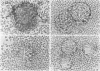
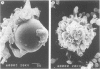
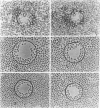
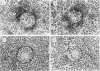
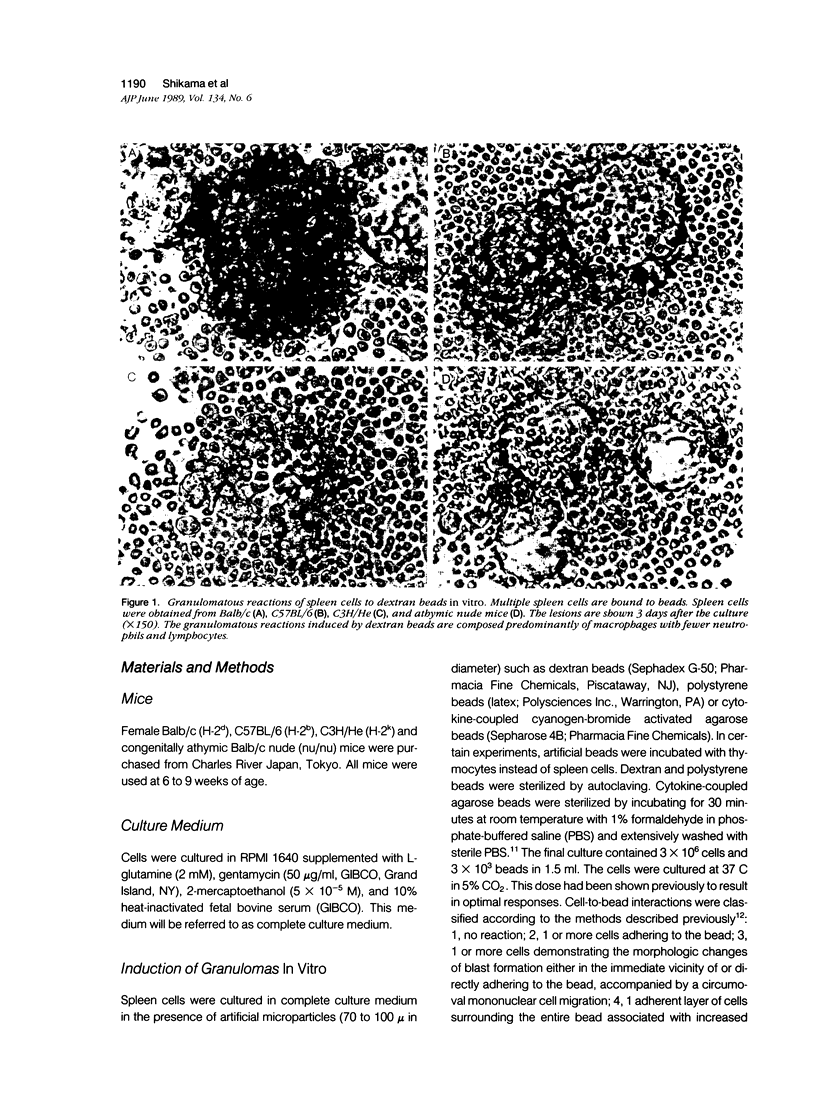
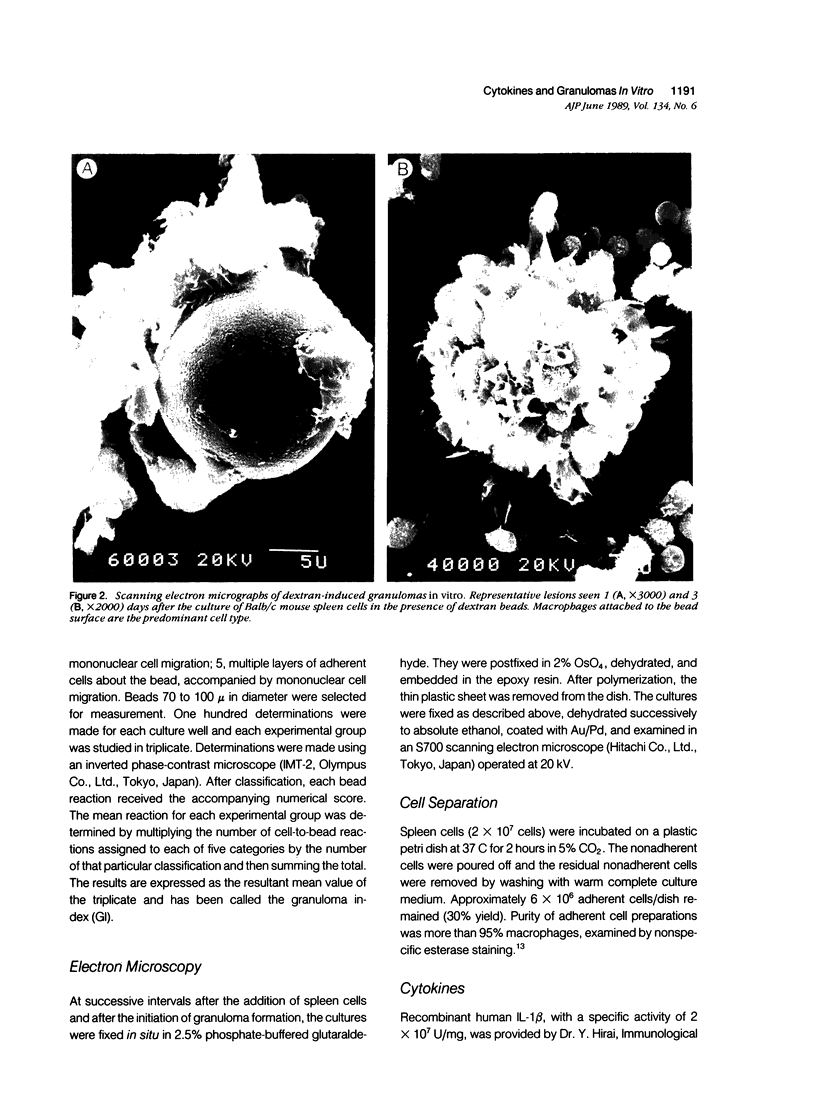
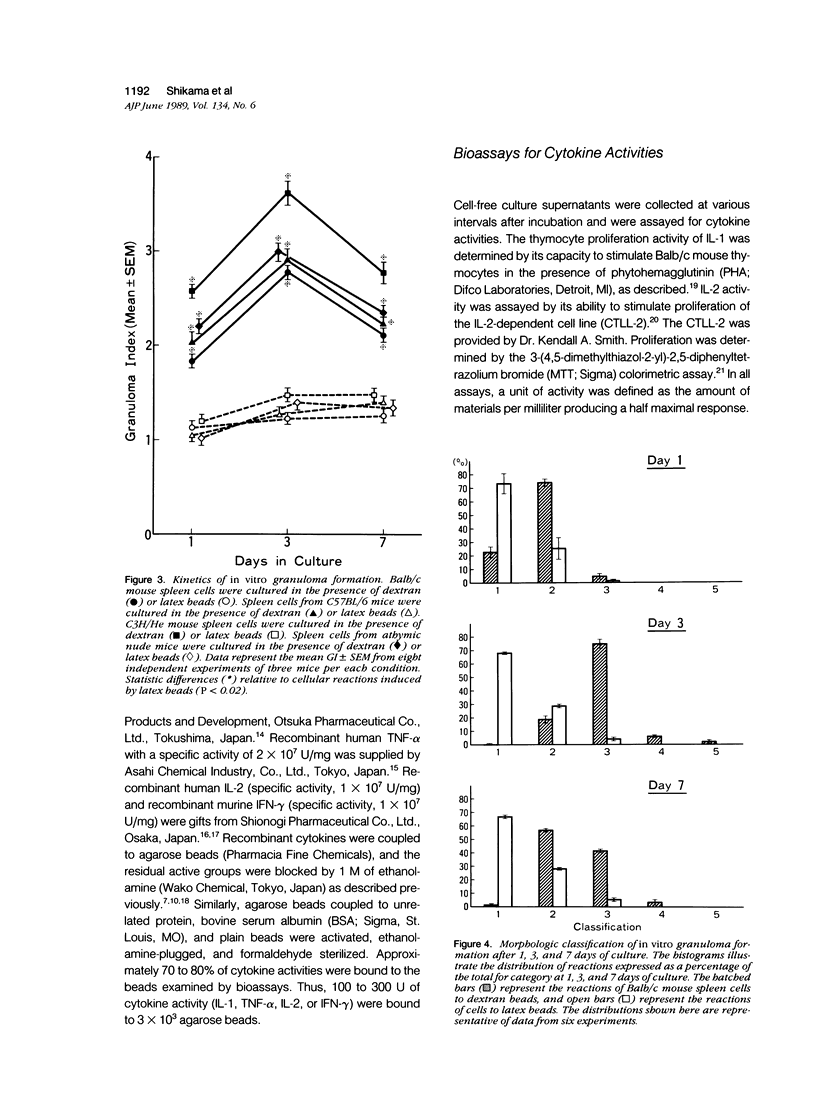
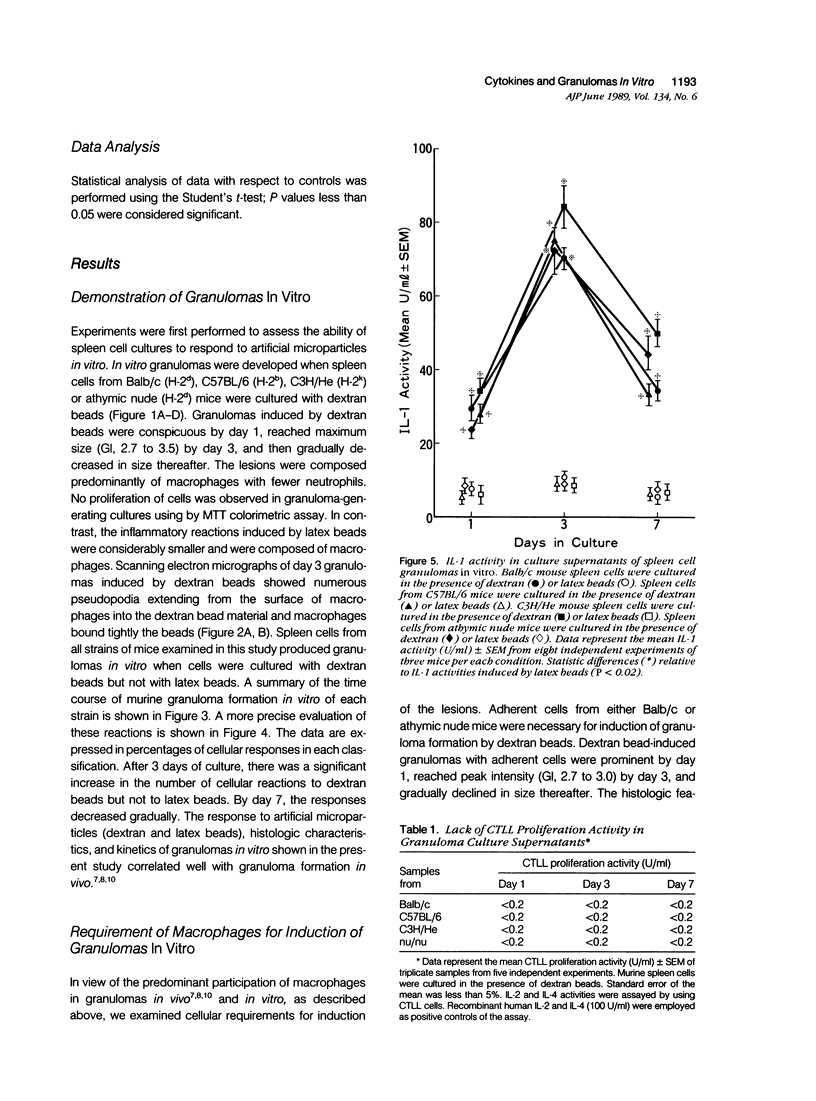
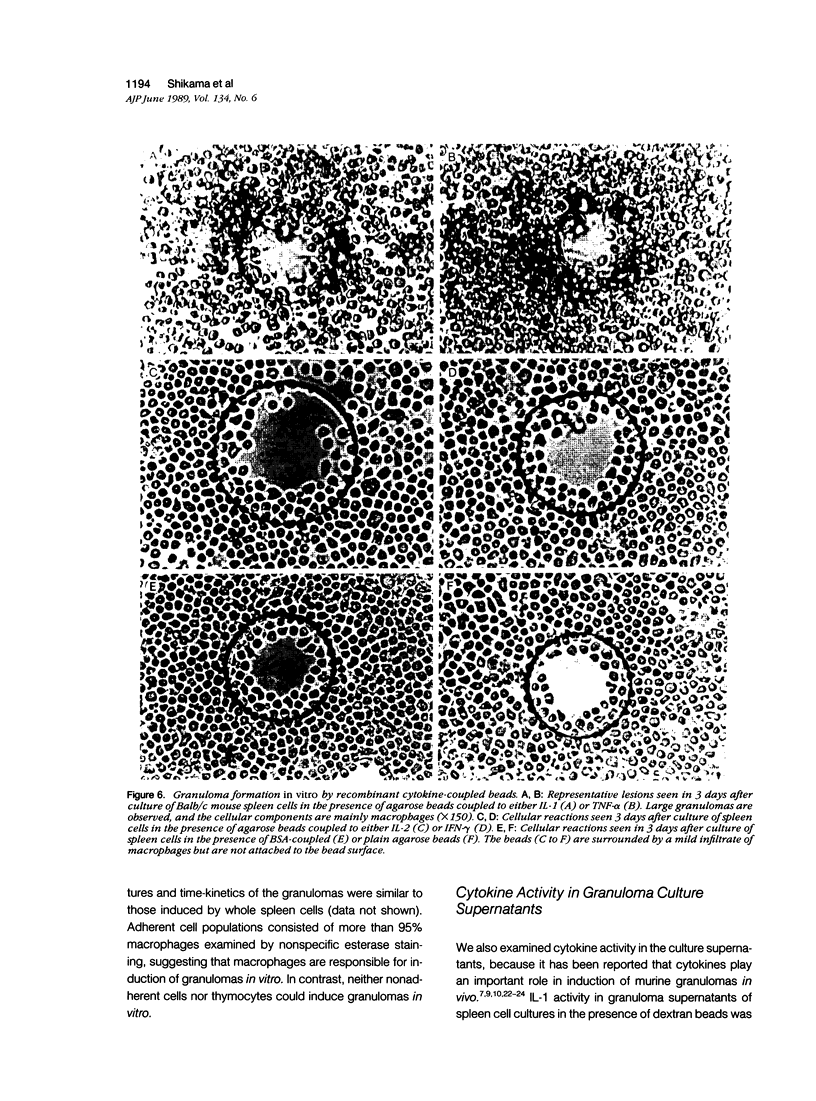
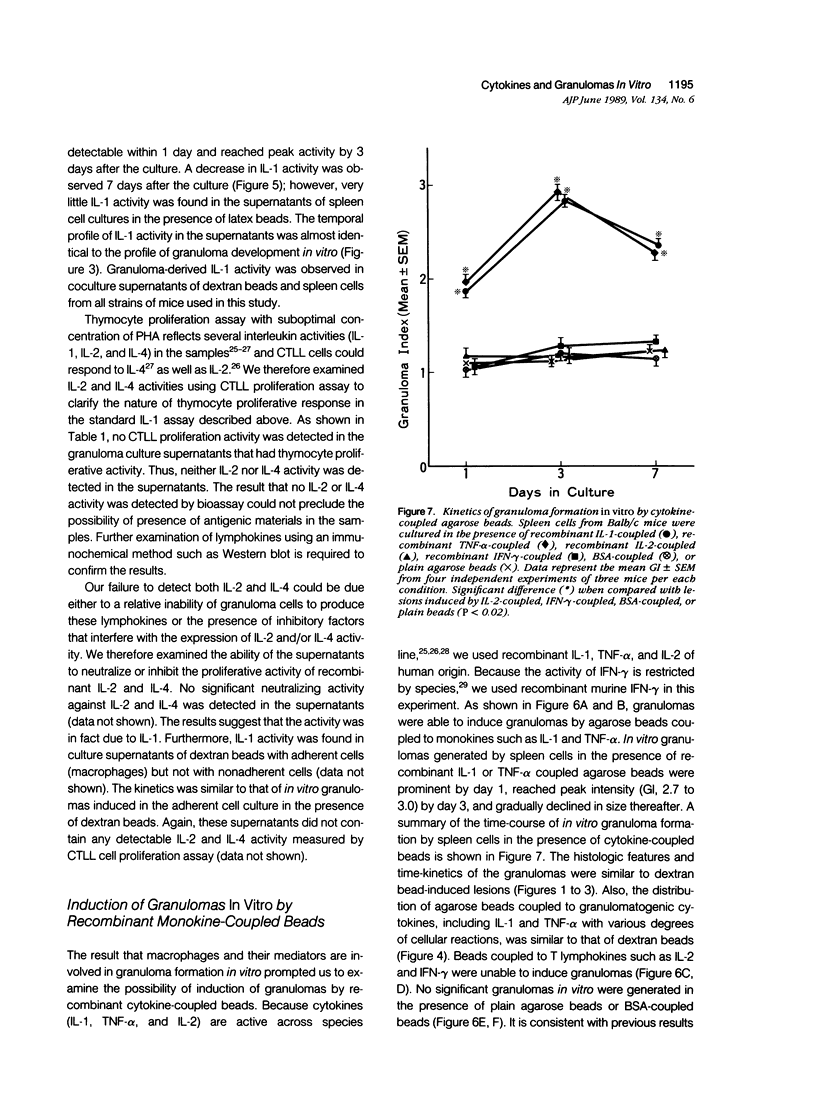
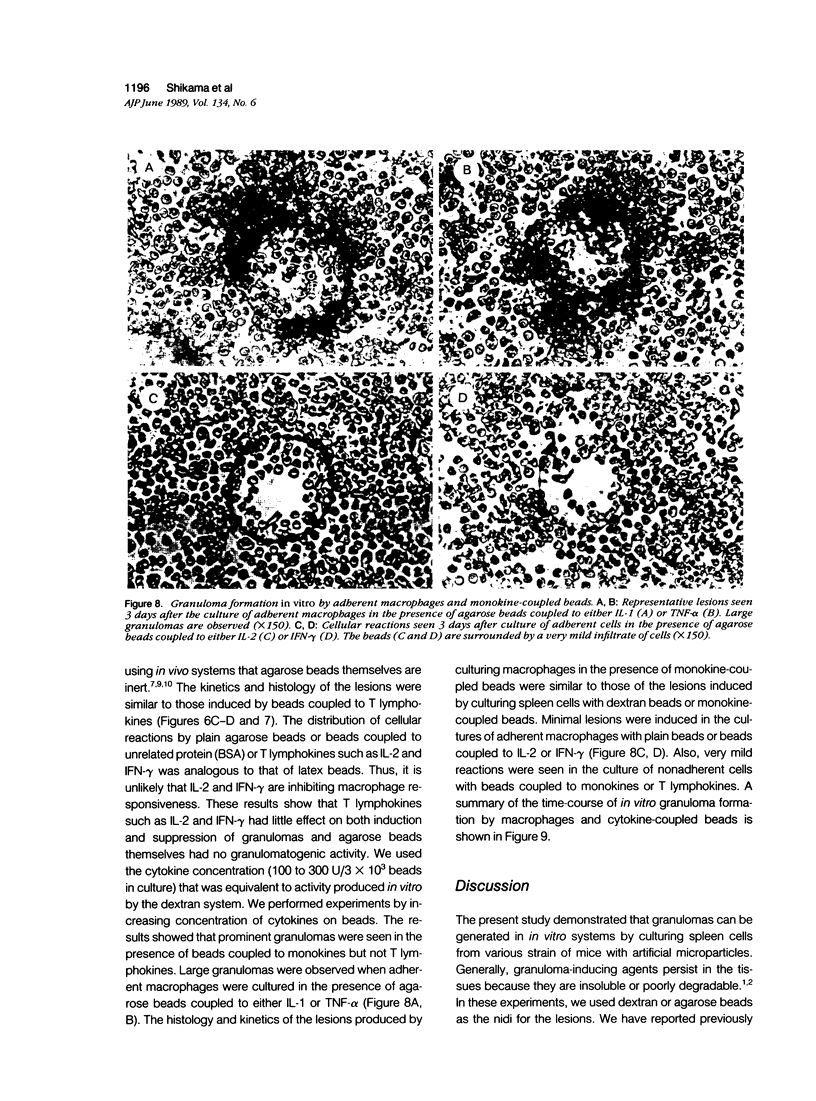
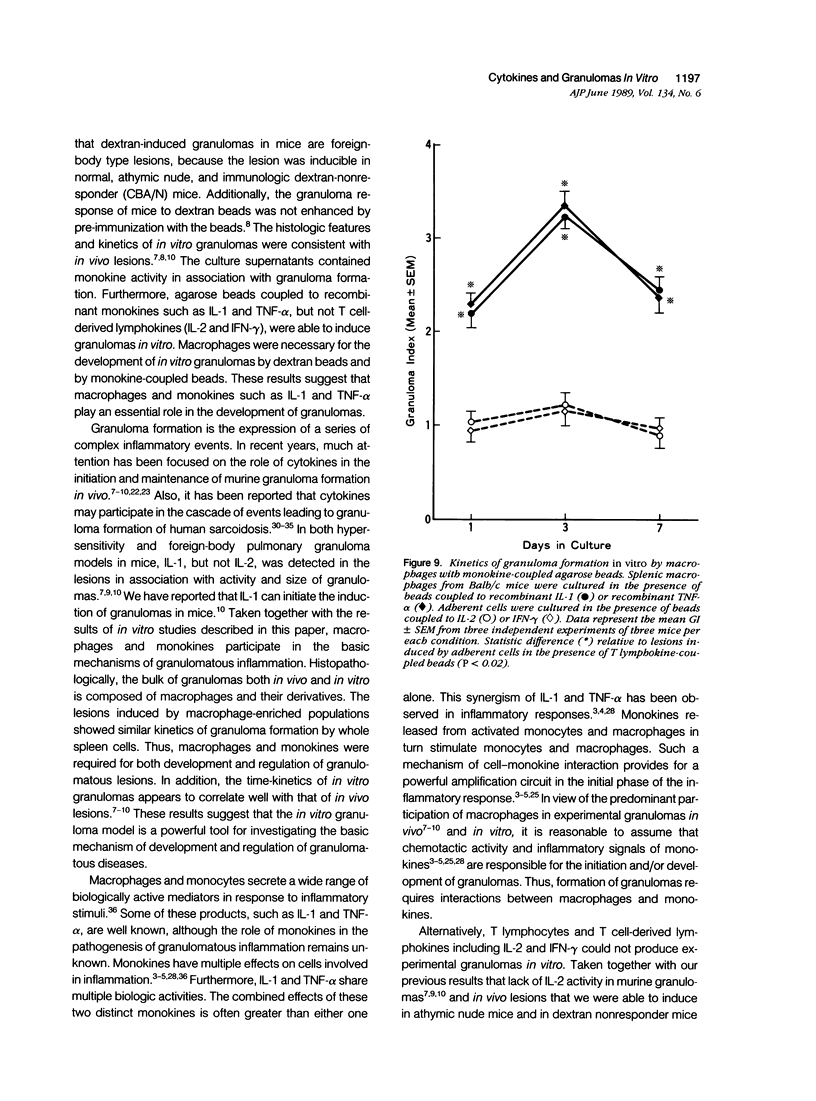
To investigate the basic mechanisms of granuloma formation, in vitro granulomas were induced by culturing murine spleen cells in the presence of artificial microparticles. Large granulomas developed around dextran beads. The lesions were inducible by spleen cells from either normal mice or athymic nude mice. Minimal inflammation was produced around latex beads. The histologic features and time kinetics of granulomas in vitro. Culture supernatants of dextran induced granulomas contained high levels of interleukin-1 (IL-1) activity but not interleukin-2 (IL-2) or interleukin-4 (IL-4) activity. IL-1 activity was correlated with granuloma size. Additionally, granulomas were produced by culturing spleen cells in the presence of agarose beads coupled to recombinant IL-1 or recombinant tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). Granulomatous lesions also were induced by macrophage-enriched populations in the presence of monokine-coupled beads. Adherent macrophages, but not nonadherent cells, were required for induction of granulomas in vitro. In contrast, very small lesions were seen when spleen cells or adherent cells were cultured in the presence of beads coupled to recombinant IL-2 or recombinant interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). These results suggest that macrophages and monokines such as IL-1 and TNF-alpha play an essential role in granuloma formation in vitro.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O. The granulomatous inflammatory response. A review. Am J Pathol. 1976 Jul;84(1):164–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allred D. C., Kobayashi K., Yoshida T. Anergy-like immunosuppression in mice bearing pulmonary foreign-body granulomatous inflammation. Am J Pathol. 1985 Dec;121(3):466–473. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachwich P. R., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Larrick J., Spengler M., Kunkel S. L. Tumor necrosis factor production by human sarcoid alveolar macrophages. Am J Pathol. 1986 Dec;125(3):421–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilosi M., Menestrina F., Capelli P., Montagna L., Lestani M., Pizzolo G., Cipriani A., Agostini C., Trentin L., Zambello R. Immunohistochemical analysis of sarcoid granulomas. Evaluation of Ki67+ and interleukin-1+ cells. Am J Pathol. 1988 May;131(2):191–198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Biology of interleukin 1. FASEB J. 1988 Feb;2(2):108–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Mier J. W. Lymphokines. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 8;317(15):940–945. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710083171506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doughty B. L., Phillips S. M. Delayed hypersensitivity granuloma formation around Schistosoma mansoni eggs in vitro. I. Definition of the model. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):30–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott D. E., Righthand V. F., Boros D. L. Characterization of regulatory (interferon-alpha/beta) and accessory (LAF/IL 1) monokine activities from liver granuloma macrophages of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2653–2662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghetie V., Mota G., Sjöquist J. Separation of cells by affinity chromatography on SpA-sepharose 6MB. J Immunol Methods. 1978;21(1-2):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90230-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock W. W., Kobzik L., Colby A. J., O'Hara C. J., Cooper A. G., Godleski J. J. Detection of lymphokines and lymphokine receptors in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Immunohistologic evidence that inflammatory macrophages express IL-2 receptors. Am J Pathol. 1986 Apr;123(1):1–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W. Release of interleukin-1 by alveolar macrophages of patients with active pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Apr;129(4):569–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara K., Kobayashi K., Shikama Y., Yoneya I., Soezima K., Ide H., Takahashi T. Direct evidence for granuloma-inducing activity of interleukin-1. Induction of experimental pulmonary granuloma formation in mice by interleukin-1-coupled beads. Am J Pathol. 1988 Mar;130(3):629–638. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Allred C., Castriotta R., Yoshida T. Strain variation of bacillus Calmette-Guerin-induced pulmonary granuloma formation is correlated with anergy and the local production of migration inhibition factor and interleukin 1. Am J Pathol. 1985 May;119(2):223–235. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Allred C., Cohen S., Yoshida T. Role of interleukin 1 in experimental pulmonary granuloma in mice. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):358–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Allred C., Yoshida T. Mechanisms of suppressed cell-mediated immunity and impaired antigen-induced interleukin 2 production in granuloma-bearing mice. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):2996–3003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai K., Itoh K., Hinuma S., Tada M. Pretreatment of plastic Petri dishes with fetal calf serum. A simple method for macrophage isolation. J Immunol Methods. 1979;29(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):234–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March C. J., Mosley B., Larsen A., Cerretti D. P., Braedt G., Price V., Gillis S., Henney C. S., Kronheim S. R., Grabstein K. Cloning, sequence and expression of two distinct human interleukin-1 complementary DNAs. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):641–647. doi: 10.1038/315641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. J., Shneyour A., Kook A. I. Enhancement of DNA synthesis and cAMP content of mouse thymocytes by mediator(s) derived from adherent cells. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1466–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkston P., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Spontaneous release of interleukin-2 by lung T lymphocytes in active pulmonary sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 1983 Apr 7;308(14):793–800. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198304073081401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson B. W., McLemore T. L., Crystal R. G. Gamma interferon is spontaneously released by alveolar macrophages and lung T lymphocytes in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1488–1495. doi: 10.1172/JCI111852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai T., Yamaguchi H., Ito H., Todd C. W., Wallace R. B. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene for human tumour necrosis factor. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):803–806. doi: 10.1038/313803a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sideras P., Noma T., Honjo T. Structure and function of interleukin 4 and 5. Immunol Rev. 1988 Feb;102:189–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00745.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Ruscetti F. W. T-cell growth factor and the culture of cloned functional T cells. Adv Immunol. 1981;31:137–175. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60920-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki R., Suzuki S., Igarashi M., Kumagai K. Induction of interleukin 3 but not interleukin 2 or interferon production in the syngeneic mixed lymphocyte reaction. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1564–1572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Matsui H., Fujita T., Takaoka C., Kashima N., Yoshimoto R., Hamuro J. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for human interleukin-2. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):305–310. doi: 10.1038/302305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]