Abstract
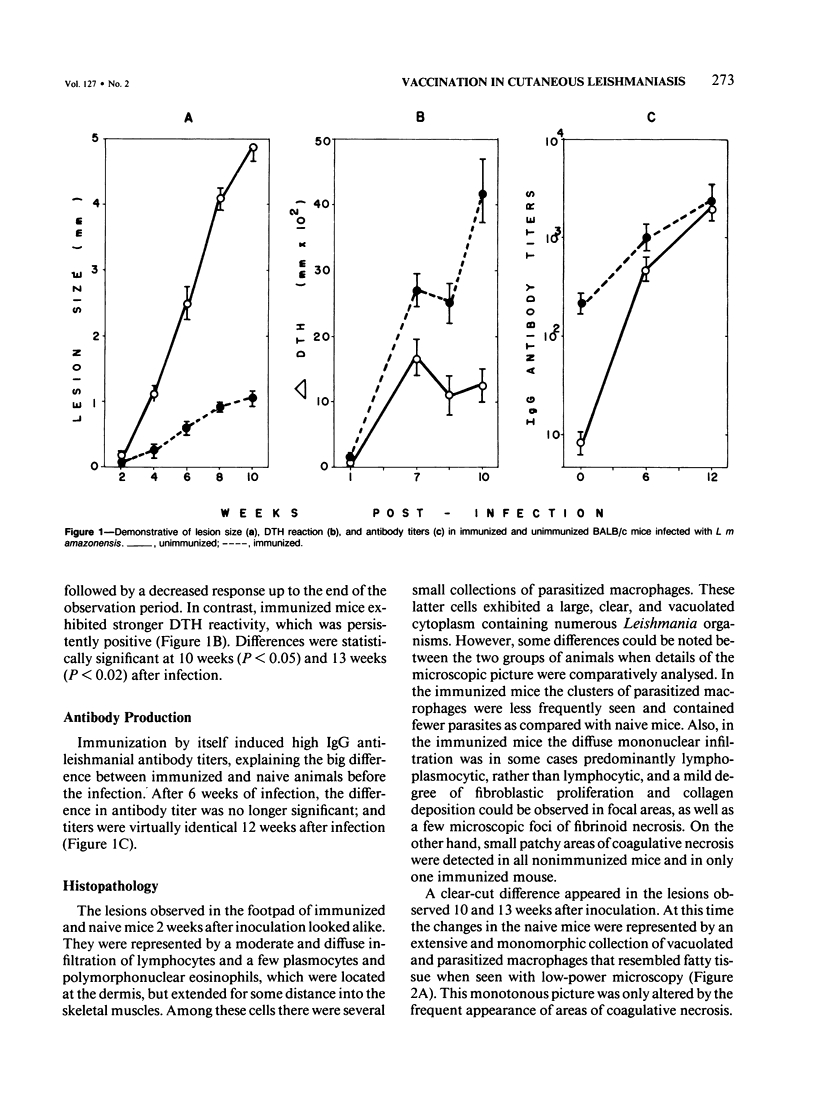
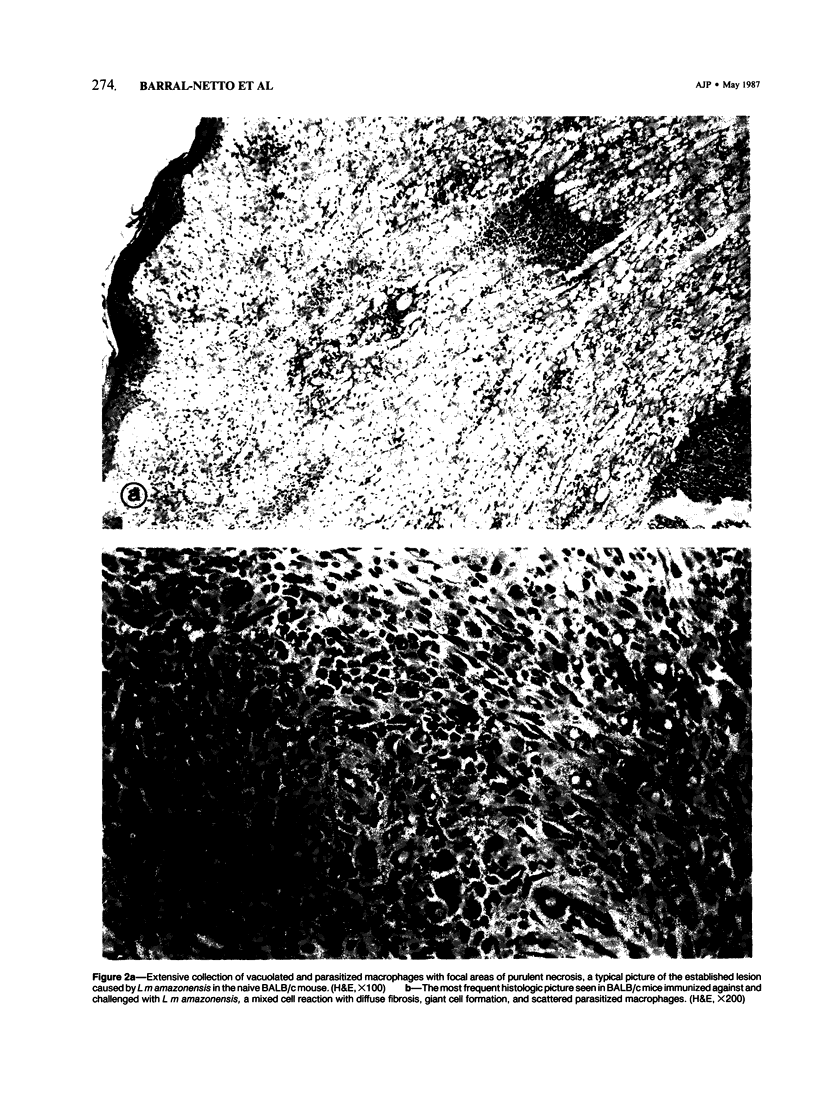
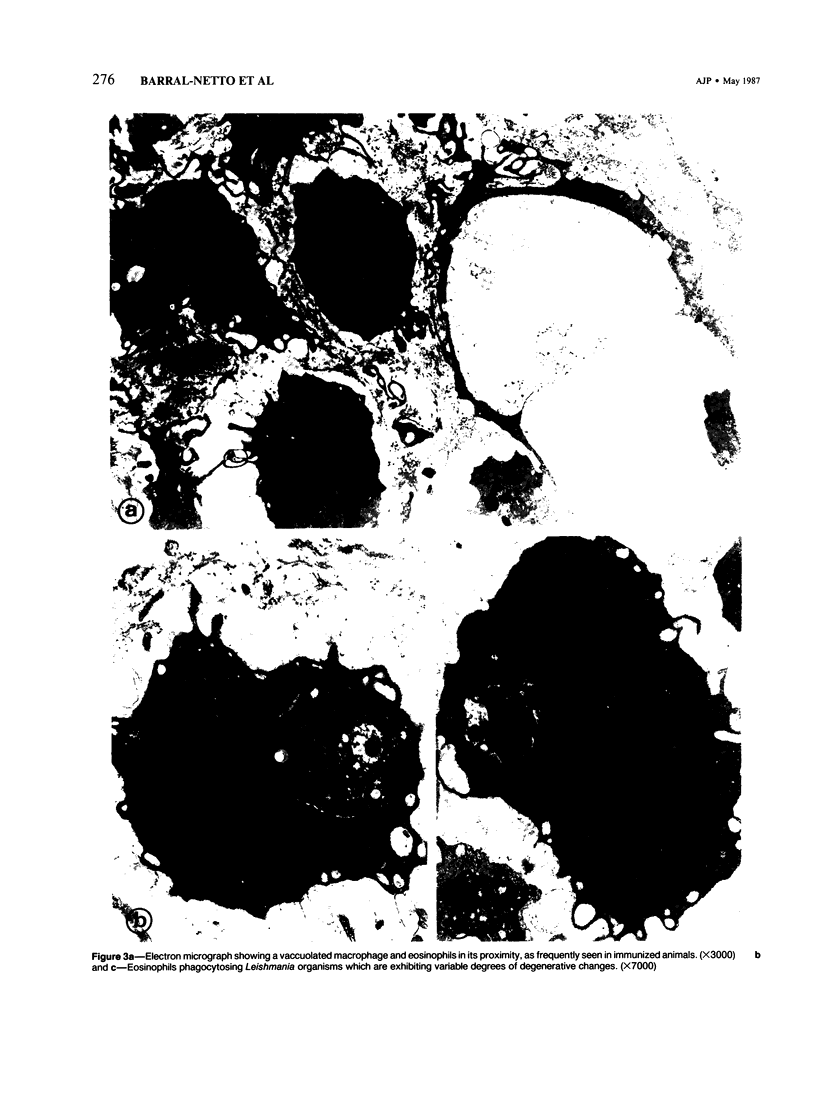
Highly susceptible BALB/c mice became partially resistant to Leishmania mexicana amazonensis infection after intravenous immunization with solubilized homologous promastigote antigen. Immunized BALB/c mice exhibited mixed mononuclear cell reactions, with granulomatous inflammation, collagen deposition, and fibrinoid necrosis at the site of infection. In contrast, naive animals displayed a monomorphic picture composed of largely vacuolated and parasitized macrophages with areas of coagulative necrosis. Electron microscopy revealed an increased number of eosinophils, sometimes in close contact with parasitized macrophages, in immunized animals. These findings illustrate that histologic changes reflect host immune status in cutaneous leishmaniasis, and that susceptibility of BALB/c mice to L m amazonensis, although dependent on genetic background, can be artificially modified.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J., Kaye P. M. Immunoregulatory pathways in murine leishmaniasis: different regulatory control during Leishmania mexicana mexicana and Leishmania major infections. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Sep;61(3):674–682. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade Z. A., Reed S. G., Roters S. B., Sadigursky M. Immunopathology of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jan;114(1):137–148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barral A., Petersen E. A., Sacks D. L., Neva F. A. Late metastatic Leishmaniasis in the mouse. A model for mucocutaneous disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Mar;32(2):277–285. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryceson A. D. Diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis in Ethiopia. I. The clinical and histological features of the disease. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1969;63(6):708–737. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(69)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Convit J., Pinardi M. E., Rondón A. J. Diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis: a disease due to an immunological defect of the host. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1972;66(4):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(72)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DESTOMBES P. [Application of the concept of "polar classification" to cutaneous leishmaniasis]. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1960 Mar-Apr;53:299–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Jr, Soares M. J., Moriearty P. L. Tissue eosinophilia and Leishmania mexicana mexicana eosinophil interactions in murine cutaneous leishmaniasis. Parasite Immunol. 1984 Sep;6(5):397–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1984.tb00811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Hale C., Liew F. Y. Immunological regulation of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. III. Nature and significance of specific suppression of cell-mediated immunity in mice highly susceptible to Leishmania tropica. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):594–607. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Hale C., Liew F. Y. Immunological regulation of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. IV. Prophylactic effect of sublethal irradiation as a result of abrogation of suppressor T cell generation in mice genetically susceptible to Leishmania tropica. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):557–568. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Liew F. Y., Hale C., Nicklin S. Prophylactic immunization against experimental leishmaniasis. II. Further characterization of the protective immunity against fatal Leishmania tropica infection induced by irradiated promastigotes. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):450–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Nicklin S., Hale C., Liew F. Y. Prophylactic immunization against experimental leishmaniasis: I. Protection induced in mice genetically vulnerable to fatal Leishmania tropica infection. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2206–2212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y. Specific suppression of responses to Leishmania tropica by a cloned T-cell line. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):630–632. doi: 10.1038/305630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez H., Labrador F., Torrealba J. W. Variations in the response of five strains of mice to Leishmania mexicana. Int J Parasitol. 1979 Feb;9(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(79)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Marsden P. D., Cuba C. C., Barreto A. C. A histological classification of mucocutaneous leishmaniasis in Brazil and its clinical evaluation. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(4):508–514. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Ridley M. J. The evolution of the lesion in cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Pathol. 1983 Sep;141(1):83–96. doi: 10.1002/path.1711410109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Ceredig R., Cerottini J. C., Louis J. A. Therapeutic effect of anti-L3T4 monoclonal antibody GK1.5 on cutaneous leishmaniasis in genetically-susceptible BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2108–2114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Lima G. C., Engers H. D., Louis J. A. Exacerbation of murine cutaneous leishmaniasis by adoptive transfer of parasite-specific helper T cell populations capable of mediating Leishmania major-specific delayed-type hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1594–1600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]