Abstract
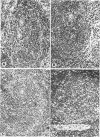
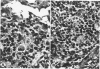
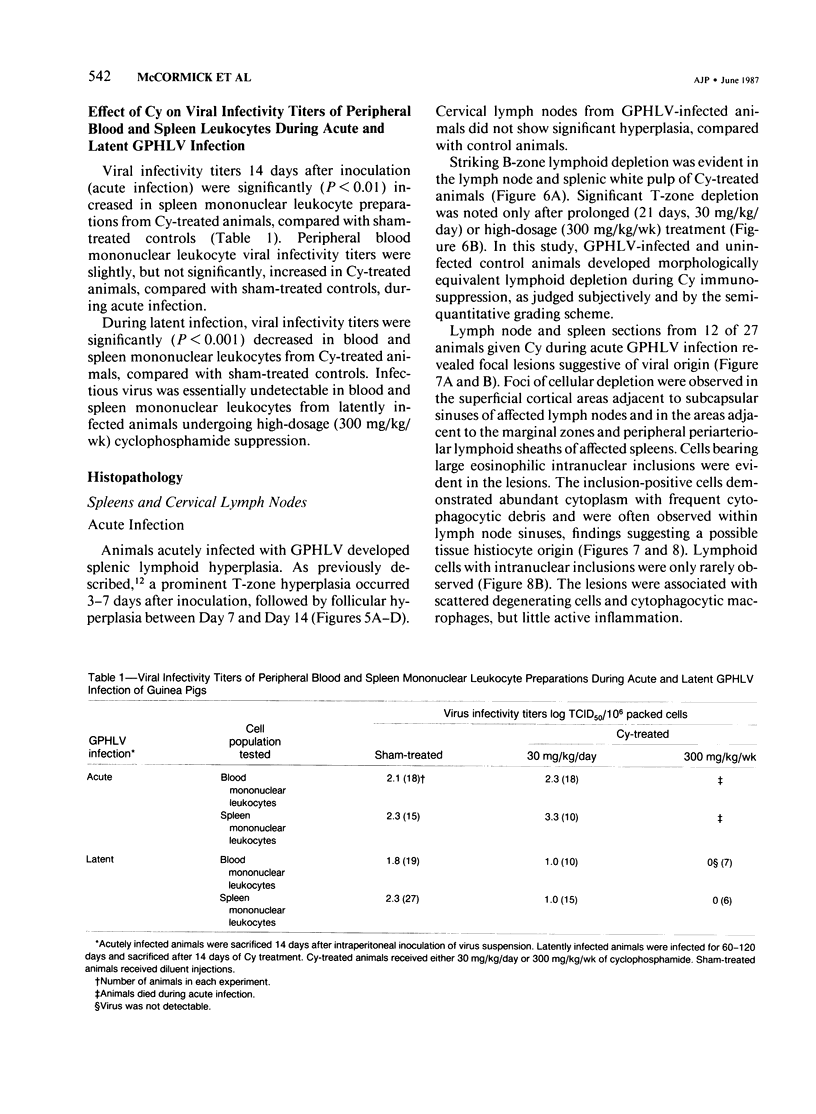
Guinea pigs infected with lymphotropic herpesvirus (GPHLV) were given the immunosuppressive agent cyclophosphamide (Cy). All Cy-treated animals revealed the expected lymphoid depletion of spleen and lymph node B zones. Acute GPHLV infection of Cy-treated animals resulted in increased blood and spleen leukocyte viral infectivity titers and lymphoid tissue lesions containing cells positive for GPHLV antigen and intranuclear inclusions. During latent GPHLV infection, Cy treatment resulted in declining leukocyte viral infectivity titers without pathologic lesions. Morphologic data suggest that tissue histiocytic cells may be involved in the productive viral infection observed in Cy-immunosuppressed animals during acute GPHLV infection. During latency, however, infectious virus appears restricted to a Cy-sensitive, probably lymphoid, cell. This animal model appears useful for the study of lymphotropic viral infection during immunosuppression.
Full text
PDF


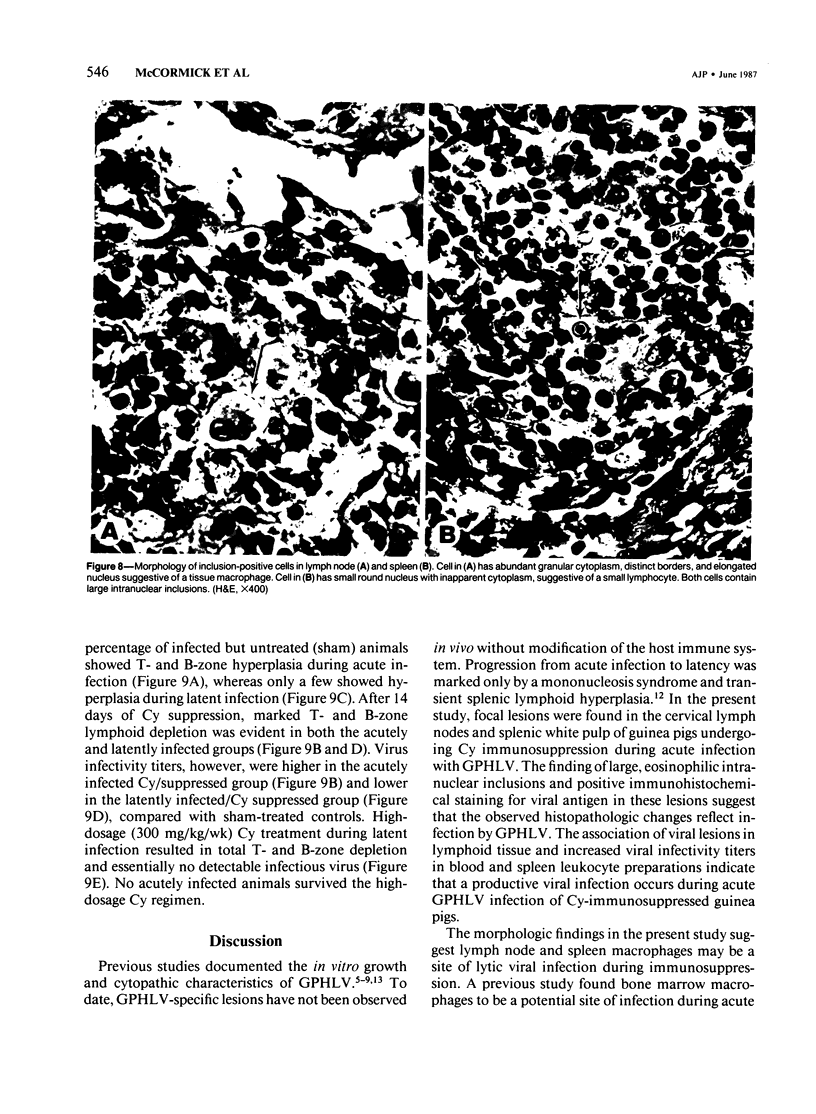
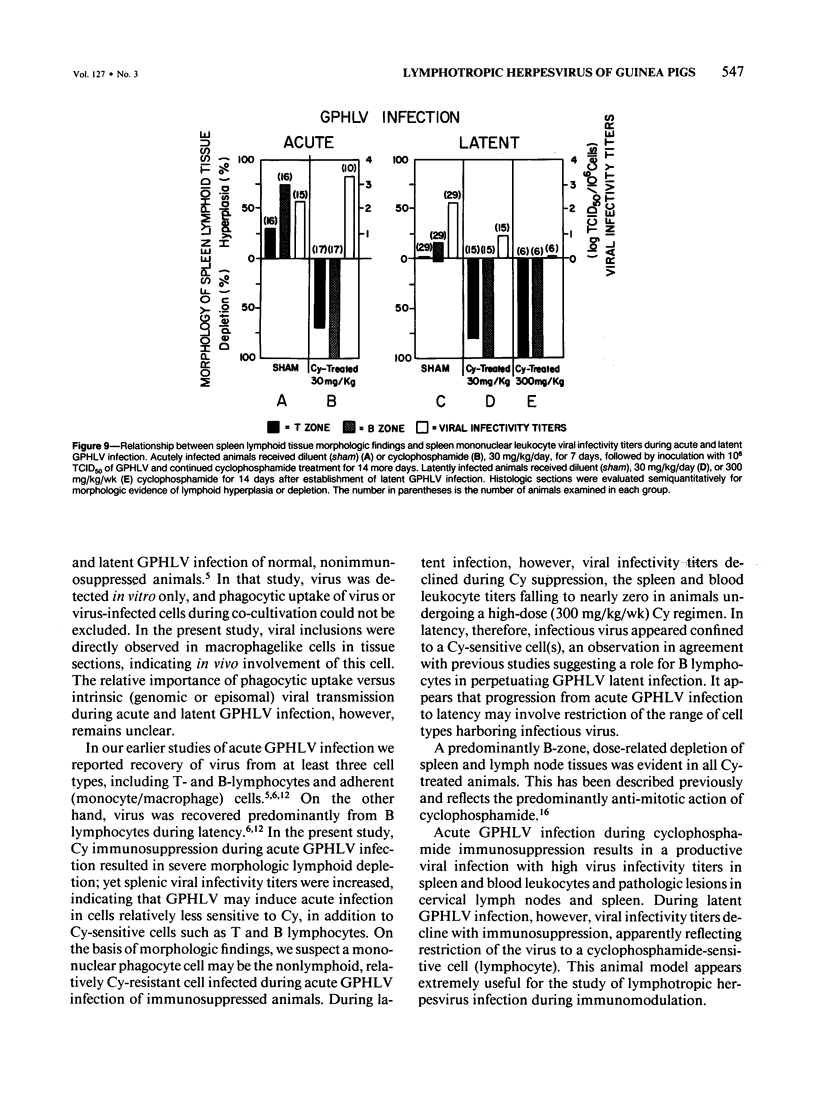

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booss J., Hsiung G. D. Herpes-like virus of the guinea pig: propagation in brain tissue of guinea pigs and mice. J Infect Dis. 1971 Mar;123(3):284–291. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.3.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottier H., Turk J., Sobin L. A proposal for a standardized system of reporting human lymph node morphology in relation to immunological function. J Clin Pathol. 1973 May;26(5):317–331. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.5.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowler K. W., McCormick S., Armstrong J. A., Hsiung G. D. Lymphoproliferative changes induced by infection with a lymphotropic herpesvirus of guinea pigs. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jul;150(1):105–111. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong C. K., Hsiung G. D. In vitro transformation of hamster embryo cells by a guinea pig herpes-like virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Dec;144(3):974–978. doi: 10.3181/00379727-144-37723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Serva A., Hsiung G. D. Expression of herpesvirus in adherent cells derived from bone marrow of latently infected guinea pigs. Am J Pathol. 1978 Jun;91(3):483–496. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith B. P., Hsiung G. D. Persistence and expression of herpes virus in guinea pig B and T spleen cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Oct;162(1):202–206. doi: 10.3181/00379727-162-40647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M., Miller G., Atchison R. W., Breinig M. K., Dummer J. S., Andiman W., Starzl T. E., Eastman R., Griffith B. P., Hardesty R. L. Epstein-Barr virus infections and DNA hybridization studies in posttransplantation lymphoma and lymphoproliferative lesions: the role of primary infection. J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):876–886. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiung G. D., Kaplow L. S., Booss J. Herpesvirus infection of guinea pigs. I. Isolation, characterization and pathogenicity. Am J Epidemiol. 1971 Apr;93(4):298–307. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiung G. D., Kaplow L. S. Herpeslike virus isolated from spontaneously degenerated tissue culture derived from leukemia-susceptible guinea pigs. J Virol. 1969 Mar;3(3):355–357. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.3.355-357.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiung G. D. Virological studies of guinea pig leukemia: an overview with reference to herpesvirus and oncornavirus. Fed Proc. 1977 Aug;36(9):2285–2289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. M., Hsiung G. D. Further studies on the mode of transmission of herpes-like virus in guinea pigs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Nov;138(2):422–426. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R. B., Jaffe E. S., Berard C. W. Malignant lymphomas--a conceptual understanding of morphologic diversity. A review. Am J Pathol. 1979 Jan;94(1):105–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., Klein G. Introduction to Epstein-Barr virus and lymphoproliferative diseases in immunodeficient individuals. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4209–4209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhim J. S. Malignant transformation of rat embryo cells by a herpesvirus isolated from L2C guinea pig leukemia. Virology. 1977 Oct 1;82(1):100–110. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenser R. B., Hsiung G. D. Infection of thymus cells in vivo and in vitro with a guinea pig herpes-like virus and the effect of antibody on virus replication in organ culture. J Immunol. 1973 Feb;110(2):552–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L., Poulter L. W. Selective depletion of lymphoid tissue by cyclophosphamide. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Feb;10(2):285–296. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]