Abstract
1. The effects of selective neurokinin agents on pial artery diameter, measured with an on-line image analyser, have been studied in anaesthetized guinea-pigs in order to characterize the neurokinin receptors present on pial arteries. 2. Perivascular injection of either substance P (0.01-1 microM) or the selective NK1 receptor agonists, substance P methyl ester (SPOMe, 0.01-1 microM) and GR73632 (0.1 microM), increased pial artery diameter. 3. In contrast, the selective NK2 receptor agonist, GR64349 (1 microM), produced a small vasoconstriction while the NK3 receptor-selective agonist, senktide (1 microM) was inactive. 4. Co-administration of GR82334 (1 microM), a selective NK1 receptor antagonist, inhibited the vasodilatation produced by SPOMe (0.1 microM) but not that caused by calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP, 0.01 microM). 5. The results are consistent with an involvement of NK1 receptors in the neurokinin-induced increase in guinea-pig pial artery diameter.
Full text
PDF
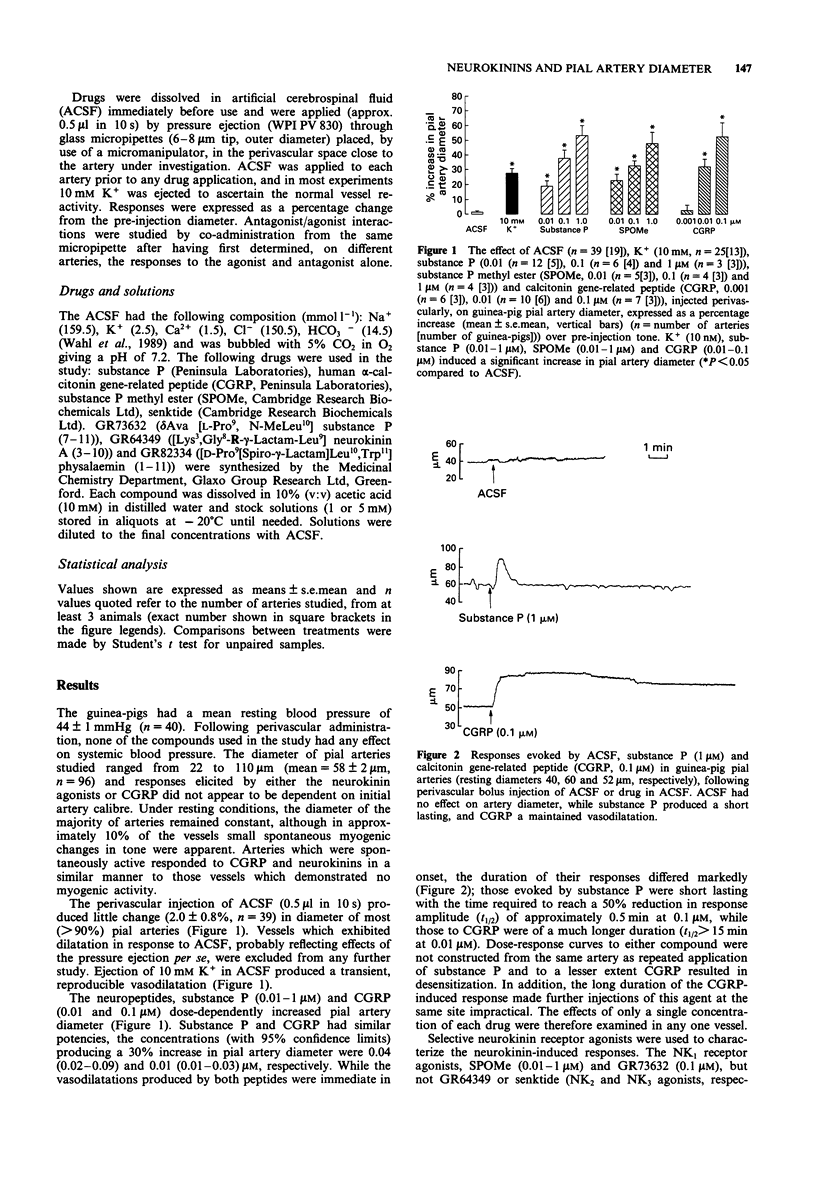
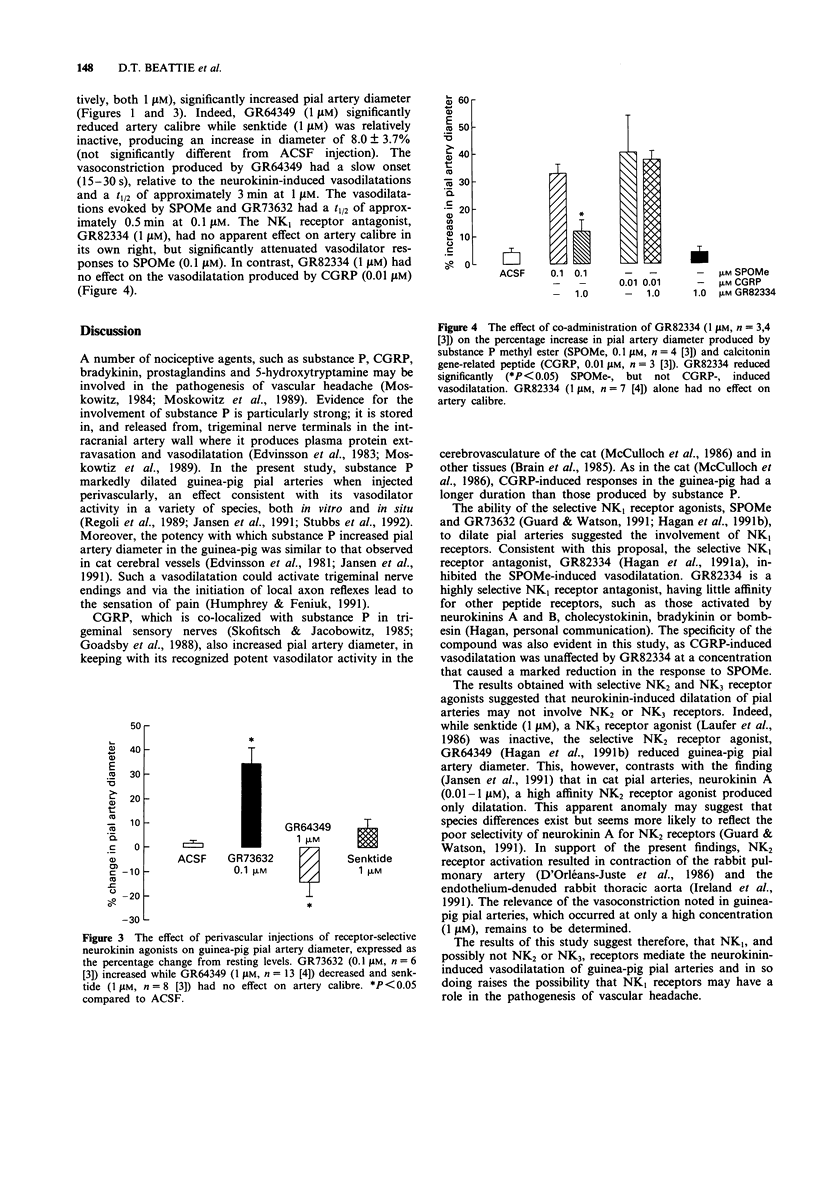

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brain S. D., Williams T. J., Tippins J. R., Morris H. R., MacIntyre I. Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature. 1985 Jan 3;313(5997):54–56. doi: 10.1038/313054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Orléans-Juste P., Dion S., Drapeau G., Regoli D. Different receptors are involved in the endothelium-mediated relaxation and the smooth muscle contraction of the rabbit pulmonary artery in response to substance P and related neurokinins. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Jun 5;125(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., McCulloch J., Uddman R. Substance P: immunohistochemical localization and effect upon cat pial arteries in vitro and in situ. J Physiol. 1981 Sep;318:251–258. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Rosendal-Helgesen S., Uddman R. Substance P: localization, concentration and release in cerebral arteries, choroid plexus and dura mater. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;234(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00217397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goadsby P. J., Edvinsson L., Ekman R. Release of vasoactive peptides in the extracerebral circulation of humans and the cat during activation of the trigeminovascular system. Ann Neurol. 1988 Feb;23(2):193–196. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan R. M., Ireland S. J., Jordan C. C., Beresford I. J., Deal M. J., Ward P. Receptor-selective, peptidase-resistant agonists at neurokinin NK-1 and NK-2 receptors: new tools for investigating neurokinin function. Neuropeptides. 1991 Jun;19(2):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(91)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey P. P., Feniuk W. Mode of action of the anti-migraine drug sumatriptan. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Dec;12(12):444–446. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90630-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireland S. J., Bailey F., Cook A., Hagan R. M., Jordan C. C., Stephens-Smith M. L. Receptors mediating tachykinin-induced contractile responses in guinea-pig trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1463–1469. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09812.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen I., Alafaci C., McCulloch J., Uddman R., Edvinsson L. Tachykinins (substance P, neurokinin A, neuropeptide K, and neurokinin B) in the cerebral circulation: vasomotor responses in vitro and in situ. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1991 Jul;11(4):567–575. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1991.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer R., Gilon C., Chorev M., Selinger Z. Characterization of a neurokinin B receptor site in rat brain using a highly selective radioligand. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10257–10263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Campbell N. J., Williams B. J., Iversen L. L. Multiple tachykinin binding sites in peripheral tissues and in brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov 4;130(3):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Chen L. Y., Mayberg M. R., Moskowitz M. A. Immunohistochemical evidence for a substance P-containing trigeminovascular pathway to pial arteries in cats. Brain Res. 1983 May 23;268(1):162–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90402-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S., Saito K., Moskowitz M. A. Neurogenically mediated leakage of plasma protein occurs from blood vessels in dura mater but not brain. J Neurosci. 1987 Dec;7(12):4129–4136. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-12-04129.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCulloch J., Uddman R., Kingman T. A., Edvinsson L. Calcitonin gene-related peptide: functional role in cerebrovascular regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5731–5735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A., Brody M., Liu-Chen L. Y. In vitro release of immunoreactive substance P from putative afferent nerve endings in bovine pia arachnoid. Neuroscience. 1983 Aug;9(4):809–814. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90269-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A., Buzzi M. G., Sakas D. E., Linnik M. D. Pain mechanisms underlying vascular headaches. Progress Report 1989. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1989;145(3):181–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A. The neurobiology of vascular head pain. Ann Neurol. 1984 Aug;16(2):157–168. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Drapeau G., Dion S., D'Orléans-Juste P. Receptors for substance P and related neurokinins. Pharmacology. 1989;38(1):1–15. doi: 10.1159/000138512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skofitsch G., Jacobowitz D. M. Calcitonin gene-related peptide coexists with substance P in capsaicin sensitive neurons and sensory ganglia of the rat. Peptides. 1985 Jul-Aug;6(4):747–754. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs C. M., Waldron G. J., Connor H. E., Feniuk W. Characterization of the receptor mediating relaxation to substance P in canine middle cerebral artery: no evidence for involvement of substance P in neurogenically mediated relaxation. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;105(4):875–880. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09071.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M., Schilling L., Whalley E. T. Cerebrovascular effects of prostanoids. In-situ studies in pial arteries of the cat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;340(3):314–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00168516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Sandberg B. E., Hanley M. R., Iversen L. L. Tissue selectivity of substance P alkyl esters: suggesting multiple receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 28;87(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormser U., Laufer R., Hart Y., Chorev M., Gilon C., Selinger Z. Highly selective agonists for substance P receptor subtypes. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2805–2808. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04571.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


