Abstract
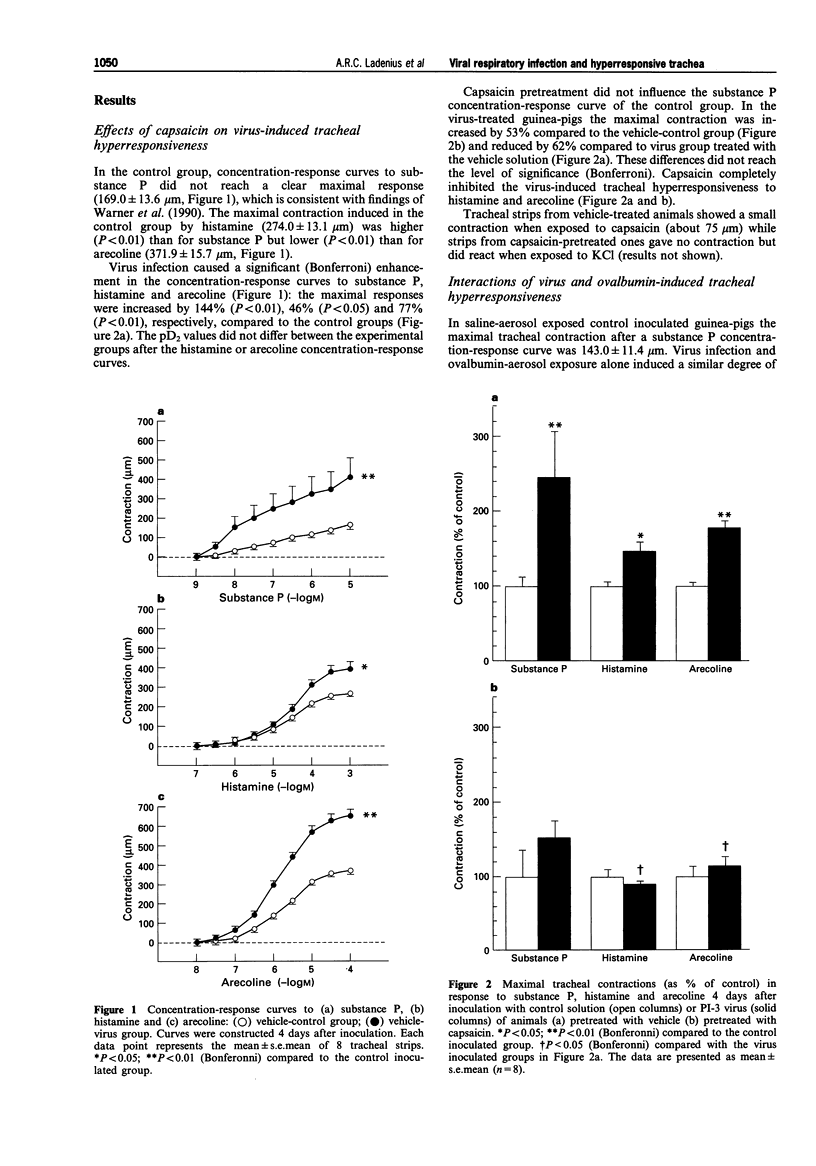
1. We investigated whether virus-induced airway hyperresponsiveness in guinea-pigs could be modulated by pretreatment with capsaicin and whether viral respiratory infections could potentiate ovalbumin-aerosol-induced tracheal hyperresponsiveness. 2. Animals were inoculated intratracheally with bovine parainfluenza-3 virus or control medium 7 days after treatment with capsaicin (50 mg kg-1, s.c.). Four days after inoculation, tracheal contractions were measured to increasing concentrations of substance P, histamine and the cholinoceptor agonist, arecoline. 3. In tracheae from virus-infected guinea-pigs, contractions in response to substance P, histamine and arecoline were significantly enhanced (P < 0.01) by 144%, 46% and 77%, respectively. Capsaicin pretreatment inhibited the hyperresponsiveness to substance P partly (62%) and to histamine and arecoline completely. 4. In another series of experiments animals were first sensitized with ovalbumin (20 mg kg-1, i.p.). After 14 days animals were exposed to either saline or ovalbumin aerosols for 8 days. After 4 aerosol exposures (4 days) animals were inoculated with either parainfluenza-3 virus or control medium. One day after the last ovalbumin aerosol, tracheal contraction in response to increasing concentrations of substance P, histamine and arecoline was measured. 5. Tracheae from ovalbumin-aerosol-exposed control inoculated animals showed a similar degree of airway hyperresponsiveness to saline-aerosol-exposed virus-treated guinea-pigs. Virus inoculation of ovalbumin-treated animals significantly potentiated the tracheal contractions to substance P compared to either of the treatments alone. The contractions in response to histamine and arecoline were only slightly enhanced.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

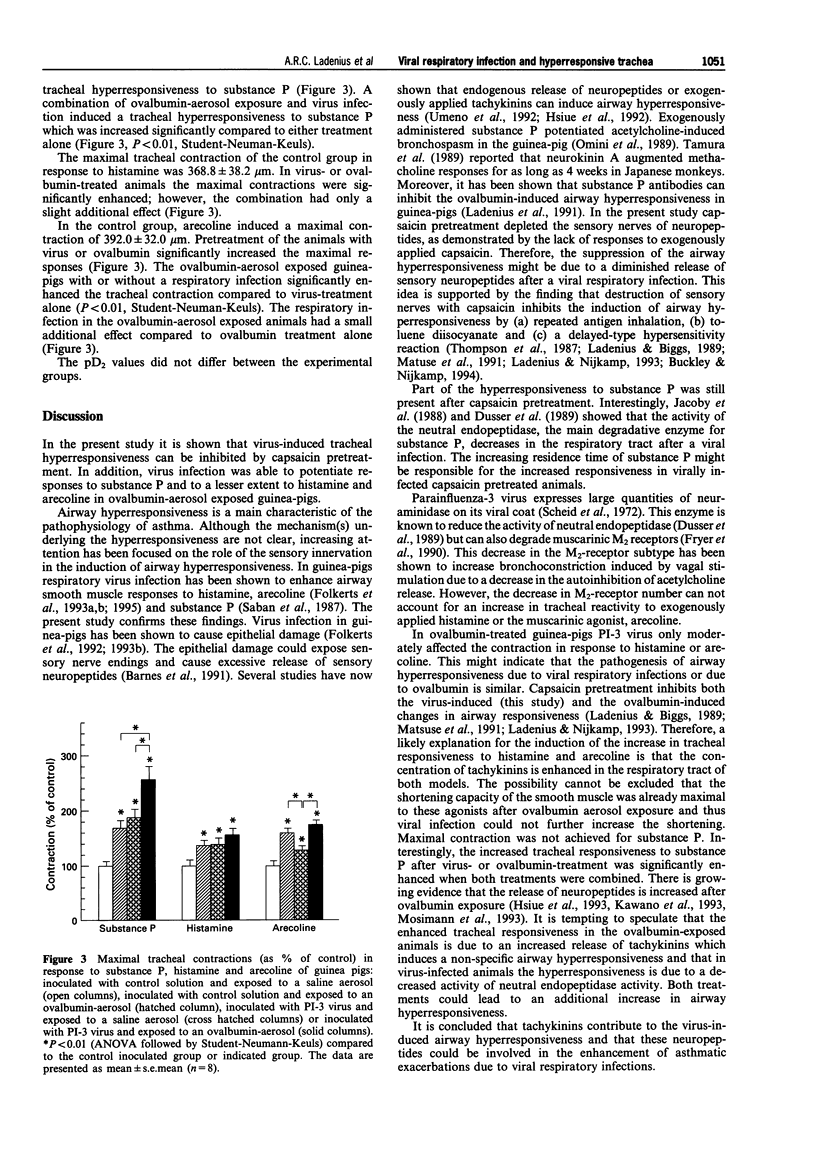

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. J., Baraniuk J. N., Belvisi M. G. Neuropeptides in the respiratory tract. Part I. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Nov;144(5):1187–1198. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.5.1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley T. L., Nijkamp F. P. Airways hyperreactivity and cellular accumulation in a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction in the mouse. Modulation by capsaicin-sensitive nerves. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Feb;149(2 Pt 1):400–407. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.2.8306037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusser D. J., Jacoby D. B., Djokic T. D., Rubinstein I., Borson D. B., Nadel J. A. Virus induces airway hyperresponsiveness to tachykinins: role of neutral endopeptidase. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Oct;67(4):1504–1511. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.4.1504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Empey D. W., Laitinen L. A., Jacobs L., Gold W. M., Nadel J. A. Mechanisms of bronchial hyperreactivity in normal subjects after upper respiratory tract infection. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Feb;113(2):131–139. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkerts G., De Clerck F., Reijnart I., Span P., Nijkamp F. P. Virus-induced airway hyperresponsiveness in the guinea-pig: possible involvement of histamine and inflammatory cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Apr;108(4):1083–1093. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkerts G., Verheyen A. K., Geuens G. M., Folkerts H. F., Nijkamp F. P. Virus-induced changes in airway responsiveness, morphology, and histamine levels in guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Jun;147(6 Pt 1):1569–1577. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.6_Pt_1.1569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkerts G., Verheyen A., Nijkamp F. P. Viral infection in guinea pigs induces a sustained non-specific airway hyperresponsiveness and morphological changes of the respiratory tract. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep 1;228(2-3):121–130. doi: 10.1016/0926-6917(92)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkerts G., van der Linde H. J., Nijkamp F. P. Virus-induced airway hyperresponsiveness in guinea pigs is related to a deficiency in nitric oxide. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jan;95(1):26–30. doi: 10.1172/JCI117649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryer A. D., el-Fakahany E. E., Jacoby D. B. Parainfluenza virus type 1 reduces the affinity of agonists for muscarinic receptors in guinea-pig lung and heart. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 May 31;181(1-2):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90244-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiue T. R., Garland A., Ray D. W., Hershenson M. B., Leff A. R., Solway J. Endogenous sensory neuropeptide release enhances nonspecific airway responsiveness in guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Jul;146(1):148–153. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.1.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiue T. R., Leff A. R., Garland A., Hershenson M. B., Ray D. W., Solway J. Impaired sensorineural function after allergen-induced mediator release. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Aug;148(2):447–454. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.2.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida K., Kelly L. J., Thomson R. J., Beattie L. L., Schellenberg R. R. Repeated antigen challenge induces airway hyperresponsiveness with tissue eosinophilia in guinea pigs. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Sep;67(3):1133–1139. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.3.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby D. B., Tamaoki J., Borson D. B., Nadel J. A. Influenza infection causes airway hyperresponsiveness by decreasing enkephalinase. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Jun;64(6):2653–2658. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.64.6.2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawano O., Kohrogi H., Yamaguchi T., Araki S., Ando M. Neutral endopeptidase inhibitor potentiates allergic bronchoconstriction in guinea pigs in vivo. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1993 Jul;75(1):185–190. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1993.75.1.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladenius A. R., Nijkamp F. P. Capsaicin pretreatment of guinea pigs in vivo prevents ovalbumin-induced tracheal hyperreactivity in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Apr 22;235(1):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90831-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuse T., Thomson R. J., Chen X. R., Salari H., Schellenberg R. R. Capsaicin inhibits airway hyperresponsiveness but not lipoxygenase activity or eosinophilia after repeated aerosolized antigen in guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Aug;144(2):368–372. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.2.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh K., Ellis E. F., Hoffman L. S., Lybass T. G., Eller J. J., Fulginiti V. A. The association of viral and bacterial respiratory infections with exacerbations of wheezing in young asthmatic children. J Pediatr. 1973 Apr;82(4):578–590. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(73)80582-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosimann B. L., White M. V., Hohman R. J., Goldrich M. S., Kaulbach H. C., Kaliner M. A. Substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide, and vasoactive intestinal peptide increase in nasal secretions after allergen challenge in atopic patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993 Jul;92(1 Pt 1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(93)90043-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omini C., Brunelli G., Hernandez A., Daffonchio L. Bradykinin and substance P potentiate acetylcholine-induced bronchospasm in guinea-pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Apr 12;163(1):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90419-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette J. J., Reed C. E. Increased response of asthmatic subjects to methacholine after influenza vaccine. J Allergy. 1965 Nov-Dec;36(6):558–563. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(65)90193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saban R., Dick E. C., Fishleder R. I., Buckner C. K. Enhancement by parainfluenza 3 infection of contractile responses to substance P and capsaicin in airway smooth muscle from the guinea pig. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Sep;136(3):586–591. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.3.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saria A., Martling C. R., Yan Z., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Gamse R., Lundberg J. M. Release of multiple tachykinins from capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves in the lung by bradykinin, histamine, dimethylphenyl piperazinium, and vagal nerve stimulation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jun;137(6):1330–1335. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.6.1330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Caliguiri L. A., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Isolation of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Association of both hemagglutinating and neuraminidase activities with the larger SV5 glycoprotein. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):640–652. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura G., Sakai K., Taniguchi Y., Iijima H., Honma M., Katsumata U., Maruyama N., Aizawa T., Takishima T. Neurokinin A-induced bronchial hyperresponsiveness to methacholine in Japanese monkeys. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1989 Sep;159(1):69–73. doi: 10.1620/tjem.159.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. E., Scypinski L. A., Gordon T., Sheppard D. Tachykinins mediate the acute increase in airway responsiveness caused by toluene diisocyanate in guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jul;136(1):43–49. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeno E., Hirose T., Nishima S. Pretreatment with aerosolized capsaicin potentiates histamine-induced bronchoconstriction in guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Jul;146(1):159–162. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner E. A., Krell R. D., Buckner C. K. Pharmacologic studies on the differential influence of inhibitors of neutral endopeptidase on nonadrenergic, noncholinergic contractile responses of the guinea pig isolated hilar bronchus to transmural electrical stimulation and exogenously applied tachykinins. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Sep;254(3):824–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


