Abstract
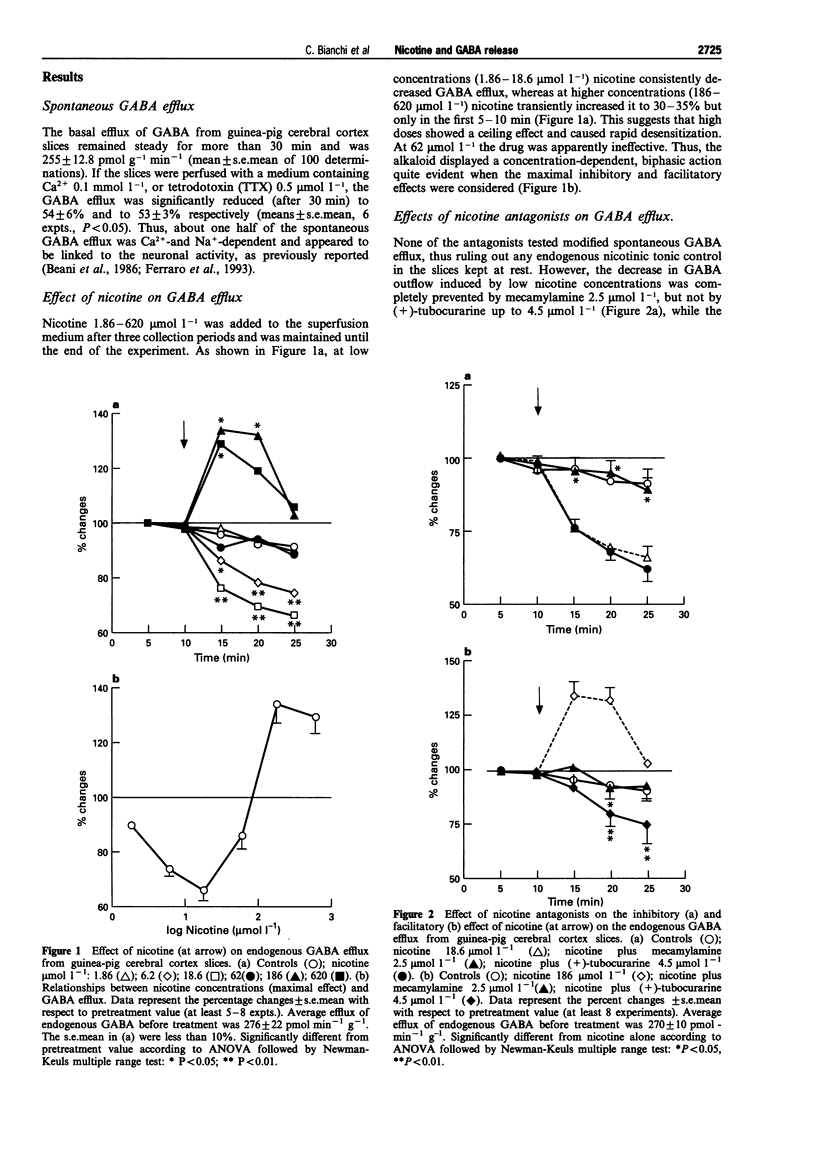
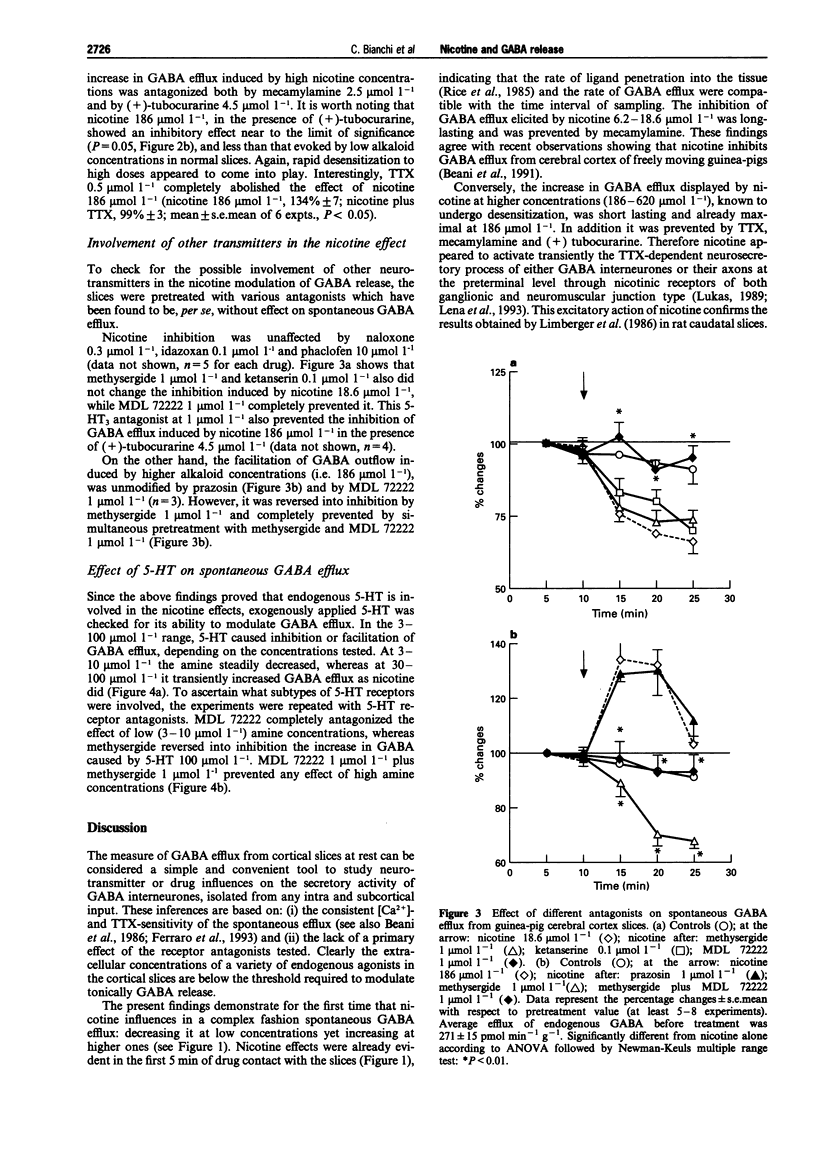
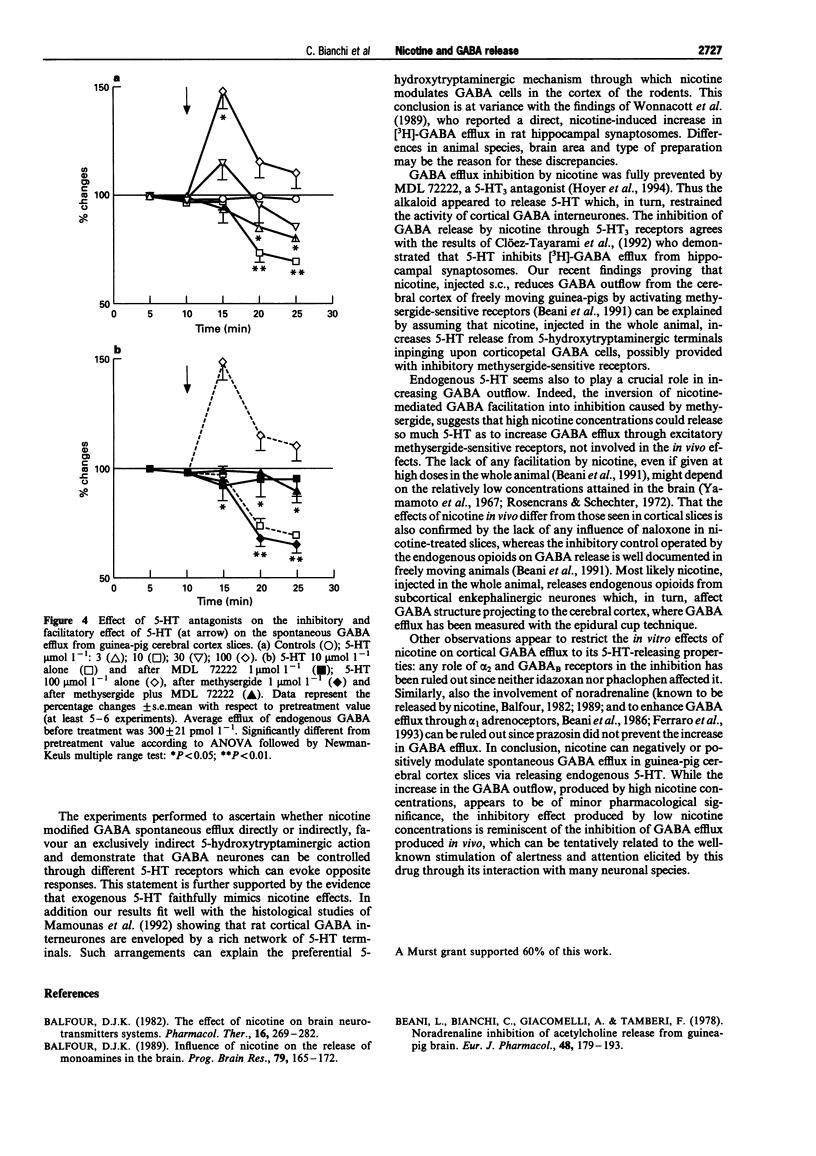
1. The effect of nicotine on endogenous basal GABA outflow was studied in guinea-pig cerebral cortex slices. 2. Nicotine 1.86-18.6 mumol l-1 significantly decreased the basal, tetrodotoxin-sensitive GABA efflux, whereas at higher concentrations (186-620 mumol l-1) nicotine increased it. The inhibition was prevented by mecamylamine while the facilitation was blocked by mecamylamine, (+)-tubocurarine and tetrodotoxin. 3. The effect of nicotine was due to an indirect 5-hydroxytryptaminergic action. In fact, MDL 72222 (1 mumol l-1) completely prevented the alkaloid inhibition and methysergide (1 mumol l-1) reversed the facilitation into inhibition; concomitant treatment with methysergide and MDL 72222 antagonized the effect of nicotine at 186 mumol l-1 4. Lower concentrations of 5-HT (3-10 mumol l-1) decreased, whereas higher concentrations (30-100 mumol l-1) increased, spontaneous GABA outflow. The inhibition of GABA efflux was prevented by MDL 72222 whereas the facilitation was reversed by methysergide (1 mumol l-1) into inhibition, and prevented by MDL 72222 1 mumol l-11. 5. These results suggest that, by activating nicotinic receptors present on 5-hydroxytryptaminergic terminals, nicotine releases 5-HT which, in turn, inhibits or increases the secretory activity of cortical GABA interneurones via 5-HT3 and methysergide-sensitive receptors, respectively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balfour D. J. Influence of nicotine on the release of monoamines in the brain. Prog Brain Res. 1989;79:165–172. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62476-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balfour D. J. The effects of nicotine on brain neurotransmitter systems. Pharmacol Ther. 1982;16(2):269–282. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(82)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beani L., Bianchi C., Giacomelli A., Tamberi F. Noradrenaline inhibition of acetylcholine release from guinea-pig brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Mar 15;48(2):179–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90327-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beani L., Bianchi C., Nilsson L., Nordberg A., Romanelli L., Sivilotti L. The effect of nicotine and cytisine on 3H-acetylcholine release from cortical slices of guinea-pig brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;331(2-3):293–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00634252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beani L., Tanganelli S., Antonelli T., Bianchi C. Noradrenergic modulation of cortical acetylcholine release is both direct and gamma-aminobutyric acid-mediated. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jan;236(1):230–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beani L., Tanganelli S., Antonelli T., Ferraro L., Morari M., Spalluto P., Nordberg A., Bianchi C. Effect of acute and subchronic nicotine treatment on cortical efflux of [3H]-D-aspartate and endogenous GABA in freely moving guinea-pigs. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;104(1):15–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12377.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertilsson L., Costa E. Mass fragmentographic quantitation of glutamic acid and gamma-aminobutyric acid in cerebellar nuclei and sympathetic ganglia of rats. J Chromatogr. 1976 Apr 7;118(3):395–402. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)82177-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carboni E., Acquas E., Frau R., Di Chiara G. Differential inhibitory effects of a 5-HT3 antagonist on drug-induced stimulation of dopamine release. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 30;164(3):515–519. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90259-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloëz-Tayarani I., Harel-Dupas C., Fillion G. Inhibition of [3H] gamma-aminobutyric acid release from guinea-pig hippocampal synaptosomes by serotonergic agents. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1992;6(8-9):333–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.1992.tb00128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferraro L., Tanganelli S., Caló G., Antonelli T., Fabrizi A., Acciarri N., Bianchi C., Beani L., Simonato M. Noradrenergic modulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid outflow from the human cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1993 Nov 26;629(1):103–108. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90487-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperato A., Mulas A., Di Chiara G. Nicotine preferentially stimulates dopamine release in the limbic system of freely moving rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Dec 16;132(2-3):337–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90629-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger N., Späth L., Starke K. A search for receptors modulating the release of gamma-[3H]aminobutyric acid in rabbit caudate nucleus slices. J Neurochem. 1986 Apr;46(4):1109–1117. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb00625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukas R. J. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor diversity: agonist binding and functional potency. Prog Brain Res. 1989;79:117–127. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62471-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léna C., Changeux J. P., Mulle C. Evidence for "preterminal" nicotinic receptors on GABAergic axons in the rat interpeduncular nucleus. J Neurosci. 1993 Jun;13(6):2680–2688. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-06-02680.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHugh D., Beech D. J. Inhibition of delayed rectifier K(+)-current by levcromakalim in single intestinal smooth muscle cells: effects of cations and dependence on K(+)-flux. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;114(2):391–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisell M., Nomikos G. G., Svensson T. H. Systemic nicotine-induced dopamine release in the rat nucleus accumbens is regulated by nicotinic receptors in the ventral tegmental area. Synapse. 1994 Jan;16(1):36–44. doi: 10.1002/syn.890160105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordberg A., Romanelli L., Sundwall A., Bianchi C., Beani L. Effect of acute and subchronic nicotine treatment on cortical acetylcholine release and on nicotinic receptors in rats and guinea-pigs. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;98(1):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb16864.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez de la Mora M., Méndez-Franco J., Salceda R., Aguirre J. A., Fuxe K. Neurochemical effects of nicotine on glutamate and GABA mechanisms in the rat brain. Acta Physiol Scand. 1991 Feb;141(2):241–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1991.tb09074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro E. B., Bettiker R. L., Bogdanov M., Wurtman R. J. Effects of systemic nicotine on serotonin release in rat brain. Brain Res. 1993 Sep 10;621(2):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice M. E., Gerhardt G. A., Hierl P. M., Nagy G., Adams R. N. Diffusion coefficients of neurotransmitters and their metabolites in brain extracellular fluid space. Neuroscience. 1985 Jul;15(3):891–902. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosecrans J. A., Schechter M. D. Brain area nicotine levels in male and female rats of two strains. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1972 Mar;196(1):46–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth E., Vizi E. S., Lajtha A. Effect of nicotine on levels of extracellular amino acids in regions of the rat brain in vivo. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Aug;32(8):827–832. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westfall T. C., Grant H., Perry H. Release of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine from rat striatal slices following activation of nicotinic cholinergic receptors. Gen Pharmacol. 1983;14(3):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(83)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wonnacott S., Irons J., Rapier C., Thorne B., Lunt G. G. Presynaptic modulation of transmitter release by nicotinic receptors. Prog Brain Res. 1989;79:157–163. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62475-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto I., Inoki R., Tamari Y., Iwatsubo K. Effect of reserpine on brain levels of 14C-nicotine in relation to nicotine-induced convulsions. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1967 Mar;166(1):102–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Garza R., Freedman R., Hoffer J. Nicotine-induced inhibition of cerebellar Purkinje neurons: specific actions of nicotine and selective blockade by mecamylamine. Neuropharmacology. 1989 May;28(5):495–501. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(89)90085-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


