Abstract
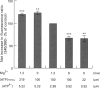
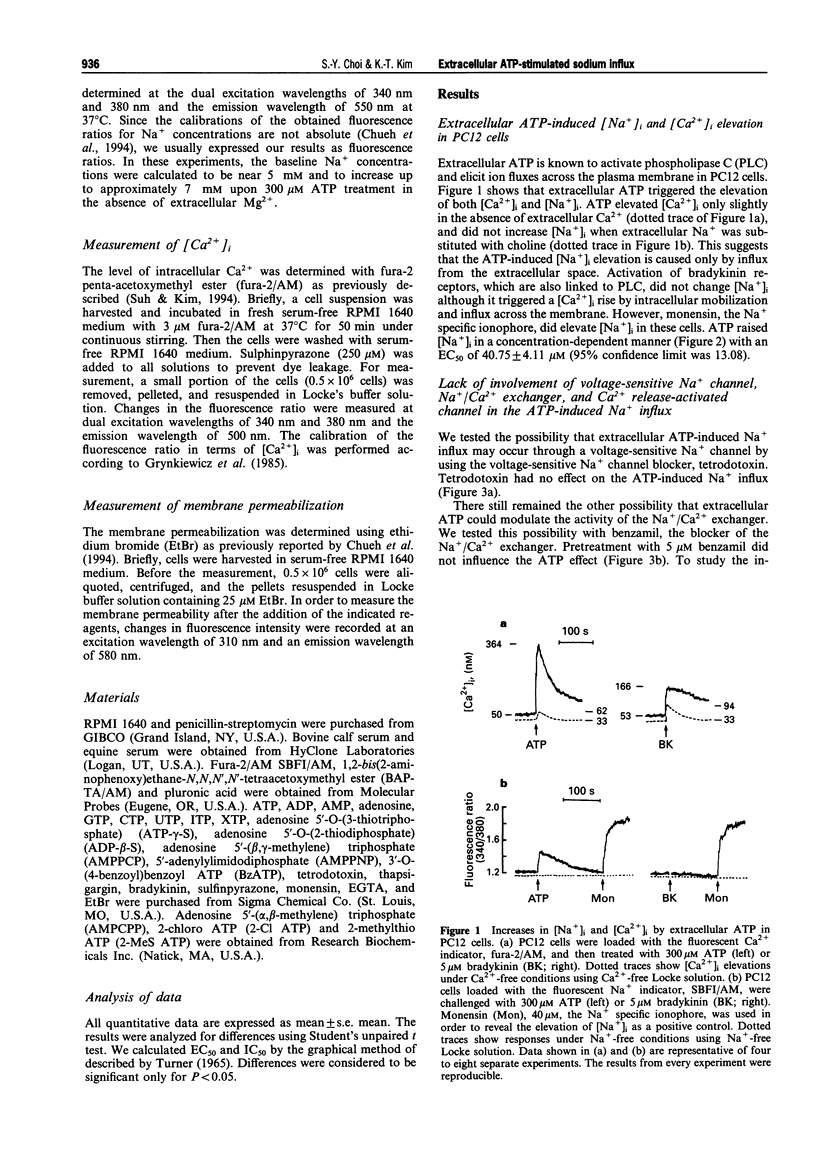
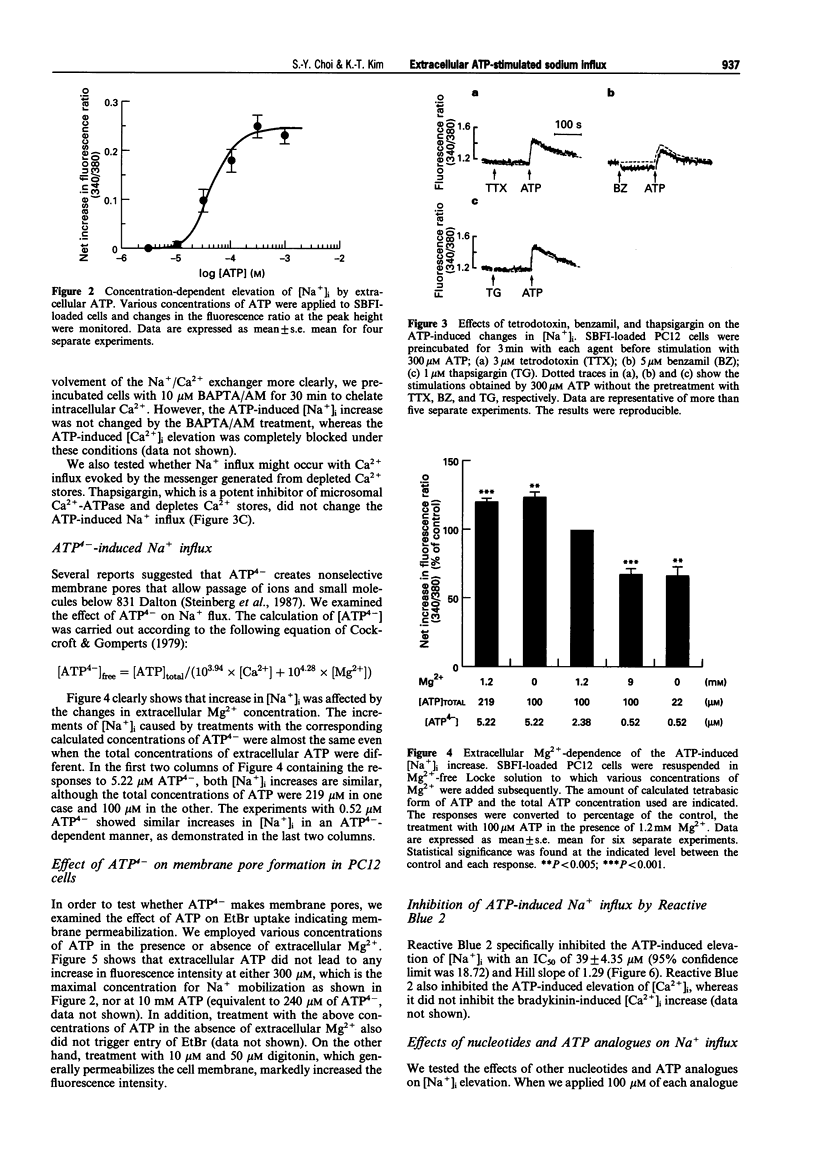
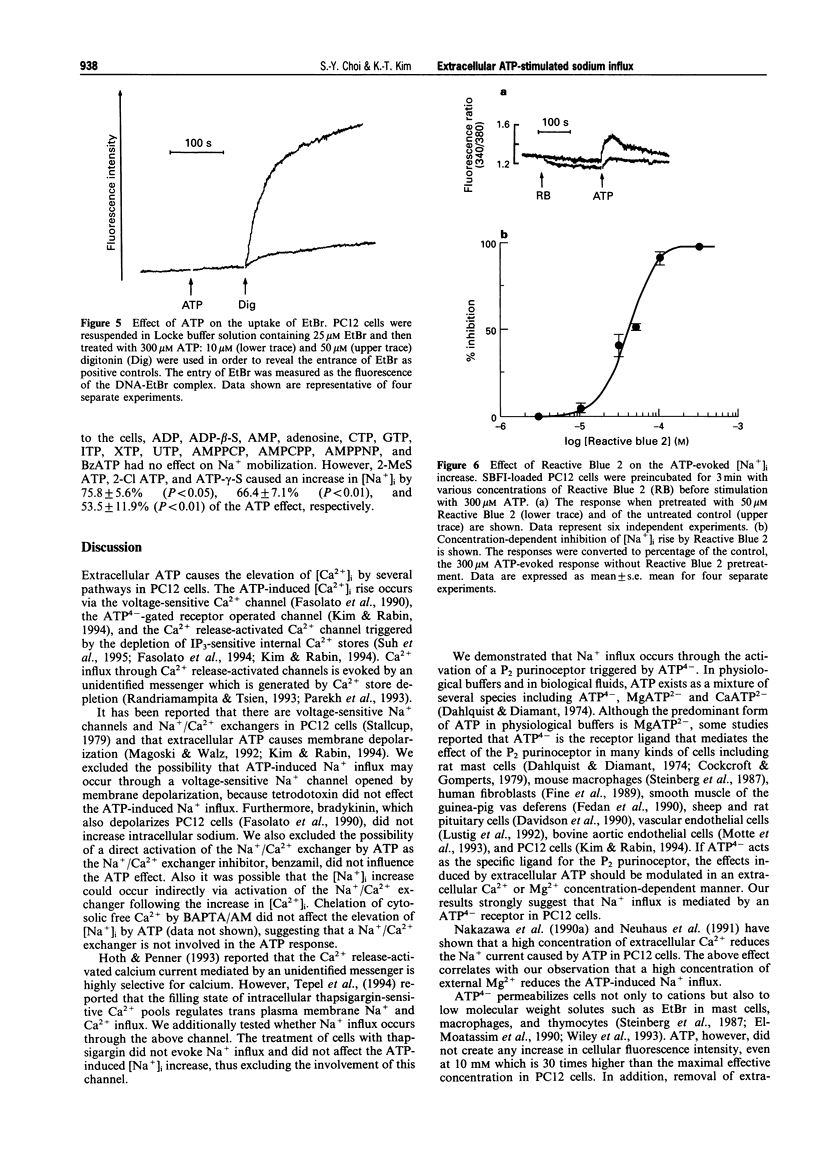
1. Micromolar levels of extracellular ATP increased cytosolic Na+ concentration ([Na+]i) as well as cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) in PC12 cells. 2. Pretreatment of cells with tetrodotoxin, benzamil or thapsigargin did not alter the ATP-induced Na+ influx. 3. Increased extracellular Mg2+ concentration decreased the ATP effect. Furthermore, when the extracellular ATP pool was treated to contain corresponding calculated concentrations of ATP4-, the increase in [Na+]i stayed linked to the ATP4- concentration rather than to the total ATP concentrations in the stimulants. 4. Extracellular ATP does not create nonselective pores as shown by the fact that ethidium bromide does not enter the cells upon ATP stimulation. 5. Among the tested nucleotides, only adenosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate), 2-methylthio ATP and 2-chloro ATP also caused Na+ influx. 6. Reactive Blue 2 specifically decreased the ATP effect in a concentration-dependent manner. 7. The results suggest that extracellular ATP triggers Na+ influx through a P2 purinoceptor which is activated by ATP4- in PC12 cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brake A. J., Wagenbach M. J., Julius D. New structural motif for ligand-gated ion channels defined by an ionotropic ATP receptor. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):519–523. doi: 10.1038/371519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chueh S. H., Hsu L. S., Song S. L. Two distinct ATP signaling mechanisms in differentiated neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid NG108-15 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;45(3):532–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Activation and inhibition of calcium-dependent histamine secretion by ATP ions applied to rat mast cells. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:229–243. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlquist R., Diamant B. Interaction of ATP and calcium on the rat mast cell: effect on histamine release. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1974 May;34(5):368–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1974.tb03533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. S., Wakefield I. K., Sohnius U., van der Merwe P. A., Millar R. P. A novel extracellular nucleotide receptor coupled to phosphoinositidase-C in pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1990 Jan;126(1):80–87. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-1-80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R., el-Moatassim C. Signal transduction via P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP and other nucleotides. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 1):C577–C606. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.3.C577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. J., Lewis C., Buell G., Valera S., North R. A., Surprenant A. Pharmacological characterization of heterologously expressed ATP-gated cation channels (P2x purinoceptors). Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Aug;48(2):178–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasolato C., Innocenti B., Pozzan T. Receptor-activated Ca2+ influx: how many mechanisms for how many channels? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Mar;15(3):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasolato C., Pizzo P., Pozzan T. Receptor-mediated calcium influx in PC12 cells. ATP and bradykinin activate two independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20351–20355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedan J. S., Dagirmanjian J. P., Attfield M. D., Chideckel E. W. Evidence that the P2x purinoceptor of the smooth muscle of the guinea pig vas deferens is an ATP4- receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Oct;255(1):46–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedan J. S., Lamport S. J. P2-purinoceptor antagonists. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:182–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37672.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J., Cole P., Davidson J. S. Extracellular nucleotides stimulate receptor-mediated calcium mobilization and inositol phosphate production in human fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 15;263(2):371–376. doi: 10.1042/bj2630371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Abbracchio M. P., Burnstock G., Daly J. W., Harden T. K., Jacobson K. A., Leff P., Williams M. Nomenclature and classification of purinoceptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1994 Jun;46(2):143–156. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoth M., Penner R. Calcium release-activated calcium current in rat mast cells. J Physiol. 1993 Jun;465:359–386. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illes P., Nörenberg W. Neuronal ATP receptors and their mechanism of action. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Feb;14(2):50–54. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90030-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Nakazawa K., Ohara-Imaizumi M., Obama T., Fujimori K., Takanaka A. Antagonism by reactive blue 2 but not by brilliant blue G of extracellular ATP-evoked responses in PC12 phaeochromocytoma cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;102(4):851–854. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12265.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C., Leff P. How should P2X purinoceptors be classified pharmacologically? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995 May;16(5):168–174. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(00)89010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim W. K., Rabin R. A. Characterization of the purinergic P2 receptors in PC12 cells. Evidence for a novel subtype. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6471–6477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig K. D., Sportiello M. G., Erb L., Weisman G. A. A nucleotide receptor in vascular endothelial cells is specifically activated by the fully ionized forms of ATP and UTP. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 15;284(Pt 3):733–739. doi: 10.1042/bj2840733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magoski N. S., Walz W. Ionic dependence of a P2-purinoceptor mediated depolarization of cultured astrocytes. J Neurosci Res. 1992 Aug;32(4):530–538. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490320408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majid M. A., Okajima F., Kondo Y. Characterization of ATP receptor which mediates norepinephrine release in PC12 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Sep 9;1136(3):283–289. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90118-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minta A., Tsien R. Y. Fluorescent indicators for cytosolic sodium. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19449–19457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motte S., Pirotton S., Boeynaems J. M. Evidence that a form of ATP uncomplexed with divalent cations is the ligand of P2y and nucleotide/P2u receptors on aortic endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;109(4):967–971. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13715.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa K., Fujimori K., Takanaka A., Inoue K. An ATP-activated conductance in pheochromocytoma cells and its suppression by extracellular calcium. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:257–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa K., Inoue K., Fujimori K., Takanaka A. ATP-activated single-channel currents recorded from cell-free patches of pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Oct 30;119(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90741-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus R., Reber B. F., Reuter H. Regulation of bradykinin- and ATP-activated Ca(2+)-permeable channels in rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. J Neurosci. 1991 Dec;11(12):3984–3990. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-12-03984.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parekh A. B., Terlau H., Stühmer W. Depletion of InsP3 stores activates a Ca2+ and K+ current by means of a phosphatase and a diffusible messenger. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):814–818. doi: 10.1038/364814a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randriamampita C., Tsien R. Y. Emptying of intracellular Ca2+ stores releases a novel small messenger that stimulates Ca2+ influx. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):809–814. doi: 10.1038/364809a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reber B. F., Neuhaus R., Reuter H. Activation of different pathways for calcium elevation by bradykinin and ATP in rat pheochromocytoma (PC 12) cells. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Feb;420(2):213–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00374993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallcup W. B. Sodium and calcium fluxes in a clonal nerve cell line. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:525–540. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg T. H., Newman A. S., Swanson J. A., Silverstein S. C. ATP4- permeabilizes the plasma membrane of mouse macrophages to fluorescent dyes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8884–8888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh B. C., Kim K. T. Inhibition by ethaverine of catecholamine secretion through blocking L-type Ca2+ channels in PC12 cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Mar 29;47(7):1262–1266. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90399-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh B. C., Lee C. O., Kim K. T. Signal flows from two phospholipase C-linked receptors are independent in PC12 cells. J Neurochem. 1995 Mar;64(3):1071–1079. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.64031071.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepel M., Kühnapfel S., Theilmeier G., Teupe C., Schlotmann R., Zidek W. Filling state of intracellular Ca2+ pools triggers trans plasma membrane Na+ and Ca2+ influx by a tyrosine kinase-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 21;269(42):26239–26242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley J. S., Chen R., Jamieson G. P. The ATP4- receptor-operated channel (P2Z class) of human lymphocytes allows Ba2+ and ethidium+ uptake: inhibition of fluxes by suramin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Aug 15;305(1):54–60. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Moatassim C., Mani J. C., Dornand J. Extracellular ATP4- permeabilizes thymocytes not only to cations but also to low-molecular-weight solutes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 May 31;181(1-2):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90251-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Starke K. Noradrenaline-ATP co-transmission in the sympathetic nervous system. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Sep;12(9):319–324. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90587-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]