Abstract
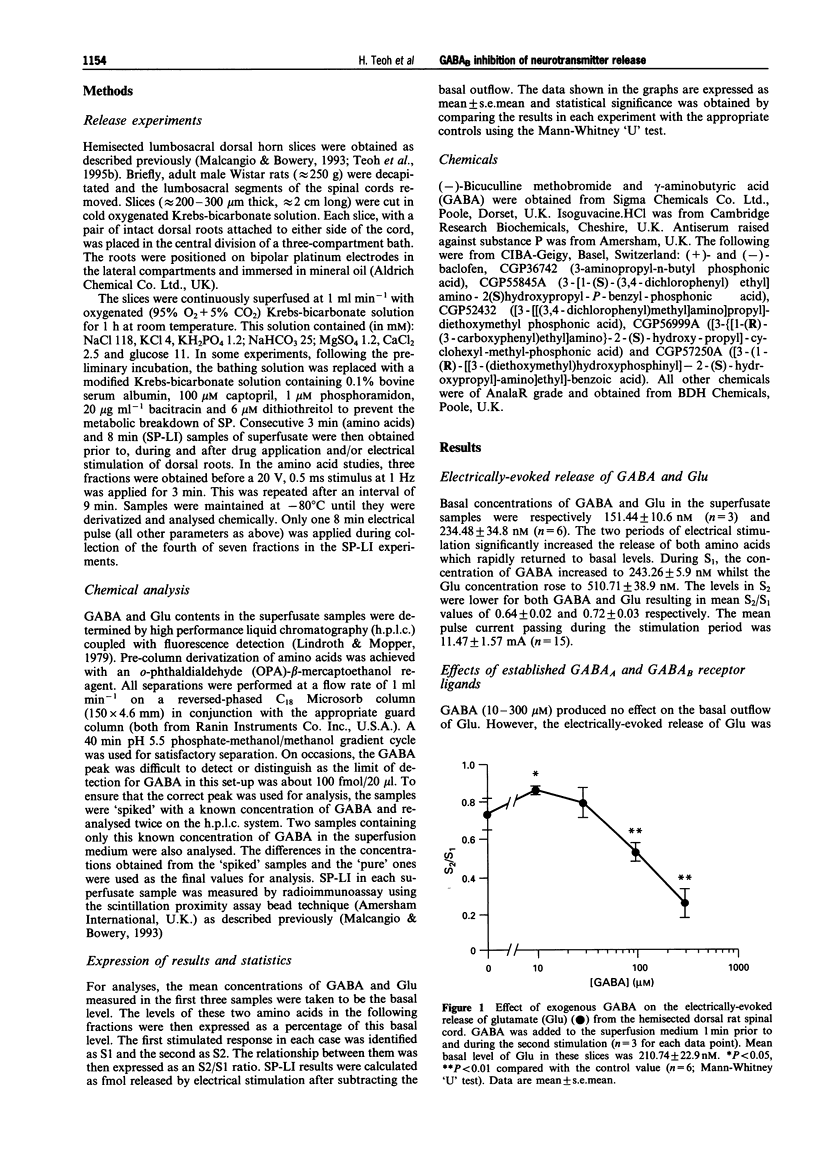
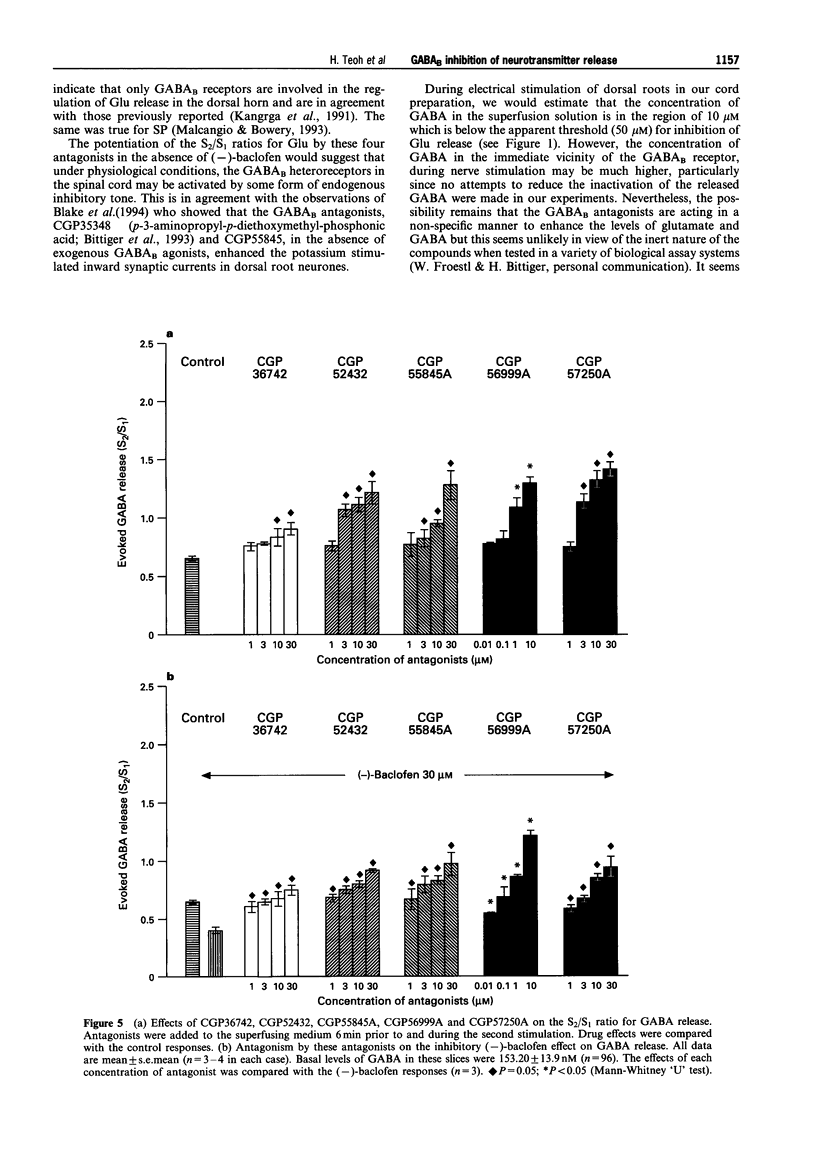
1. The effects of various GABA receptor ligands on the electrically-evoked release of endogenous GABA, glutamate and substance P-like immunoreactivity from the dorsal horn of rat isolated spinal cord were examined. 2. Exogenous GABA (10-300 microM) significantly decreased the evoked, but not basal, release of endogenous glutamate in a concentration-dependent manner. The GABAA agonist, isoguvacine (1-100 microM), failed to decrease the release of glutamate although it did reduce the release of GABA. Baclofen (0.1-1000 microM), the GABAB agonist, reduced the release of GABA and glutamate in a stereospecific and concentration-dependent manner. 3. The actions of five GABAB antagonists on these release systems were compared. CGP36742, CGP52432, CGP55845A and CGP57250A significantly increased the evoked release of GABA and glutamate. They also reversed the effects of (-)-baclofen in a concentration-dependent manner. On the other hand, while CGP56999A had no effect on glutamate release, it was an effective antagonist of the baclofen-induced inhibition of GABA and substance P release. 4. These results suggest that GABAB receptors on nerve terminals within the dorsal horn spinal cord may be heterogeneous. However, this is based solely on the data obtained with CGP56999A which affected only GABA and substance P, but not glutamate, release.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aanonsen L. M., Wilcox G. L. Nociceptive action of excitatory amino acids in the mouse: effects of spinally administered opioids, phencyclidine and sigma agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Oct;243(1):9–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aley K. O., Kulkarni S. K. Baclofen analgesia in mice: a GABAB-mediated response. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;13(10):681–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. A., Mitchell R. Evidence for GABAB autoreceptors in median eminence. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Dec 3;118(3):355–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber R. P., Vaughn J. E., Saito K., McLaughlin B. J., Roberts E. GABAergic terminals are presynaptic to primary afferent terminals in the substantia gelatinosa of the rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1978 Feb 3;141(1):35–55. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90615-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P. A., Wicki P., Stierlin C., Waldmeier P. C. Investigations on GABAB receptor-mediated autoinhibition of GABA release. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Jan-Feb;341(1-2):88–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00195063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoliel J. J., Bourgoin S., Mauborgne A., Pohl M., Legrand J. C., Hamon M., Cesselin F. GABA, acting at both GABAA and GABAB receptors, inhibits the release of cholecystokinin-like material from the rat spinal cord in vitro. Brain Res. 1992 Sep 11;590(1-2):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91103-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittiger H., Froestl W., Mickel S., Olpe H. R. GABAB receptor antagonists: from synthesis to therapeutic applications. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Nov;14(11):391–394. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90056-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonanno G., Cavazzani P., Andrioli G. C., Asaro D., Pellegrini G., Raiteri M. Release-regulating autoreceptors of the GABAB-type in human cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;96(2):341–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11823.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonanno G., Pellegrini G., Asaro D., Fontana G., Raiteri M. GABAB autoreceptors in rat cortex synaptosomes: response under different depolarizing and ionic conditions. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar 7;172(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(89)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonanno G., Raiteri M. Functional evidence for multiple gamma-aminobutyric acidB receptor subtypes in the rat cerebral cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jul;262(1):114–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonanno G., Raiteri M. Multiple GABAB receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Jul;14(7):259–261. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G. GABAB receptor pharmacology. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993;33:109–147. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.33.040193.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L. Characteristics of GABAB receptor binding sites on rat whole brain synaptic membranes. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan;78(1):191–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb09380.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L., Doble A., Middlemiss D. N., Shaw J., Turnbull M. (-)Baclofen decreases neurotransmitter release in the mammalian CNS by an action at a novel GABA receptor. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):92–94. doi: 10.1038/283092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. J., Cantrill R. C., Oldfield M., Krogsgaard-Larsen P. Inhibition of gamma-aminobutyric acid release by gamma-aminobutyric acid agonist drugs. Pharmacology of the gamma-aminobutyric acid autoreceptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Jan;19(1):27–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G. The dorsal horn of the spinal cord. Q J Exp Physiol. 1982 Apr;67(2):193–212. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1982.sp002630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervero F., Iggo A. The substantia gelatinosa of the spinal cord: a critical review. Brain. 1980 Dec;103(4):717–772. doi: 10.1093/brain/103.4.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann U., Meyer D. K., Sperk G. Stimulation of receptors of gamma-aminobutyric acid modulates the release of cholecystokinin-like immunoreactivity from slices of rat neostriatum. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Dec;89(4):845–852. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11190.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Duggan A. W., Felix D., Johnston G. A. Bicuculline, an antagonist of GABA and synaptic inhibition in the spinal cord of the cat. Brain Res. 1971 Sep 10;32(1):69–96. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting D. A., Jordan C. C. Alternative approaches to analgesia: baclofen as a model compound. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Jun;54(2):171–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb06926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Biasi S., Rustioni A. Glutamate and substance P coexist in primary afferent terminals in the superficial laminae of spinal cord. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7820–7824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutar P., Nicoll R. A. A physiological role for GABAB receptors in the central nervous system. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):156–158. doi: 10.1038/332156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Désarmenien M., Feltz P., Occhipinti G., Santangelo F., Schlichter R. Coexistence of GABAA and GABAB receptors on A delta and C primary afferents. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Feb;81(2):327–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10082.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E., Foster A. C. Amino acid neurotransmitters and their pathways in the mammalian central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1983 Aug;9(4):701–719. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemignani A., Paudice P., Bonanno G., Raiteri M. Pharmacological discrimination between gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptors regulating cholecystokinin and somatostatin release from rat neocortex synaptosomes. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Sep;46(3):558–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R., Bowery N. G. 3H-baclofen and 3H-GABA bind to bicuculline-insensitive GABA B sites in rat brain. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):149–152. doi: 10.1038/290149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang A. S., Wilcox G. L. Baclofen, gamma-aminobutyric acidB receptors and substance P in the mouse spinal cord. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Mar;248(3):1026–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeftinija S., Jeftinija K., Liu F., Skilling S. R., Smullin D. H., Larson A. A. Excitatory amino acids are released from rat primary afferent neurons in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Apr 29;125(2):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90025-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangrga I., Jiang M. C., Randić M. Actions of (-)-baclofen on rat dorsal horn neurons. Brain Res. 1991 Oct 25;562(2):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90630-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangrga I., Larew J. S., Randic M. The effects of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide on the efflux of endogenous glutamate and aspartate from the rat spinal dorsal horn in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Jan 1;108(1-2):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90723-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangrga I., Randic M. Tachykinins and calcitonin gene-related peptide enhance release of endogenous glutamate and aspartate from the rat spinal dorsal horn slice. J Neurosci. 1990 Jun;10(6):2026–2038. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-06-02026.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr D. I., Ong J., Prager R. H., Gynther B. D., Curtis D. R. Phaclofen: a peripheral and central baclofen antagonist. Brain Res. 1987 Mar 3;405(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90999-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanza M., Fassio A., Gemignani A., Bonanno G., Raiteri M. CGP 52432: a novel potent and selective GABAB autoreceptor antagonist in rat cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jun 24;237(2-3):191–195. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90268-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. A., Proudfit H. K. Analgesia produced by microinjection of baclofen and morphine at brain stem sites. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Jul 15;57(1):43–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90102-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman J. M., Pastor G. Antinociceptive effects of baclofen and muscimol upon intraventricular administration. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Feb 8;61(3):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson D. S., Dickenson A. H. Lamina-specific effects of morphine and naloxone in dorsal horn of rat spinal cord in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Dec;66(6):1941–1950. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.66.6.1941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcangio M., Bowery N. G. Gamma-aminobutyric acidB, but not gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor activation, inhibits electrically evoked substance P-like immunoreactivity release from the rat spinal cord in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Sep;266(3):1490–1496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcangio M., Ghelardini C., Giotti A., Malmberg-Aiello P., Bartolini A. CGP 35348, a new GABAB antagonist, prevents antinociception and muscle-relaxant effect induced by baclofen. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1303–1308. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09784.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J., Price D. D., Mayer D. J. Thermal hyperalgesia in association with the development of morphine tolerance in rats: roles of excitatory amino acid receptors and protein kinase C. J Neurosci. 1994 Apr;14(4):2301–2312. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-04-02301.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The physiology of excitatory amino acids in the vertebrate central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1987;28(3):197–276. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan M. K., Hammond D. L. Intrathecal GABAB antagonists attenuate the antinociception produced by microinjection of L-glutamate into the ventromedial medulla of the rat. Brain Res. 1993 Apr 2;607(1-2):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91487-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. R., Martin I. L. Is GABA release modulated by presynaptic receptors? Nature. 1978 Aug 31;274(5674):904–905. doi: 10.1038/274904a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parpura V., Basarsky T. A., Liu F., Jeftinija K., Jeftinija S., Haydon P. G. Glutamate-mediated astrocyte-neuron signalling. Nature. 1994 Jun 30;369(6483):744–747. doi: 10.1038/369744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pende M., Lanza M., Bonanno G., Raiteri M. Release of endogenous glutamic and aspartic acids from cerebrocortex synaptosomes and its modulation through activation of a gamma-aminobutyric acidB (GABAB) receptor subtype. Brain Res. 1993 Feb 26;604(1-2):325–330. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90384-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittaluga A., Asaro D., Pellegrini G., Raiteri M. Studies on [3H]GABA and endogenous GABA release in rat cerebral cortex suggest the presence of autoreceptors of the GABAB type. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Nov 24;144(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price G. W., Wilkin G. P., Turnbull M. J., Bowery N. G. Are baclofen-sensitive GABAB receptors present on primary afferent terminals of the spinal cord? Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):71–74. doi: 10.1038/307071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfit H. K., Levy R. A. Delimitation of neuronal substrates necessary for the analgesic action of baclofen and morphine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Jan 15;47(2):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90387-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raiteri M., Bonanno G., Fedele E. Release of gamma-[3H]aminobutyric acid (GABA) from electrically stimulated rat cortical slices and its modulation by GABAB autoreceptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Aug;250(2):648–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren K., Williams G. M., Hylden J. L., Ruda M. A., Dubner R. The intrathecal administration of excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists selectively attenuated carrageenan-induced behavioral hyperalgesia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug 25;219(2):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90301-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago M., Machado A., Cano J. In vivo release of dopamine from rat striatum, substantia nigra and prefrontal cortex: differential modulation by baclofen. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):814–818. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13647.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J. GABAergic mechanisms of analgesia: an update. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1987 Feb;26(2):463–474. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(87)90148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer E., Placheta P. Reduction of [3H]muscimol binding sites in rat dorsal spinal cord after neonatal capsaicin treatment. Brain Res. 1980 Dec 8;202(2):484–487. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smullin D. H., Skilling S. R., Larson A. A. Interactions between substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide, taurine and excitatory amino acids in the spinal cord. Pain. 1990 Jul;42(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(90)91095-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorkin L. S., McAdoo D. J. Amino acids and serotonin are released into the lumbar spinal cord of the anesthetized cat following intradermal capsaicin injections. Brain Res. 1993 Apr 2;607(1-2):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91492-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teoh H., Fowler L. J., Bowery N. G. Effect of lamotrigine on the electrically-evoked release of endogenous amino acids from slices of dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. Neuropharmacology. 1995 Oct;34(10):1273–1278. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(95)00104-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmeier P. C., Wicki P., Feldtrauer J. J., Baumann P. A. Potential involvement of a baclofen-sensitive autoreceptor in the modulation of the release of endogenous GABA from rat brain slices in vitro. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;337(3):289–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00168841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmeier P. C., Wicki P., Feldtrauer J. J., Baumann P. A. The measurement of the release of endogenous GABA from rat brain slices by liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;337(3):284–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00168840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmeier P. C., Wicki P., Feldtrauer J. J., Mickel S. J., Bittiger H., Baumann P. A. GABA and glutamate release affected by GABAB receptor antagonists with similar potency: no evidence for pharmacologically different presynaptic receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1515–1521. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17168.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. R., Yaksh T. L. Baclofen is antinociceptive in the spinal intrathecal space of animals. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Oct 15;51(4):323–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90423-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




