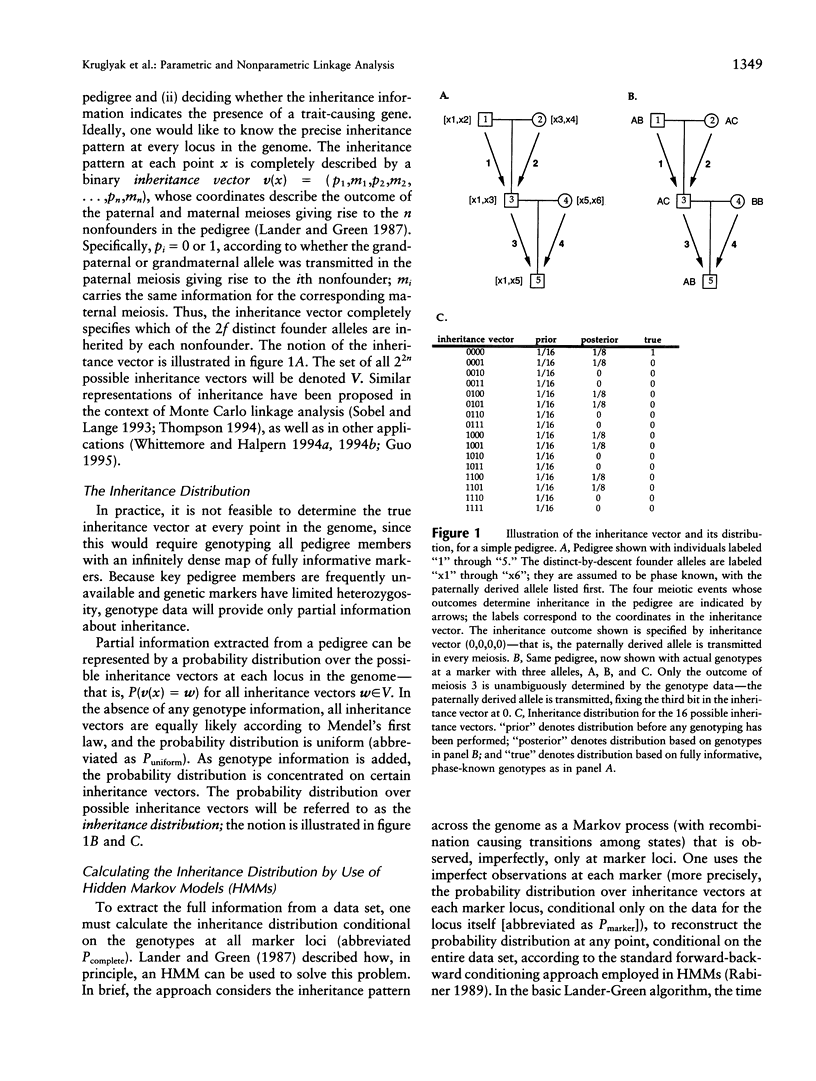
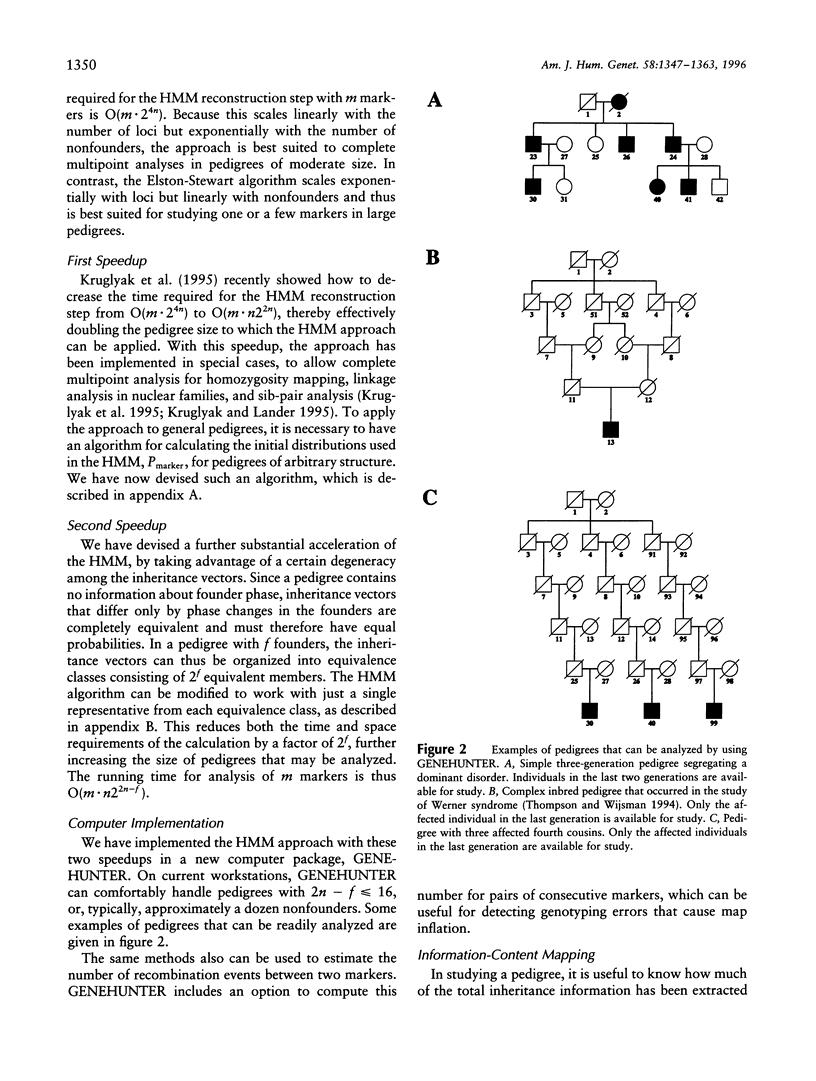
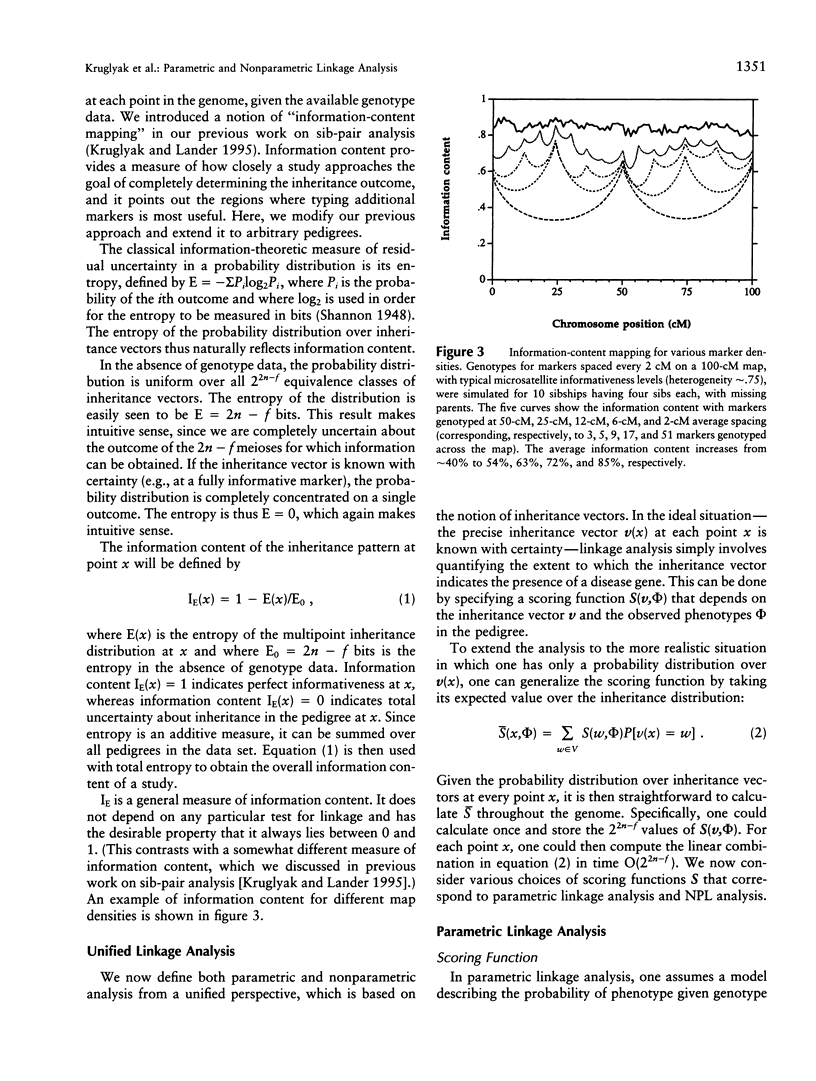
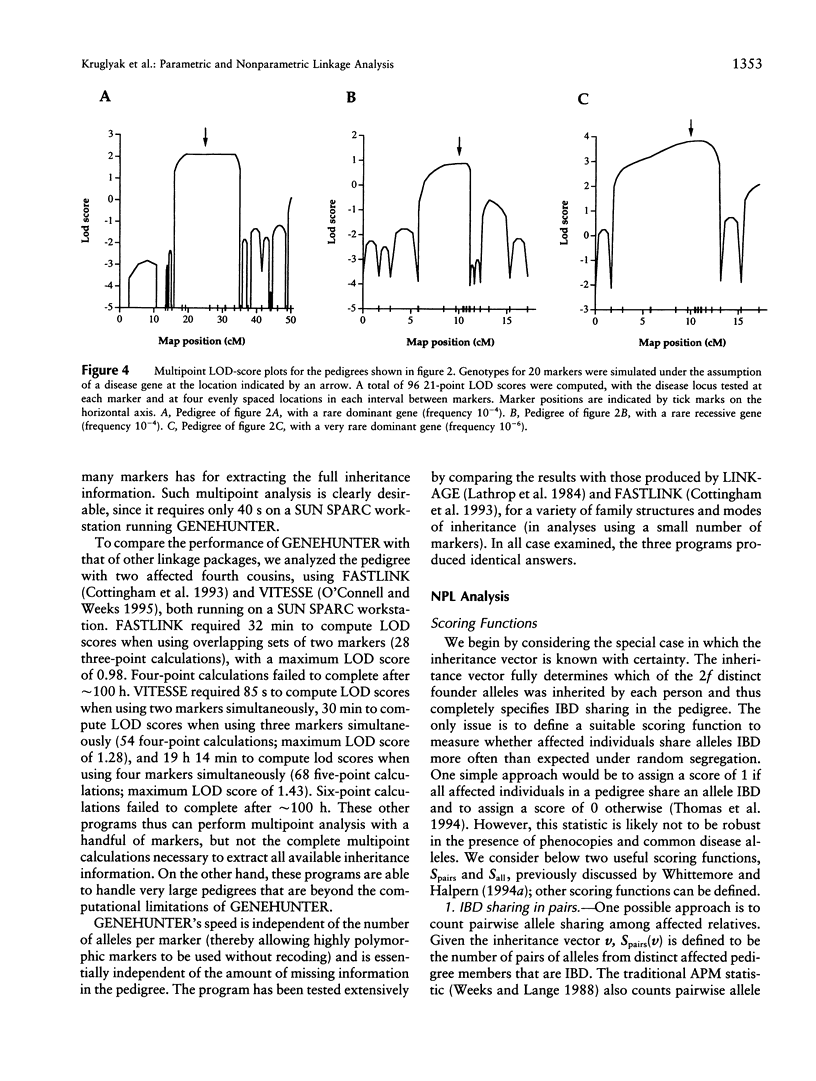
Abstract
In complex disease studies, it is crucial to perform multipoint linkage analysis with many markers and to use robust nonparametric methods that take account of all pedigree information. Currently available methods fall short in both regards. In this paper, we describe how to extract complete multipoint inheritance information from general pedigrees of moderate size. This information is captured in the multipoint inheritance distribution, which provides a framework for a unified approach to both parametric and nonparametric methods of linkage analysis. Specifically, the approach includes the following: (1) Rapid exact computation of multipoint LOD scores involving dozens of highly polymorphic markers, even in the presence of loops and missing data. (2) Non-parametric linkage (NPL) analysis, a powerful new approach to pedigree analysis. We show that NPL is robust to uncertainty about mode of inheritance, is much more powerful than commonly used nonparametric methods, and loses little power relative to parametric linkage analysis. NPL thus appears to be the method of choice for pedigree studies of complex traits. (3) Information-content mapping, which measures the fraction of the total inheritance information extracted by the available marker data and points out the regions in which typing additional markers is most useful. (4) Maximum-likelihood reconstruction of many-marker haplotypes, even in pedigrees with missing data. We have implemented NPL analysis, LOD-score computation, information-content mapping, and haplotype reconstruction in a new computer package, GENEHUNTER. The package allows efficient multipoint analysis of pedigree data to be performed rapidly in a single user-friendly environment.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babron M. C., Martinez M., Bonaïti-Pellié C., Clerget-Darpoux F. Linkage detection by the Affected-Pedigree-Member method: what is really tested? Genet Epidemiol. 1993;10(6):389–394. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370100610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerget-Darpoux F., Bonaïti-Pellié C., Hochez J. Effects of misspecifying genetic parameters in lod score analysis. Biometrics. 1986 Jun;42(2):393–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottingham R. W., Jr, Idury R. M., Schäffer A. A. Faster sequential genetic linkage computations. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):252–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D., Sham P. C. Using risk calculation to implement an extended relative pair analysis. Ann Hum Genet. 1994 May;58(Pt 2):151–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1994.tb01884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C., Stewart J. A general model for the genetic analysis of pedigree data. Hum Hered. 1971;21(6):523–542. doi: 10.1159/000152448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo S. W. Proportion of genome shared identical by descent by relatives: concept, computation, and applications. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jun;56(6):1468–1476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruglyak L., Daly M. J., Lander E. S. Rapid multipoint linkage analysis of recessive traits in nuclear families, including homozygosity mapping. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Feb;56(2):519–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruglyak L., Lander E. S. Complete multipoint sib-pair analysis of qualitative and quantitative traits. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Aug;57(2):439–454. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Green P. Construction of multilocus genetic linkage maps in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2363–2367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Elston R. C. Extensions to pedigree analysis I. Likehood calculations for simple and complex pedigrees. Hum Hered. 1975;25(2):95–105. doi: 10.1159/000152714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., White R. L. Construction of human linkage maps: likelihood calculations for multilocus linkage analysis. Genet Epidemiol. 1986;3(1):39–52. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370030105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. Sequential tests for the detection of linkage. Am J Hum Genet. 1955 Sep;7(3):277–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell J. R., Weeks D. E. The VITESSE algorithm for rapid exact multilocus linkage analysis via genotype set-recoding and fuzzy inheritance. Nat Genet. 1995 Dec;11(4):402–408. doi: 10.1038/ng1295-402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel E., Lange K. Metropolis sampling in pedigree analysis. Stat Methods Med Res. 1993;2(3):263–282. doi: 10.1177/096228029300200305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
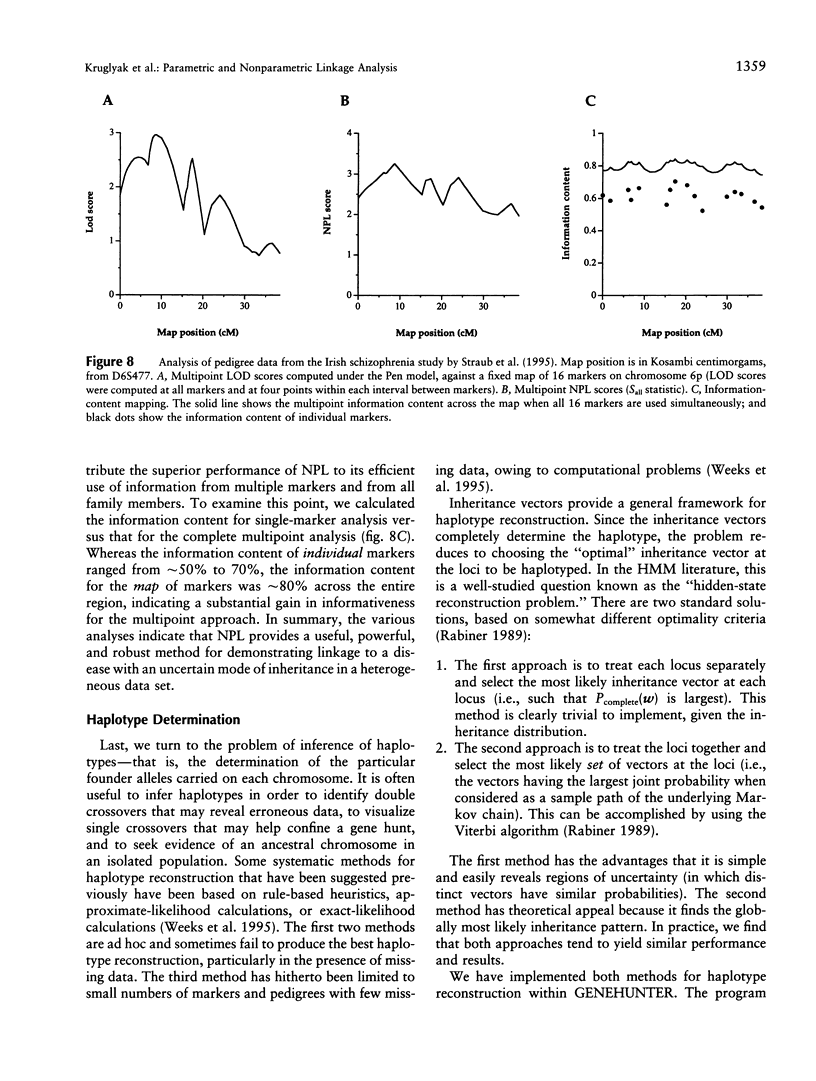
- Straub R. E., MacLean C. J., O'Neill F. A., Burke J., Murphy B., Duke F., Shinkwin R., Webb B. T., Zhang J., Walsh D. A potential vulnerability locus for schizophrenia on chromosome 6p24-22: evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):287–293. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A., Skolnick M. H., Lewis C. M. Genomic mismatch scanning in pedigrees. IMA J Math Appl Med Biol. 1994;11(1):1–16. doi: 10.1093/imammb/11.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. E., Harby L. D. The affected-pedigree-member method: power to detect linkage. Hum Hered. 1995 Jan-Feb;45(1):13–24. doi: 10.1159/000154250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. E., Lange K. The affected-pedigree-member method of linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):315–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. E., Sobel E., O'Connell J. R., Lange K. Computer programs for multilocus haplotyping of general pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jun;56(6):1506–1507. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittemore A. S., Halpern J. A class of tests for linkage using affected pedigree members. Biometrics. 1994 Mar;50(1):118–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zara F., Bianchi A., Avanzini G., Di Donato S., Castellotti B., Patel P. I., Pandolfo M. Mapping of genes predisposing to idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Jul;4(7):1201–1207. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.7.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


