Full text
PDF



















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CASMAN E. P., BENNETT R. W. DETECTION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL ENTEROTOXIN IN FOOD. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:181–189. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.181-189.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASMAN E. P., BERGDOLL M. S., ROBINSON J. DESIGNATION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL EXTEROTOXINS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Mar;85:715–716. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.3.715-716.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
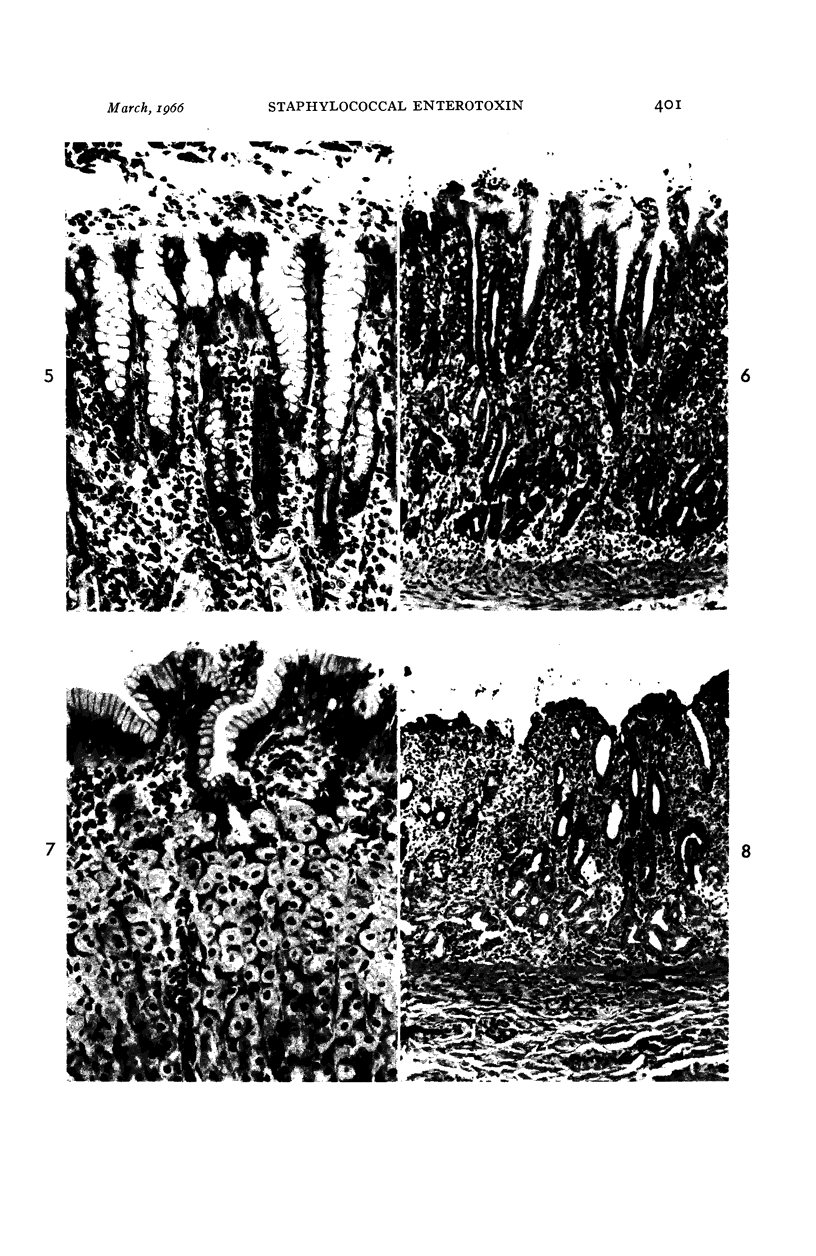
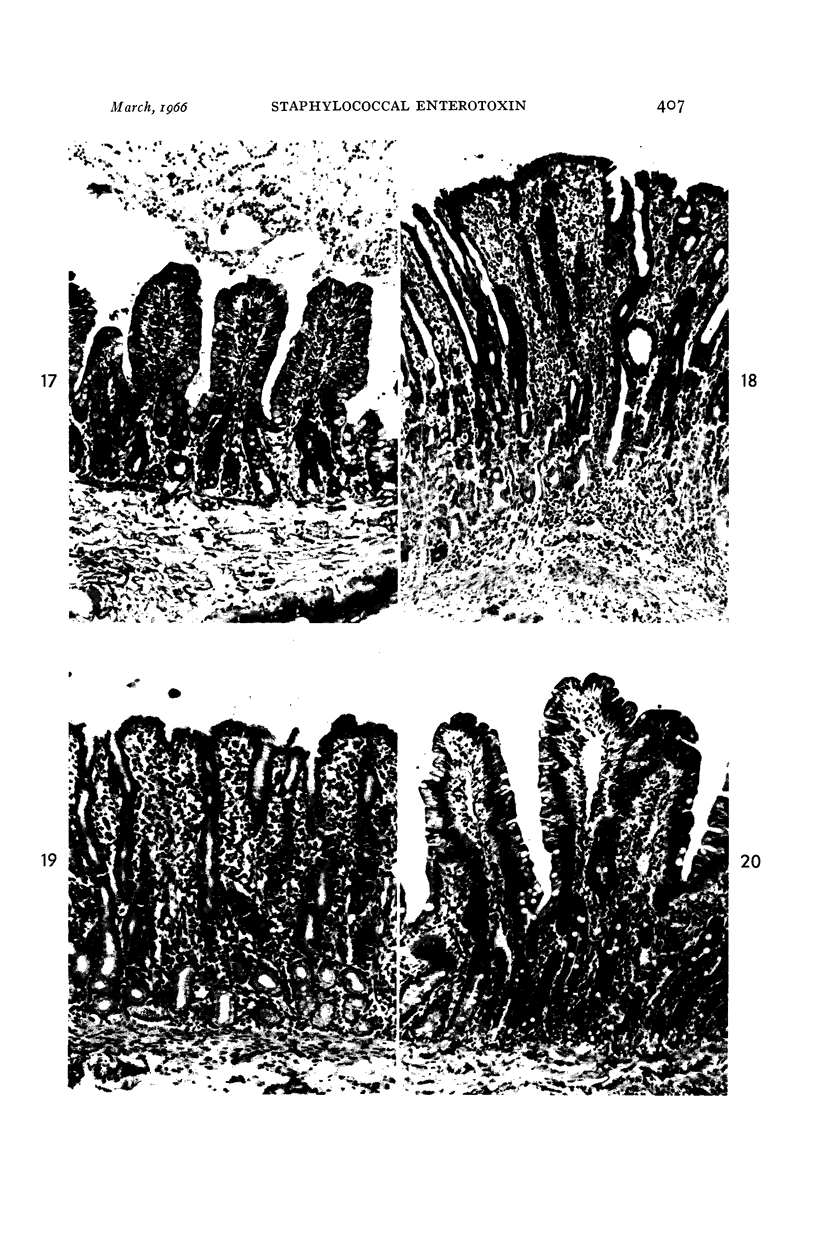
- COLLINS J. R. SMALL INTESTINAL MUCOSAL DAMAGE WITH VILLOUS ATROPHY.A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Jul;44:36–44. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/44.1.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELSENFELD O., NASUNIYA N. STAPHYLOCOCCAL ANTITOXIN VALUES IN THE SERA OF PERMANENT RESIDENTS AND VISITORS IN THAILAND. J Trop Med Hyg. 1964 Dec;67:300–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., LABREC E. H., KENT T. H., FALKOW S. ABORTIVE INTESTINAL INFECTION WITH AN ESCHERICHIA COLI-SHIGELLA FLEXNERI HYBRID STRAIN. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1374–1382. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1374-1382.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALMER E. D. The morphologic consequences of acute exogenous (Staphylococcic) gastroenteritis on the gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1951 Nov;19(3):462–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPRINZ H., SRIBHIBHADH R., GANGAROSA E. J., BENYAJATI C., KUNDEL D., HALSTEAD S. Biopsy of small bowel of Thai people. With special reference to recovery from Asiatic cholera and to an intestinal malabsorption syndrome. Am J Clin Pathol. 1962 Jul;38:43–51. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/38.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUGIYAMA H., CHOW K. L., DRAGSTEDT L. R., 2nd Study of emetic receptor sites for staphylococcal enterotoxin in monkeys. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Oct;108:92–95. doi: 10.3181/00379727-108-26855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SURGALLA M. J., BERGDOLL M. S., DACK G. M. Some observations on the assay of staphylococcal enterotoxin by the monkey-feeding test. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 May;41(5):782–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWANSON V. L., THOMASSEN R. W. PATHOLOGY OF THE JEJUNAL MUCOSA IN TROPICAL SPRUE. Am J Pathol. 1965 Apr;46:511–551. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spero L., Stefanye D., Brecher P. I., Jacoby H. M., Dalidowicz J. E., Schantz E. J. Amino acid composition and terminal amino acids of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1024–1030. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOKII S., TSUKAMOTO A. The distribution of parietal cells in the stomach in monkeys. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn. 1953 Mar;25(1):27–36. doi: 10.2535/ofaj1936.25.1_27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN S. E., JACOBSON M., MIRANY J., PROHASKA J. V. ACUTE AND CHRONIC ENTEROTOXIN ENTERITIS. J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 1;120:561–568. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.4.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN S. E., SUGIYAMA H., PROHASKA J. V. Correlation of staphylococcal enterotoxins with experimentally induced enterocolitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1963 Jan;116:29–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON B. J. Comparative susceptibility of chimpanzees and Macaca mulatta monkeys to oral administration of partially purified staphylococcal enterotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1959 Aug;78:240–242. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.2.240-242.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagman J., Edwards R. C., Schantz E. J. Molecular size, homogeneity, and hydrodynamic properties of purified staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1017–1023. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]