Abstract
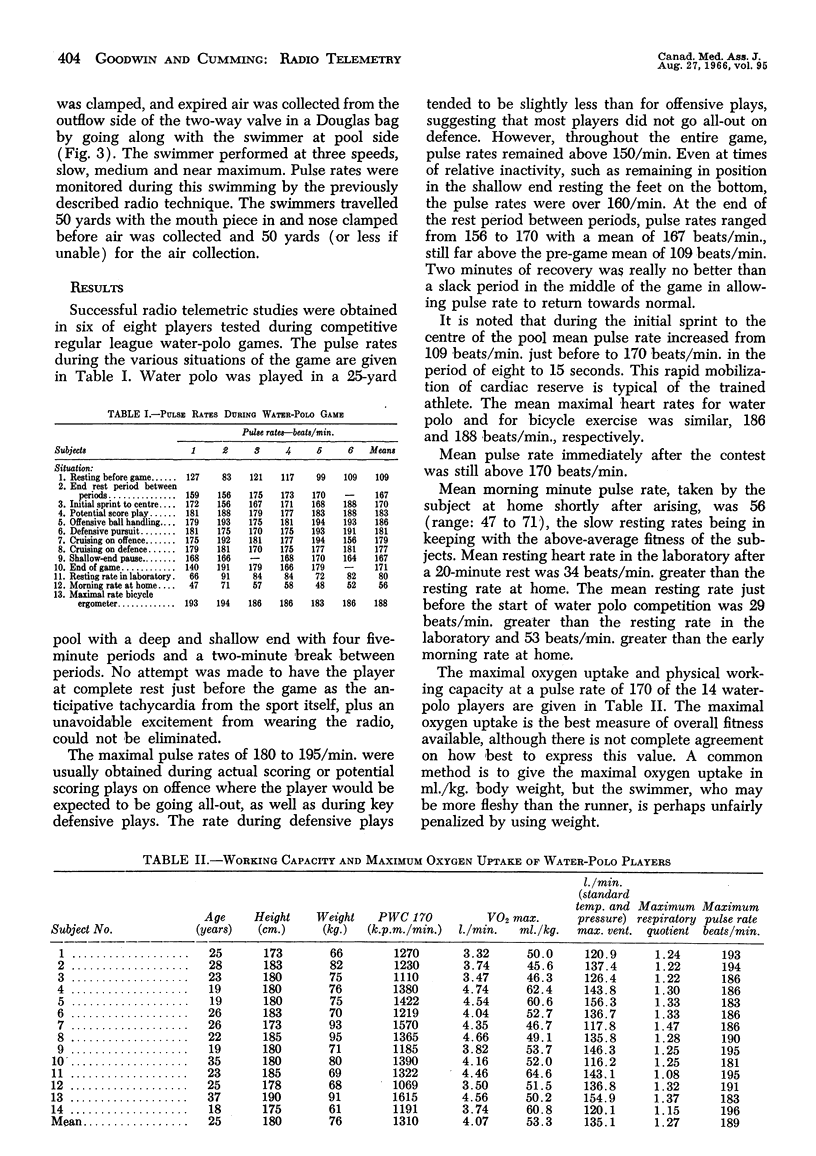
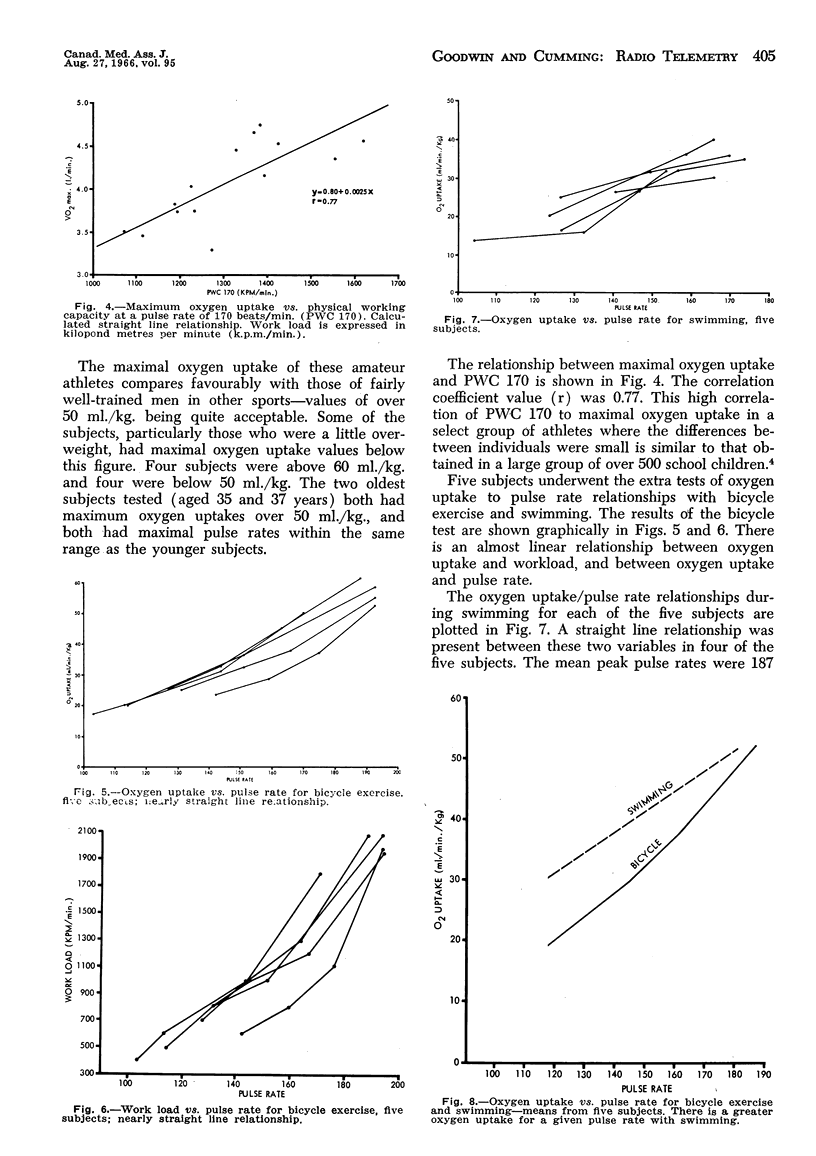
During competitive water polo, heart rate in six subjects was monitored by cupped plastic and silver electrodes glued to the skin. Minimum rates during the game averaged 156 beats/min.; maximum rates averaged 186 beats/min. Mean maximum rate with bicycle exercise was 188 beats/min. Maximum oxygen (VO2 max.) with bicycle exercise of 14 water-polo players was 53.3 ml./kg. Physical working capacity (PWC 170) was 1310 kilopond metres per square metre (k.p.m./sq.m.). PWC 170 correlated well with VO2 max. in this small group (r = 0.77).
Oxygen uptake was measured at three speeds of swimming and four levels of work on a bicycle ergometer. VO2 max. of swimming was 88% of that obtained on bicycle exercise. The slope of the oxygen uptake vs. pulse rate curves was less for the swimming than for cycling, so that for a given oxygen uptake below the maximal, pulse rate was less in the swimmers. At near-maximal swimming, respiratory quotient was 0.95 compared with 1.27 for cycling, suggesting that the swimmers were underbreathing.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEHRMANN V. G., HARTMAN F. W. Rapid CO2 determination with the Beckman O2 analyzer. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Nov;78(2):412–416. doi: 10.3181/00379727-78-19088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMING G. R., CUMMING P. M. Working capacity of normal children tested on a bicycle ergometer. Can Med Assoc J. 1963 Feb 16;88:351–355. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]