Abstract
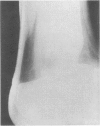
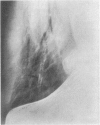
Xanthomatous infiltration of tendons is a clinical feature common to many cases of hyperlipidemia. The xanthomas can be detected and only grossly assessed by palpation. This report describes a radiological technique used to assess these lesions at the Achilles tendon level. The “mammography technique” applied to the study of Achilles tendons was used in 32 normolipemic subjects and 32 hyperlipidemic patients. Both tendons could be observed in their entire length and their thickness, greatly increased in xanthomatosis, could be accurately measured. The results of this survey suggest that the radiological approach may provide a useful tool for the routine evaluation and follow-up of tendon xanthomas.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blankenhorn D. H., Meyers H. I. Radiographic determination of Achilles tendon xanthoma size. Metabolism. 1969 Nov;18(11):882–886. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(69)90027-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson D. S., Levy R. I., Lees R. S. Fat transport in lipoproteins--an integrated approach to mechanisms and disorders. N Engl J Med. 1967 Feb 2;276(5):273–concl. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196702022760507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERSHON-COHEN J., FORMAN M. MAMMOGRAPHY OF CANCER. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1964 Sep;40:674–689. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBERT P. D., KAIN T. M., MARCH H. C. Hypercholesteremic xanthomata of the tendons. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1957 Jan;77(1):109–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GURAVICH J. L. Familial hypercholesteremic xanthomatosis: a preliminary report. I. Clinical, electrocardiographic and laboratory considerations. Am J Med. 1959 Jan;26(1):8–29. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(59)90323-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattereau A., Davignon J., Levesque H. P. Roentgenological evaluation of Achilles-tendon xanthomatosis. Lancet. 1971 Sep 25;2(7726):705–706. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92271-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS-JONES J. N., JONES E. G., WELLS P. G. Xanthomatosis and essential hypercholesterolaemia. Lancet. 1957 Apr 27;272(6974):855–857. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)91390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEONARD J. C. Hereditary hypercholesterolaemic xanthomatosis. Lancet. 1956 Dec 15;271(6955):1239–1242. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitter-Hauge S. "Juvenile" xanthomatosis--a recessive inherited disease? Acta Med Scand. 1966 Jan;179(1):71–76. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1966.tb05434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippart M., Van Bogaert L. Cholestanolosis (cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis). A follow-up study on the original family. Arch Neurol. 1969 Dec;21(6):603–610. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480180059004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNEIDER P. Xanthoma of the calcaneus. Br J Radiol. 1963 Mar;36:222–223. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-36-423-222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintrob L. A case of type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia with xanthomata. Br J Radiol. 1971 Mar;44(519):215–218. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-44-519-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]