Abstract
Amycolatopsis methanolica contains a 13.3-kb plasmid (pMEA300) which is present both in the free state and integrated at a unique genomic location. A 2.1-kb pMEA300 DNA fragment was sequenced, revealing the putative attP site and two open reading frames, xis and int, showing similarity to genes encoding excisionases and integrases, respectively.
Full text
PDF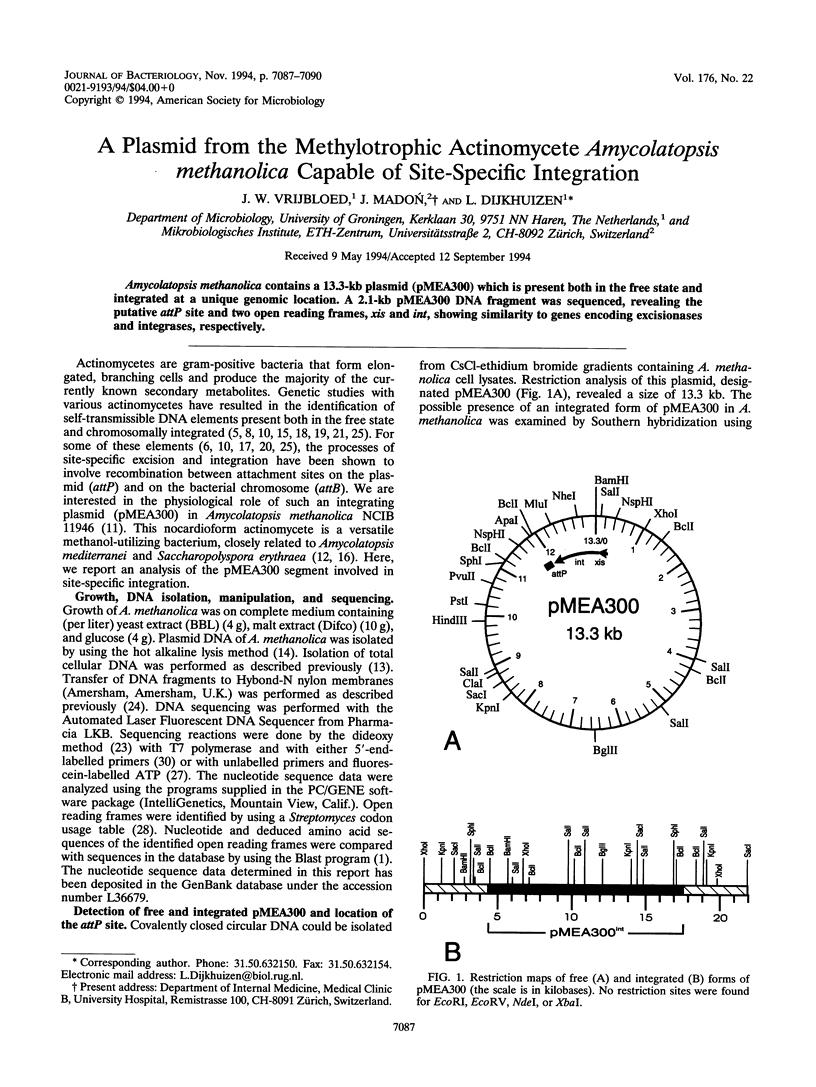



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argos P., Landy A., Abremski K., Egan J. B., Haggard-Ljungquist E., Hoess R. H., Kahn M. L., Kalionis B., Narayana S. V., Pierson L. S., 3rd The integrase family of site-specific recombinases: regional similarities and global diversity. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):433–440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Nir D., Cohen A., Goedeke M. E. tDNA(ser) sequences are involved in the excision of Streptomyces griseus plasmid pSG1. Gene. 1992 Dec 1;122(1):71–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90033-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Cohen S. N. Gene expression in Streptomyces: construction and application of promoter-probe plasmid vectors in Streptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(2):265–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00331128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Ward J. M., Kieser T., Cohen S. N., Hopwood D. A. Excision of chromosomal DNA sequences from Streptomyces coelicolor forms a novel family of plasmids detectable in Streptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):230–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00272910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boccard F., Smokvina T., Pernodet J. L., Friedmann A., Guérineau M. Structural analysis of loci involved in pSAM2 site-specific integration in Streptomyces. Plasmid. 1989 Jan;21(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(89)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boccard F., Smokvina T., Pernodet J. L., Friedmann A., Guérineau M. The integrated conjugative plasmid pSAM2 of Streptomyces ambofaciens is related to temperate bacteriophages. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):973–980. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03460.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. P., Chiang S. J., Tuan J. S., Katz L. Site-specific integration in Saccharopolyspora erythraea and multisite integration in Streptomyces lividans of actinomycete plasmid pSE101. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2287–2295. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2287-2295.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. P., Idler K. B., Backer D. M., Donadio S., Katz L. Characterization of the genes and attachment sites for site-specific integration of plasmid pSE101 in Saccharopolyspora erythraea and Streptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet. 1994 Jan;242(2):185–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00391012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. P., Idler K. B., Katz L. Characterization of the genetic elements required for site-specific integration of plasmid pSE211 in Saccharopolyspora erythraea. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1877–1888. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1877-1888.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintermann G., Crameri R., Vögtli M., Hütter R. Streptomycin-sensitivity in Streptomyces glaucescens is due to deletions comprising the structural gene coding for a specific phosphotransferase. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):513–520. doi: 10.1007/BF00436201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Hintermann G., Kieser T., Wright H. M. Integrated DNA sequences in three streptomycetes form related autonomous plasmids after transfer to Streptomyces lividans. Plasmid. 1984 Jan;11(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madon J., Moretti P., Hütter R. Site-specific integration and excision of pMEA100 in Nocardia mediterranei. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):257–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00329651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretti P., Hintermann G., Hütter R. Isolation and characterization of an extrachromosomal element from Nocardia mediterranei. Plasmid. 1985 Sep;14(2):126–133. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omer C. A., Cohen S. N. Plasmid formation in Streptomyces: excision and integration of the SLP1 replicon at a specific chromosomal site. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):429–438. doi: 10.1007/BF00436190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omer C. A., Cohen S. N. Structural analysis of plasmid and chromosomal loci involved in site-specific excision and integration of the SLP1 element of Streptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):999–1006. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.999-1006.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernodet J. L., Simonet J. M., Guérineau M. Plasmids in different strains of Streptomyces ambofaciens: free and integrated form of plasmid pSAM2. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;198(2):35–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00328697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Yeats S. Transfer RNA genes frequently serve as integration sites for prokaryotic genetic elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1907–1914. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosio M., Madoń J., Hütter R. Excision of pIJ408 from the chromosome of Streptomyces glaucescens and its transfer into Streptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jul;218(1):169–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00330580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vögtli M., Cohen S. N. The chromosomal integration site for the Streptomyces plasmid SLP1 is a functional tRNA(Tyr) gene essential for cell viability. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Oct;6(20):3041–3050. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright F., Bibb M. J. Codon usage in the G+C-rich Streptomyces genome. Gene. 1992 Apr 1;113(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90669-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu B., Madoń J., Häusler A., Hütter R. Amplification on the Amycolatopsis (Nocardia) mediterranei plasmid pMEA100: sequence similarities to actinomycete att sites. Plasmid. 1990 Sep;24(2):132–142. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(90)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann J., Voss H., Schwager C., Stegemann J., Erfle H., Stucky K., Kristensen T., Ansorge W. A simplified protocol for fast plasmid DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1067–1067. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer L., Dijkhuizen L., Grobben G., Goodfellow M., Stackebrandt E., Parlett J. H., Whitehead D., Witt D. Amycolatopsis methanolica sp. nov., a facultatively methylotrophic actinomycete. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;40(2):194–204. doi: 10.1099/00207713-40-2-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]