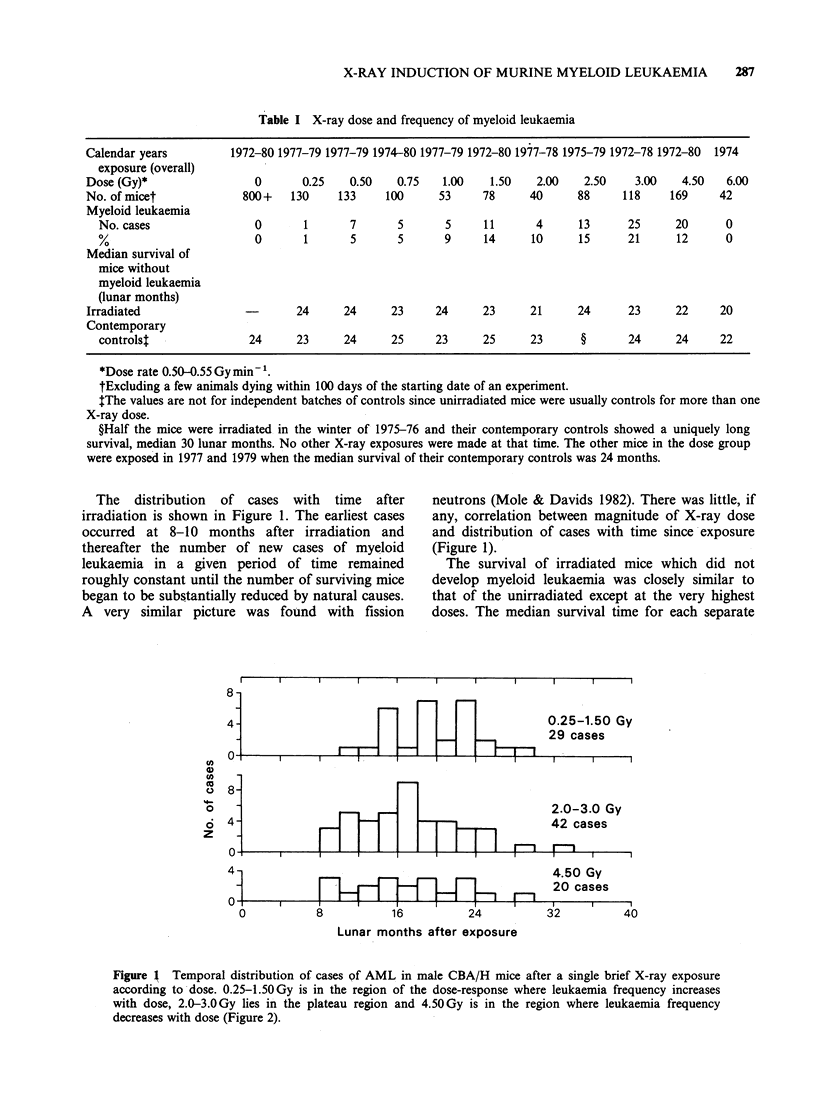
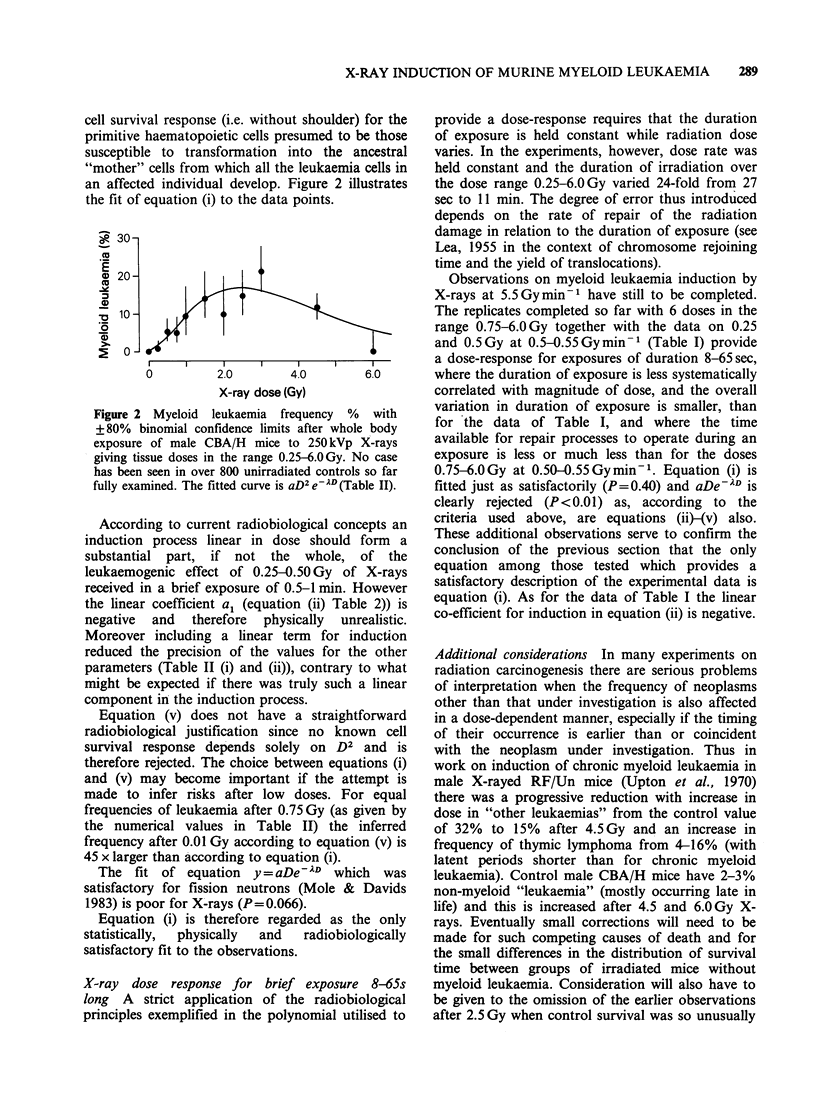
Abstract
The form of the dose-response for induction of malignant diseases in vivo by ionizing radiation is not yet established in spite of its scientific interest and its practical importance. Considerably extended observations have confirmed that the dose-response for acute myeloid leukaemia induced in male CBA/H mice by X-ray exposure is highly curvilinear. The dose-response was well fitted by the expression aD2e-lambda D (D = dose) in agreement with induction at the cellular level in proportion to D2 over the whole dose range 0.25-6.0 Gy. The factor e-lambda D accounts for the inescapable concomitant inactivating action of the inducing irradiation. The quantitative aspects of induction of myeloid leukaemia by ionizing radiation are unlike the induction of genetic mutation or cell inactivation and suggest that interaction of two adjoining cells is an essential element in radiation leukaemogenesis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. M. The shape of the dose-response curve for radiation carcinogenesis. Extrapolation to low doses. Radiat Res. 1977 Jul;71(1):34–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORP M. J. Whole body x-irradiation of experimental animals; a short summary of the methods used at the M.R.C. Radiobiological Research Unit, A.E.R.E., Harwell, between 1949-1956. Phys Med Biol. 1957 Apr;1(4):370–379. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/1/4/306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fertil B., Deschavanne P. J., Lachet B., Malaise E. P. In vitro radiosensitivity of six human cell lines: a comparative study with different statistical models. Radiat Res. 1980 May;82(2):297–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Major I. R., Mole R. H. Myeloid leukaemia in x-ray irradiated CBA mice. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):455–456. doi: 10.1038/272455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mole R. H. Carcinogenesis by thorotrast and other sources of irradiation, especially other alpha-emitters. Environ Res. 1979 Feb;18(1):192–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mole R. H. Ionizing radiation as a carcinogen: practical questions and academic pursuits The Silvanus Thompson Memorial Lecture delivered at The British Institute of Radiology on April 18, 1974. Br J Radiol. 1975 Mar;48(567):157–169. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-48-567-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mole R. H. RBE for carcinogenesis by fission neutrons. Health Phys. 1979 Mar;36(3):463–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton A. C., Randolph M. L., Conklin J. W., Kastenbaum M. A., Slater M., Melville G. S., Jr, Conte F. P., Sproul J. A., Jr Late effects of fast neutrons and gamma-rays in mice as influenced by the dose rate of irradiation: induction of neoplasia. Radiat Res. 1970 Mar;41(3):467–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


