Abstract
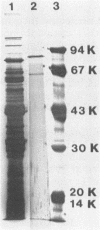
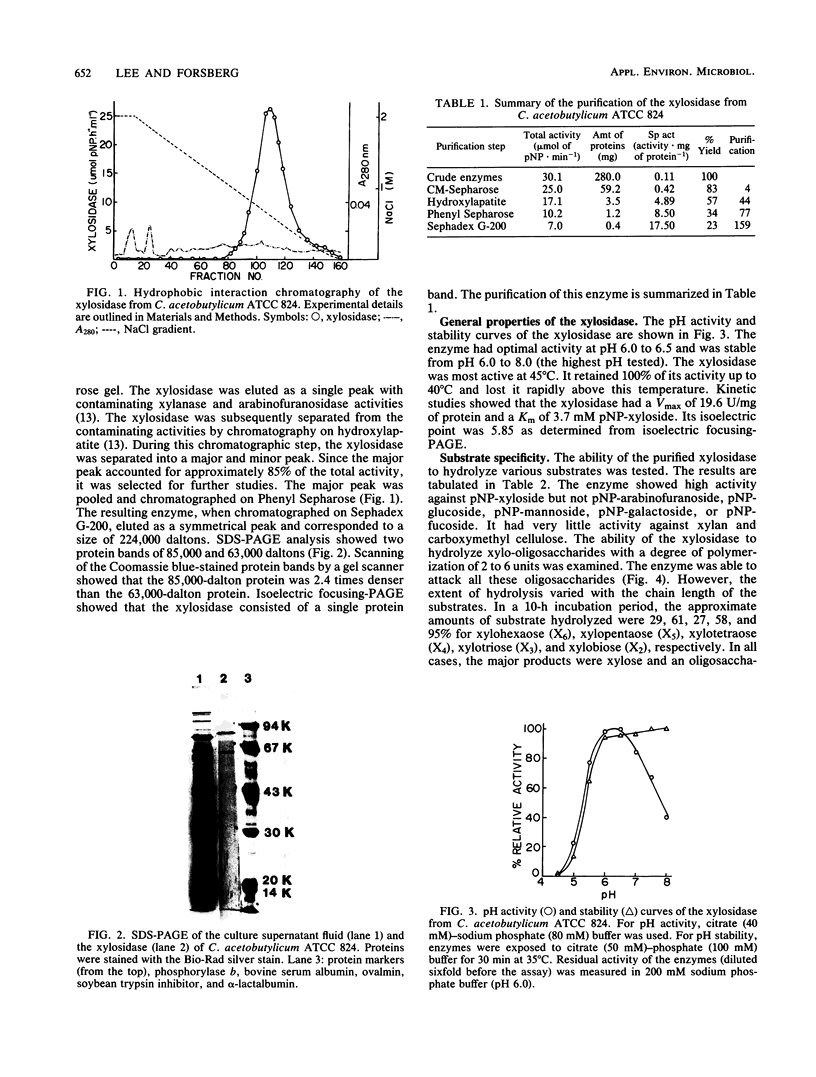
A β-d-xylosidase from C. acetobutylicum ATCC 824 was purified by column chromatography on CM-Sepharose, hydroxylapatite, Phenyl Sepharose, and Sephadex G-200. The enzyme had an apparent molecular weight of 224,000 as estimated by gel filtration. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis showed that the enzyme consisted of two subunits of 85,000 and one subunit of 63,000 daltons. It exhibited optimal activity at pH 6.0 to 6.5 and 45°C. the enzyme had an isoelectric point of 5.85. It hydrolyzed p-nitrophenylxyloside readily with a Km of 3.7 mM. The enzyme hydrolyzed xylo-oligosaccharides with chain lengths of 2 to 6 units by cleaving a single xylose from the chain end. It showed little or no activity against xylan, carboxymethyl cellulose, and other p-nitrophenylglycosides.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deleyn F., Claeyssens M., Van Beeumen J., De Bruyne C. K. Purification and properties of beta-xylosidase from Penicillium wortmanni. Can J Biochem. 1978 Jan;56(1):43–50. doi: 10.1139/o78-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve L. C., Labavitch J. M., Hungate R. E. alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase from Ruminococcus albus 8: purification and possible role in hydrolysis of alfalfa cell wall. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):1135–1140. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.1135-1140.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt R. A., Stephens G. M., Morris J. G. Production of Solvents by Clostridium acetobutylicum Cultures Maintained at Neutral pH. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1166–1170. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1166-1170.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Gibbins L. N., Forsberg C. W. Transmembrane pH gradient and membrane potential in Clostridium acetobutylicum during growth under acetogenic and solventogenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):1043–1047. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.1043-1047.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John M., Schmidt B., Schmidt J. Purification and some properties of five endo-1,4-beta-D-xylanases and a beta-D-xylosidase produced by a strain of Aspergillus niger. Can J Biochem. 1979 Feb;57(2):125–134. doi: 10.1139/o79-016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersters-Hilderson H., Loontiens F. G., Claeyssens M., De Bruyne C. K. Partial purification and properties of an induced beta-D-xylosidase of Bacillus pumilus 12. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jan;7(3):434–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. F., Forsberg C. W., Gibbins L. N. Xylanolytic Activity of Clostridium acetobutylicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):1068–1076. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.1068-1076.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. F., Forsberg C. W., Rattray J. B. Purification and Characterization of Two Endoxylanases from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):644–650. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.644-650.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panbangred W., Kawaguchi O., Tomita T., Shinmyo A., Okada H. Isolation of two beta-xylosidase genes of Bacillus pumilus and comparison of their gene products. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):267–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly P. J. Xylanases: structure and function. Basic Life Sci. 1981;18:111–129. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3980-9_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenishi S., Tsujisaka Y., Fukumoto J. Studies on hemicellulases. IV. Purification and properties of the -xylosidase produced by Aspergillus niger van Tieghem. J Biochem. 1973 Feb;73(2):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]