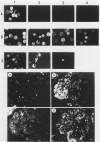
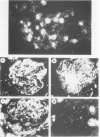
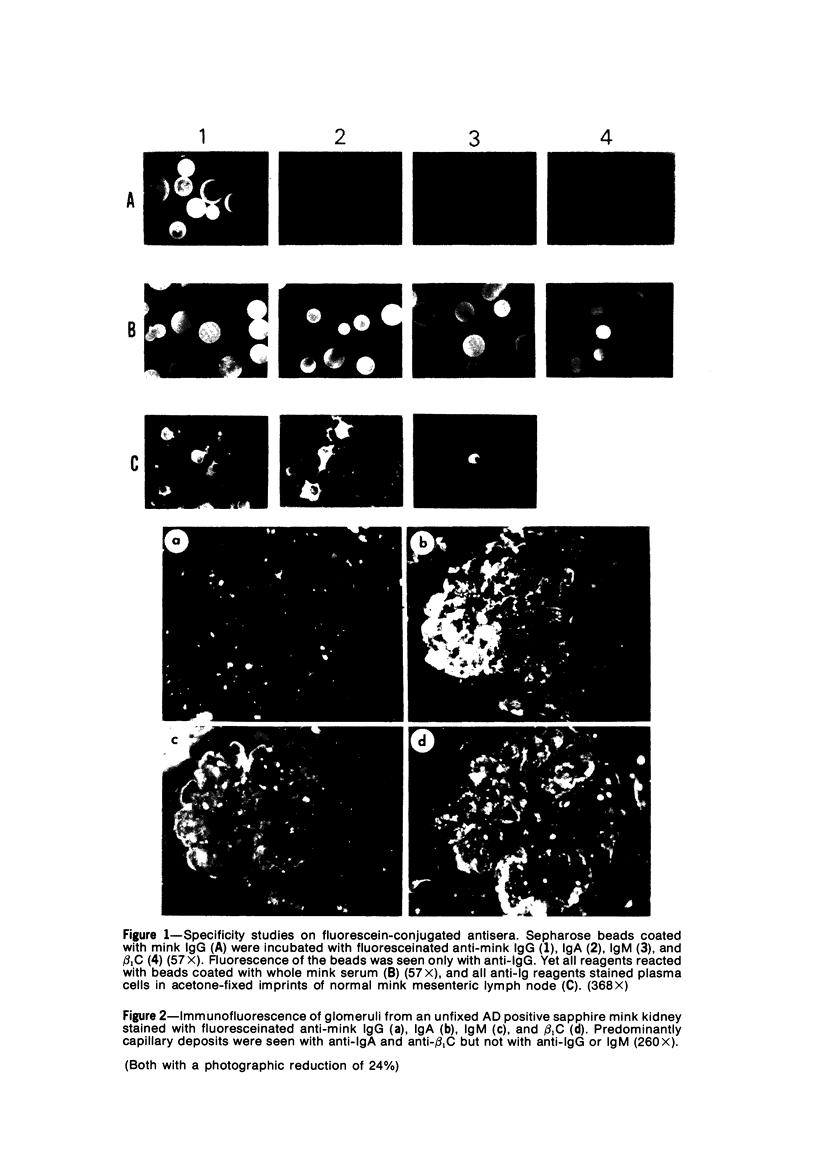
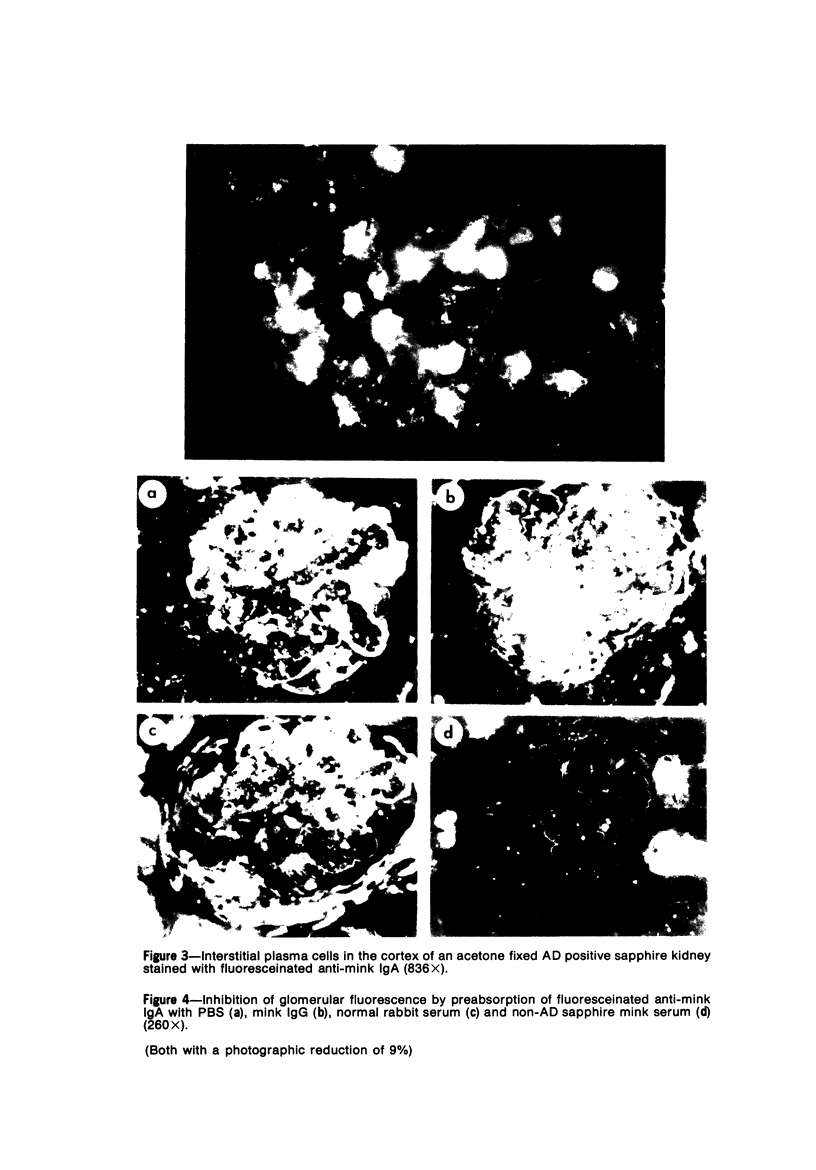
Abstract
The glomerular deposition of immunoglobulin (Ig) was studied in sapphire mink affected with terminal Aleutian disease (AD). Fluorescein conjugated Ig-class specific antiserums were used to evaluate and identify the glomerular Ig. Kidneys of all 28 mink with documented AD had deposits of IgA and beta 1 C in a capillary and mesangial distribution. Only 7 of 28 mink had demonstrable glomerular IgG and/or IgM. In addition, interstitial plasma cell infiltrates in 17 of 19 kidneys stained exclusively with anti-IgA. All antiserums used in this study were evaluated for Ig-class specificity by both gel diffusion and agarose-bead techniques. The striking Ig class restriction demonstrated for glomerular Ig deposition in AD is discussed in light of current knowledge of the pathogenesis of AD glomerulopathy.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnett E. V., Williams R. C., Jr, Kenyon A. J., Henson J. E. 'Nuclear' antigens and antinuclear antibodies in mink sera. Immunology. 1969 Feb;16(2):241–253. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Hinglais N. Les ddpôts intercapillaires d'IgA-IgG. J Urol Nephrol (Paris) 1968 Sep;74(9):694–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Hadlow W. J., Chesebro B. Aleutian disease of mink: the antibody response of sapphire and pastel mink to Aleutian disease virus. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1034–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J., Ingram D. G. Pathogenesis of aleutian disease of mink: nature of the antiglobulin reaction and elution of antibody from erythrocytes and glomeruli of infected mink. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):264–271. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.264-271.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coe J. E., Hadlow W. J. Studies on immunoglobulins of mink: definition of IgG, IgA and IgM. J Immunol. 1972 Feb;108(2):530–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coe J. E. Immunoglobulin synthesis by an SV-40-induced hamster lymphoma. Immunology. 1976 Sep;31(3):495–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Protein purification by affinity chromatography. Derivatizations of agarose and polyacrylamide beads. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3059–3065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund C. M., Hadlow W. J., Kennedy R. C., Boyle C. C., Jackson T. A. Aleutian disease of mink: properties of the etiologic agent and the host responses. J Infect Dis. 1968 Dec;118(5):510–526. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.5.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson J. B., Gorham J. R., McGuire T. C., Crawford T. B. Pathology and pathogenesis of Aleutian disease. Front Biol. 1976;44:175–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. I., Henson J. B., Gorham J. R. The influence of genotype on the development of glomerular lesions in mink with Aleutian disease virus. Am J Pathol. 1975 Nov;81(2):321–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARDINEY M. R., Jr, MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. MOUSE BETA-1C-GLOBULIN: PRODUCTION OF ANTISERUM AND CHARACTERIZATION IN THE COMPLEMENT REACTION. J Immunol. 1965 Jun;94:877–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan I. C., Tsai K. S., Karstad L. Glomerulonephritis in Aleutian disease of mink: histological and immunofluorescence studies. J Pathol. 1970 Jun;101(2):119–127. doi: 10.1002/path.1711010207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E. Aleutian disease of mink. Prog Med Virol. 1974;18(0):32–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. The pathogenesis of Aleutian disease of mink. I. In vivo viral replication and the host antibody response to viral antigen. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):575–593. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scales R. W., Jacobs N. F., Jr, Skaggs R. Use of immunoglobulin coupled to agarose beads for examining the specificity of conjugates. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Oct;2(4):292–295. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.4.292-295.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahrabadi M. S., Cho H. J., Marusyk R. G. Characterization of the protein and nucleic acid of Aleutian disease virus. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):353–362. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.353-362.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautwein G., Seidler D. Untersuchungen über die Pathogenese der Aleutenkrankheit der Nerze. V. Immunfluoreszenzmikroskopische Befunde an der niere. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1972 Feb;19(2):144–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urizar R. E., Michael A., Sisson S., Vernier R. L. Anaphylactoid purpura. II. Immunofluorescent and electron microscopic studies of the glomerular lesions. Lab Invest. 1968 Oct;19(4):437–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]