Abstract
Both a- and b-type purified flagellins from a number of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains grown in radiolabeled phosphate were shown to be phosphorylated. Analysis of partial acid-hydrolyzed flagellar filaments revealed that 32Pi was in phosphotyrosine. Three 32P-phosphopeptides apparently are common to a- and b-type flagellins, but a fourth peptide was found only in b-type hydrolysates. P. aeruginosa PAK flagellin, containing only two tyrosines, both in the variable region, was readily labeled and gave the same peptide pattern as flagellins containing additional tyrosines. Data showing that a- and b-type flagellins gave positive immunoblots with antiphosphotyrosine monoclonal antibody and that release of P(i) by alkaline phosphatase occurred indicated that unmodified tyrosine phosphate exists in flagellin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J. S., Dawson M., Drake D., Montie T. C. Electrophoretic separation and molecular weight characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa H-antigen flagellins. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):770–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.770-774.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansorg R. Flagellaspezifisches H-Antigenschema von Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1978 Nov;242(2):228–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M., Allen C., Sequeira L. Tyrosine phosphorylation of a membrane protein from Pseudomonas solanacearum. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4356–4360. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4356-4360.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Nairn A. C., Kuo J. F. Protein kinases 1988: a current perspective. FASEB J. 1988 Nov;2(14):2957–2969. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.14.2972578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourret R. B., Borkovich K. A., Simon M. I. Signal transduction pathways involving protein phosphorylation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:401–441. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadena D. L., Gill G. N. Receptor tyrosine kinases. FASEB J. 1992 Mar;6(6):2332–2337. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.6.1312047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dadssi M., Cozzone A. J. Evidence of protein-tyrosine kinase activity in the bacterium Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20996–20999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R., Thorner J., Martin G. S. Nucleotidylation, not phosphorylation, is the major source of the phosphotyrosine detected in enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):272–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.272-279.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. H., Dean A. M., Sohl J. L., Koshland D. E., Jr, Stroud R. M. Regulation of an enzyme by phosphorylation at the active site. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1012–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.2204109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. J., Aizawa S. The bacterial flagellum and flagellar motor: structure, assembly and function. Adv Microb Physiol. 1991;32:109–172. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. The flagellar filament protein. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Apr;34(4):452–458. doi: 10.1139/m88-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanto S., Okino H., Aizawa S., Yamaguchi S. Amino acids responsible for flagellar shape are distributed in terminal regions of flagellin. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jun 5;219(3):471–480. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90187-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
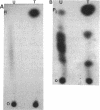
- Kelly-Wintenberg K., Anderson T., Montie T. C. Phosphorylated tyrosine in the flagellum filament protein of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5135–5139. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5135-5139.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J., Guerry P. Evidence for posttranslational modification and gene duplication of Campylobacter flagellin. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3031–3038. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3031-3038.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londesborough J. Phosphorylation of proteins in Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):595–601. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.595-601.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martensen T. M. Chemical properties, isolation, and analysis of O-phosphates in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1984;107:3–23. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)07003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
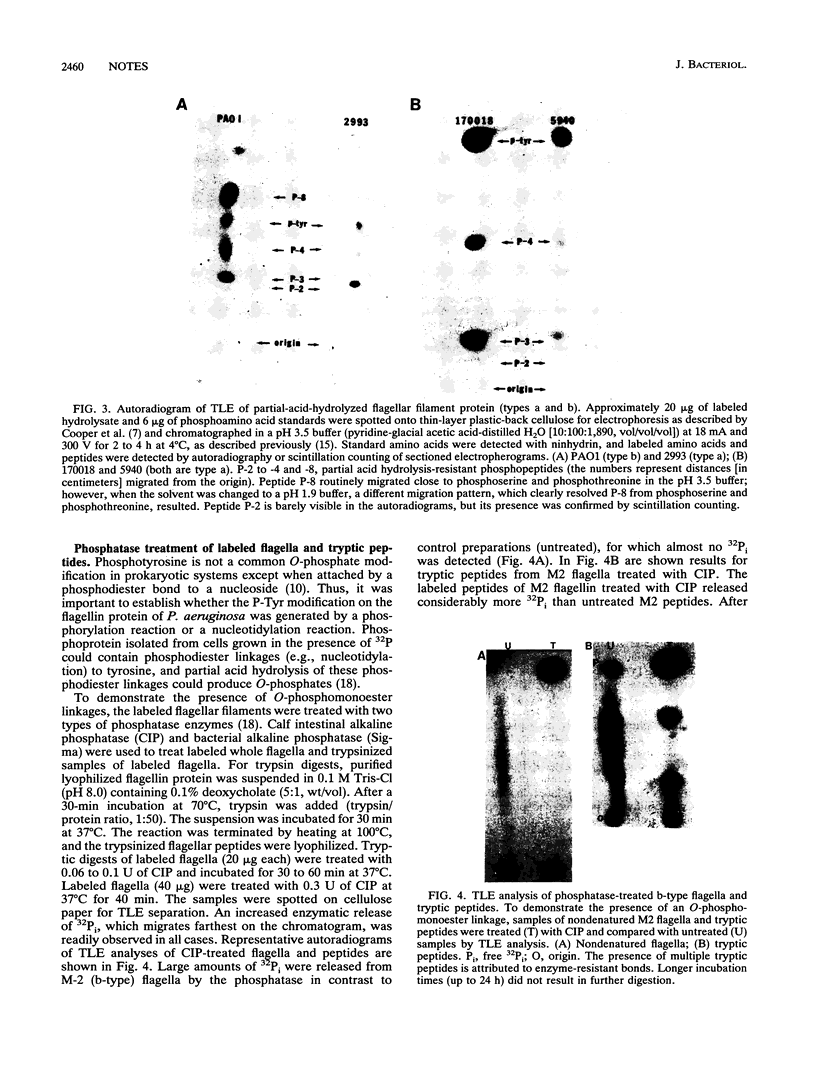
- Montie T. C., Anderson T. R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa H (flagellar) antigen. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;7(2):256–260. doi: 10.1007/BF01963097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paranchych W., Frost L. S. The physiology and biochemistry of pili. Adv Microb Physiol. 1988;29:53–114. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson E. F., Reeves H. C. Phosphorylation of isocitrate lyase in Escherichia coli. Biochimie. 1989 Sep-Oct;71(9-10):1065–1070. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(89)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotering H., Dorner F. Studies on a Pseudomonas aeruginosa flagella vaccine. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1989;42:218–228. doi: 10.1159/000417623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury S., Sakai K., Chakrabarty A. M. AlgR2 is an ATP/GTP-dependent protein kinase involved in alginate synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2659–2663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom M. S., Lory S. Amino acid substitutions in pilin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Effect on leader peptide cleavage, amino-terminal methylation, and pilus assembly. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1656–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Lory S. Characterization of the type a flagellin gene from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7188–7199. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7188-7199.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]