Abstract
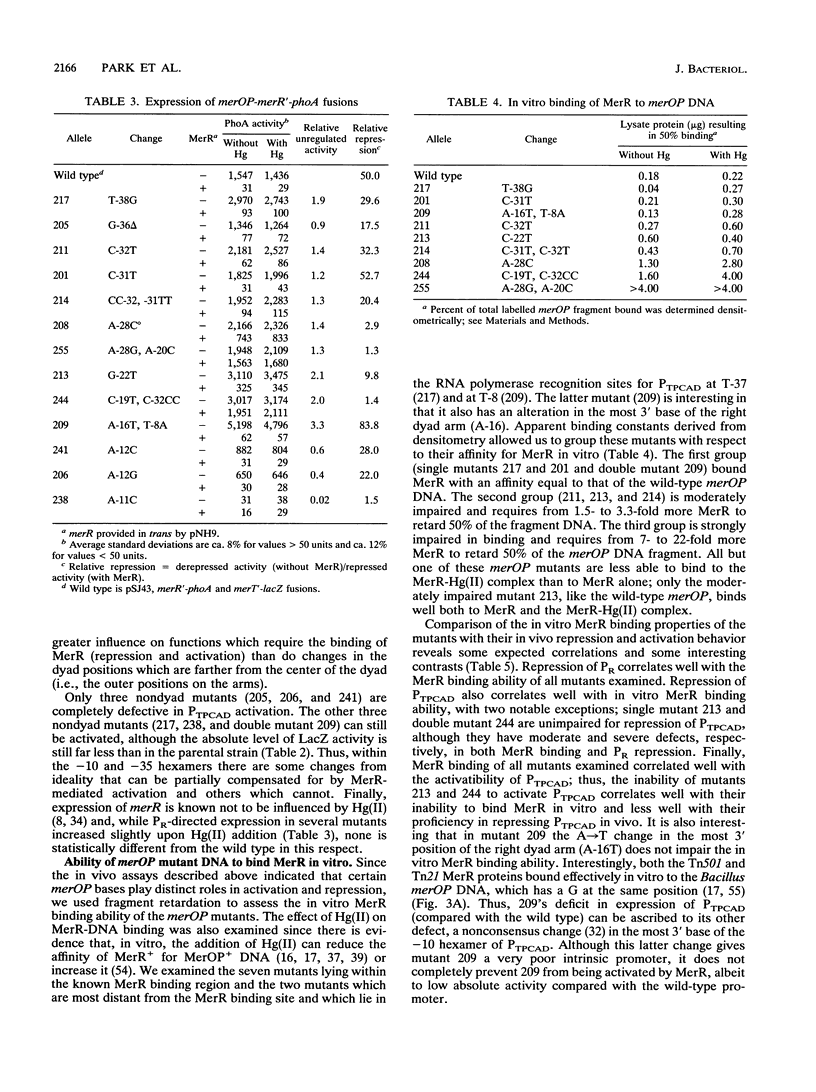
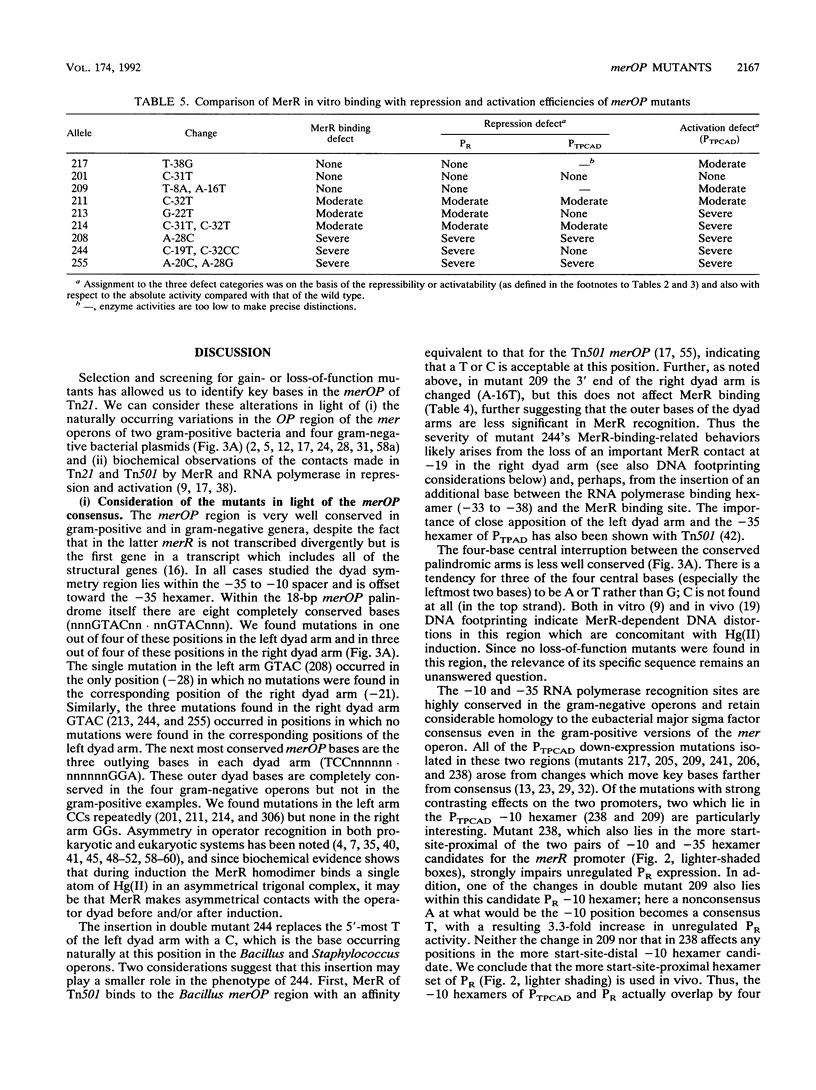
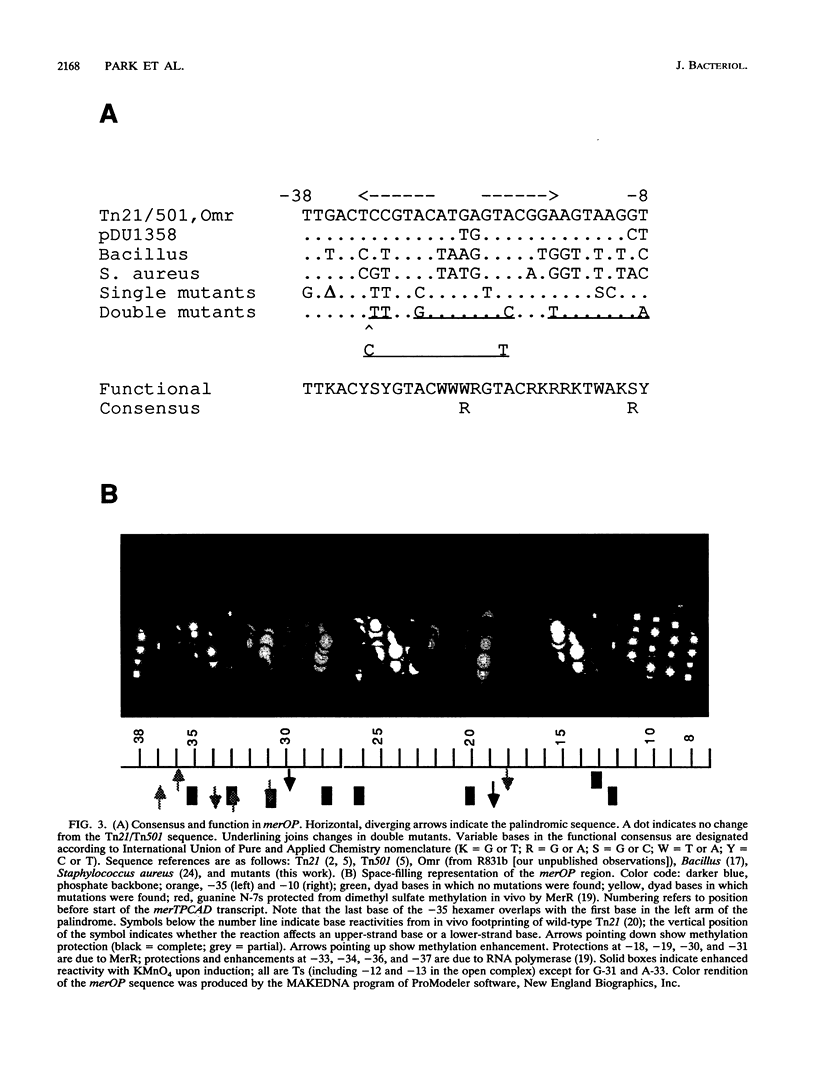
The mercury resistance operon, mer, of the transposon Tn21 is transcribed from two overlapping divergent promoters: PR for the regulatory gene, merR, and PTPCAD for the structural genes, merTPCAD. Transcription of merTPCAD is repressed in the absence of Hg(II) and activated in the presence of Hg(II) by the regulatory protein, MerR. In addition, MerR represses its own expression regardless of the presence of Hg(II). MerR binds as a dimer to a single region of dyad symmetry lying between the -35 and -10 hexamers of PTPCAD. Analysis of the expression of transcriptional fusions to hydroxylamine- and oligonucleotide-generated mutants of this divergent operator-promoter region identified key bases involved in MerR-dependent repression of PTPCAD and of PR and in activation of PTPCAD. Six of the seven mutants affecting the palindromic region were altered in their ability to bind the MerR protein in vitro as measured by fragment retardation assays. These differences in in vitro MerR binding correlated well with the in vivo measurements of repression or of activation. Bases identified as functionally relevant by this genetic analysis coincide extensively with those previously identified as relevant via in vivo footprinting. Four major points emerge from this analysis: (i) transition and transversion mutations within the spacer between the -10 and -35 hexamers of PTPCAD generally have little effect on the MerR-independent (i.e., unregulated) expression of either promoter; (ii) alteration of certain bases in the MerR-binding dyad affects repression of PTPCAD differently than repression of PR; (iii) certain dyad changes can impair activation of PTPCAD more severely than repression of this promoter; and (iv) mutations in the -10 hexamer of PTPCAD which also effect PR expression define one of two potential -10 hexamers in PR as actually functional in vivo.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auble D. T., Allen T. L., deHaseth P. L. Promoter recognition by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Effects of substitutions in the spacer DNA separating the -10 and -35 regions. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11202–11206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrineau P., Gilbert P., Jackson W. J., Jones C. S., Summers A. O., Wisdom S. The DNA sequence of the mercury resistance operon of the IncFII plasmid NR1. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(6):601–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand K. P., Postle K., Wray L. V., Jr, Reznikoff W. S. Overlapping divergent promoters control expression of Tn10 tetracycline resistance. Gene. 1983 Aug;23(2):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. G., Roderick S. L., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. Protein-DNA conformational changes in the crystal structure of a lambda Cro-operator complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8165–8169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. L., Misra T. K., Winnie J. N., Schmidt A., Seiff M., Silver S. The nucleotide sequence of the mercuric resistance operons of plasmid R100 and transposon Tn501: further evidence for mer genes which enhance the activity of the mercuric ion detoxification system. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jan;202(1):143–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00330531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire K. M., Salvo J. J., Grindley N. D. A simple and efficient procedure for saturation mutagenesis using mixed oligodeoxynucleotides. Gene. 1986;46(2-3):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J., Nakahara H., Weiss A. A., Silver S. Transposon A-generated mutations in the mercuric resistance genes of plasmid R100-1. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):167–181. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.167-181.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz B., O'Halloran T. V. DNA distortion accompanies transcriptional activation by the metal-responsive gene-regulatory protein MerR. Biochemistry. 1990 May 22;29(20):4747–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00472a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston K., Bell A., Kolb A., Buc H., Busby S. Stringent spacing requirements for transcription activation by CRP. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):733–743. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin H. G., Foster T. J., Silver S., Misra T. K. Cloning and DNA sequence of the mercuric- and organomercurial-resistance determinants of plasmid pDU1358. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3112–3116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Reynolds R. P. Analysis of E. coli promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2343–2361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C., Aggarwal A. K. DNA recognition by proteins with the helix-turn-helix motif. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:933–969. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Ballard B. T., Walsh C. T. The MerR metalloregulatory protein binds mercuric ion as a tricoordinate, metal-bridged dimer. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):946–948. doi: 10.1126/science.2305262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Wang Y., Mahler I., Walsh C. T. Homologous metalloregulatory proteins from both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria control transcription of mercury resistance operons. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):222–229. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.222-229.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heltzel A., Gambill D., Jackson W. J., Totis P. A., Summers A. O. Overexpression and DNA-binding properties of the mer-encoded regulatory protein from plasmid NR1 (Tn21). J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3379–3384. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3379-3384.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heltzel A., Lee I. W., Totis P. A., Summers A. O. Activator-dependent preinduction binding of sigma-70 RNA polymerase at the metal-regulated mer promoter. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 16;29(41):9572–9584. doi: 10.1021/bi00493a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W., Schleif R. A dimer of AraC protein contacts three adjacent major groove regions of the araI DNA site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer W., Deuschle U., Gentz R., Bujard H. Functional dissection of Escherichia coli promoters: information in the transcribed region is involved in late steps of the overall process. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2995–3000. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04597.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laddaga R. A., Chu L., Misra T. K., Silver S. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the mercurial-resistance operon from Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pI258. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5106–5110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R., Kieny M. P., Skory S., Lecocq J. P. Linker tailing: unphosphorylated linker oligonucleotides for joining DNA termini. DNA. 1984;3(2):173–182. doi: 10.1089/dna.1984.3.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. A., Brown N. L. Regulation of transcription in Escherichia coli from the mer and merR promoters in the transposon Tn501. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 20;205(2):343–353. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. A., Ford S. J., Brown N. L. Transcriptional regulation of the mercury-resistance genes of transposon Tn501. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Feb;132(2):465–480. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-2-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler I., Levinson H. S., Wang Y., Halvorson H. O. Cadmium- and mercury-resistant Bacillus strains from a salt marsh and from Boston Harbor. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Dec;52(6):1293–1298. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.6.1293-1298.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Mechanism and control of transcription initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:171–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra T. K., Brown N. L., Fritzinger D. C., Pridmore R. D., Barnes W. M., Haberstroh L., Silver S. Mercuric ion-resistance operons of plasmid R100 and transposon Tn501: the beginning of the operon including the regulatory region and the first two structural genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5975–5979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle H., Waldburger C., Susskind M. M. Hierarchies of base pair preferences in the P22 ant promoter. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):1944–1950. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.1944-1950.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay D., Yu H. R., Nucifora G., Misra T. K. Purification and functional characterization of MerD. A coregulator of the mercury resistance operon in gram-negative bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18538–18542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni'Bhriain N. N., Silver S., Foster T. J. Tn5 insertion mutations in the mercuric ion resistance genes derived from plasmid R100. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):690–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.690-703.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Halloran T. V., Frantz B., Shin M. K., Ralston D. M., Wright J. G. The MerR heavy metal receptor mediates positive activation in a topologically novel transcription complex. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90990-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Halloran T., Walsh C. Metalloregulatory DNA-binding protein encoded by the merR gene: isolation and characterization. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):211–214. doi: 10.1126/science.3798107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley M. G., Dervan P. B. Structural motif of the GCN4 DNA binding domain characterized by affinity cleaving. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):847–850. doi: 10.1126/science.2111578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R. T., Gilbert W. DNA-binding site of lac repressor probed by dimethylsulfate methylation of lac operator. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 25;132(4):709–728. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90384-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlendorf D. H., Anderson W. F., Fisher R. G., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. The molecular basis of DNA-protein recognition inferred from the structure of cro repressor. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):718–723. doi: 10.1038/298718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliphant A. R., Brandl C. J., Struhl K. Defining the sequence specificity of DNA-binding proteins by selecting binding sites from random-sequence oligonucleotides: analysis of yeast GCN4 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2944–2949. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Aggarwal A. K., Jordan S. R., Beamer L. J., Obeysekare U. R., Harrison S. C. Conserved residues make similar contacts in two repressor-operator complexes. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1210–1213. doi: 10.1126/science.2315694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhill J., Brown N. L. Site-specific insertion and deletion mutants in the mer promoter-operator region of Tn501; the nineteen base-pair spacer is essential for normal induction of the promoter by MerR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5157–5162. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poteete A. R., Ptashne M. Control of transcription by the bacteriophage P22 repressor. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):21–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90511-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston D. M., O'Halloran T. V. Ultrasensitivity and heavy-metal selectivity of the allosterically modulated MerR transcription complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3846–3850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risse G., Jooss K., Neuberg M., Brüller H. J., Müller R. Asymmetrical recognition of the palindromic AP1 binding site (TRE) by Fos protein complexes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3825–3832. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Park S. J., Summers A. O. Genetic analysis of transcriptional activation and repression in the Tn21 mer operon. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):4009–4018. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.4009-4018.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarai A., Takeda Y. Lambda repressor recognizes the approximately 2-fold symmetric half-operator sequences asymmetrically. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6513–6517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasmor H. M., Betz J. L. Symmetric lac operator derivatives: effects of half-operator sequence and spacing on repressor affinity. Gene. 1990 Apr 30;89(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90198-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schevitz R. W., Otwinowski Z., Joachimiak A., Lawson C. L., Sigler P. B. The three-dimensional structure of trp repressor. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):782–786. doi: 10.1038/317782a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider K., Beck C. F. Promoter-probe vectors for the analysis of divergently arranged promoters. Gene. 1986;42(1):37–48. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers J. W., Vincent A. C., Struhl K. Mutations that define the optimal half-site for binding yeast GCN4 activator protein and identify an ATF/CREB-like repressor that recognizes similar DNA sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5077–5086. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewchuk L. M., Helmann J. D., Ross W., Park S. J., Summers A. O., Walsh C. T. Transcriptional switching by the MerR protein: activation and repression mutants implicate distinct DNA and mercury(II) binding domains. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):2340–2344. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewchuk L. M., Verdine G. L., Walsh C. T. Transcriptional switching by the metalloregulatory MerR protein: initial characterization of DNA and mercury (II) binding activities. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):2331–2339. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staacke D., Walter B., Kisters-Woike B., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. How Trp repressor binds to its operator. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1963–1967. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers A. O. Organization, expression, and evolution of genes for mercury resistance. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:607–634. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Sarai A., Rivera V. M. Analysis of the sequence-specific interactions between Cro repressor and operator DNA by systematic base substitution experiments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):439–443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wissmann A., Meier I., Hillen W. Saturation mutagenesis of the Tn10-encoded tet operator O1. Identification of base-pairs involved in Tet repressor recognition. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vlieg J., Berendsen H. J., van Gunsteren W. F. An NMR-based molecular dynamics simulation of the interaction of the lac repressor headpiece and its operator in aqueous solution. Proteins. 1989;6(2):104–127. doi: 10.1002/prot.340060203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Bear D. G., Morgan W. D., McSwiggen J. A. Protein-nucleic acid interactions in transcription: a molecular analysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:389–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]