Abstract
The two highly homologous cbb operons of Alcaligenes eutrophus H16 that are located on the chromosome and on megaplasmid pHG1 contain genes encoding several enzymes of the Calvin carbon reduction cycle. Sequence analysis of a region from the promoter-distal part revealed two open reading frames, designated cbbT and cbbZ, at equivalent positions within the operons. Comparisons with known sequences suggested cbbT to encode transketolase (TK; EC 2.2.1.1) as an additional enzyme of the cycle. No significant overall sequence similarities were observed for cbbZ. Although both regions exhibited very high nucleotide identities, 93% (cbbZ) and 96% (cbbT), only the chromosomally encoded genes were heterologously expressed to high levels in Escherichia coli. The molecular masses of the observed gene products, CbbT (74 kDa) and CbbZ (24 kDa), correlated well with the values calculated on the basis of the sequence information. TK activities were strongly elevated in E. coli clones expressing cbbT, confirming the identity of the gene. Strains of E. coli harboring the chromosomal cbbZ gene showed high levels of activity of 2-phosphoglycolate phosphatase (PGP; EC 3.1.3.18), a key enzyme of glycolate metabolism in autotrophic organisms that is not present in wild-type E. coli. Derepression of the cbb operons during autotrophic growth resulted in considerably increased levels of TK activity and the appearance of PGP activity in A. eutrophus, although the pHG1-encoded cbbZ gene was apparently not expressed. To our knowledge, this study represents the first cloning and sequencing of a PGP gene from any organism.
Full text
PDF





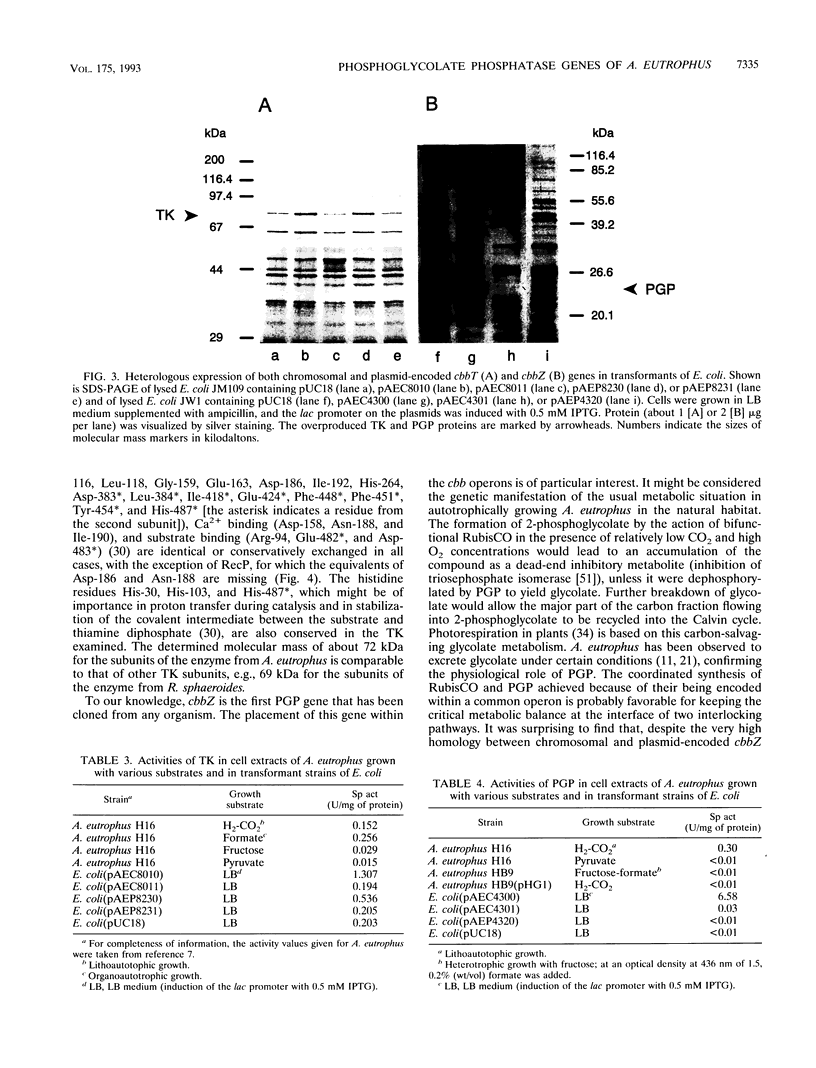





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowien B., Schlegel H. G. Physiology and biochemistry of aerobic hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:405–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavaliere S. W., Neet K. E., Sable H. Z. Enzymes of pentose biosynthesis. The quaternary structure and reacting form of transketolase from baker's yeast. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Dec;171(2):527–532. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. H., Gibson J. L., McCue L. A., Tabita F. R. Identification, expression, and deduced primary structure of transketolase and other enzymes encoded within the form II CO2 fixation operon of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20447–20452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christeller J. T., Tolbert N. E. Phosphoglycolate phosphatase. Effect of cation and pH on activity. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1786–1790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codd G. A., Bowien B., Schlegel H. G. Glycollate production and excretion by Alcaligenes eutrophus. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Nov 2;110(23):167–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00690224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essar D. W., Eberly L., Crawford I. P. Evolutionary differences in chromosomal locations of four early genes of the tryptophan pathway in fluorescent pseudomonads: DNA sequences and characterization of Pseudomonas putida trpE and trpGDC. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):867–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.867-883.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher T. S., Kwee I. L., Nakada T., Largman C., Martin B. M. DNA sequence of the yeast transketolase gene. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1892–1896. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich B., Hogrefe C., Schlegel H. G. Naturally occurring genetic transfer of hydrogen-oxidizing ability between strains of Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jul;147(1):198–205. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.1.198-205.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husic H. D., Tolbert N. E. Properties of Phosphoglycolate Phosphatase from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Anacystis nidulans. Plant Physiol. 1985 Oct;79(2):394–399. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.2.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janowicz Z. A., Eckart M. R., Drewke C., Roggenkamp R. O., Hollenberg C. P., Maat J., Ledeboer A. M., Visser C., Verrips C. T. Cloning and characterization of the DAS gene encoding the major methanol assimilatory enzyme from the methylotrophic yeast Hansenula polymorpha. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3043–3062. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jendrossek D., Krüger N., Steinbüchel A. Characterization of alcohol dehydrogenase genes of derepressible wild-type Alcaligenes eutrophus H16 and constitutive mutants. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4844–4851. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4844-4851.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjems J., Garrett R. A. Novel expression of the ribosomal RNA genes in the extreme thermophile and archaebacterium Desulfurococcus mobilis. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3521–3530. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klintworth R., Husemann M., Salnikow J., Bowien B. Chromosomal and plasmid locations for phosphoribulokinase genes in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):954–956. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.954-956.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kossmann J., Klintworth R., Bowien B. Sequence analysis of the chromosomal and plasmid genes encoding phosphoribulokinase from Alcaligenes eutrophus. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90490-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusian B., Yoo J. G., Bednarski R., Bowien B. The Calvin cycle enzyme pentose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase is encoded within the cfx operons of the chemoautotroph Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(22):7337–7344. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.22.7337-7344.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Andrews T. J., Tolbert N. E. Ribulose diphosphate oxygenase. II. Further proof of reaction products and mechanism of action. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):18–23. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radnis B. A., Rhee D. K., Morrison D. A. Genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae: nucleotide sequence and predicted amino acid sequence of recP. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3669–3674. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3669-3674.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose Z. B., Grove D. S., Seal S. N. Mechanism of activation by anions of phosphoglycolate phosphatases from spinach and human red blood cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):10996–11002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert P., Krüger N., Steinbüchel A. Molecular analysis of the Alcaligenes eutrophus poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) biosynthetic operon: identification of the N terminus of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) synthase and identification of the promoter. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):168–175. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.168-175.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., Gibson J. L., Bowien B., Dijkhuizen L., Meijer W. G. Uniform designation for genes of the Calvin-Benson-Bassham reductive pentose phosphate pathway of bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Dec 1;78(2-3):107–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb05551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toy J., Bognar A. L. Cloning and expression of the gene encoding Lactobacillus casei folylpoly-gamma-glutamate synthetase in Escherichia coli and determination of its primary structure. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2492–2499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windhövel U., Bowien B. Identification of cfxR, an activator gene of autotrophic CO2 fixation in Alcaligenes eutrophus. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2695–2705. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01978.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windhövel U., Bowien B. On the operon structure of the cfx gene clusters in Alcaligenes eutrophus. Arch Microbiol. 1990;154(1):85–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00249183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenden R. Binding of substrate and transition state analog to trisephosphate isomerase. Biochemistry. 1970 Aug 18;9(17):3404–3407. doi: 10.1021/bi00819a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. H., Ellison J., Salido E. C., Mohandas T., Shapiro L. Isolation of a new gene from the distal short arm of the human X chromosome that escapes X-inactivation. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):47–52. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Costa e Silva O., Kosuge T. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of the anthranilate synthase gene of Pseudomonas syringae subsp. savastanoi. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):463–471. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.463-471.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



